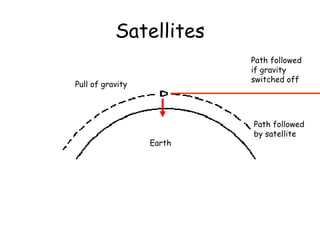
This document discusses the bodies that make up the universe and our solar system. It explains that planets and moons orbit due to gravitational forces, and describes the different types of galaxies, orbits used by satellites, and how black holes are formed from collapsed giant stars. The document aims to teach students about the structures and motions within the universe at both basic and more advanced levels.