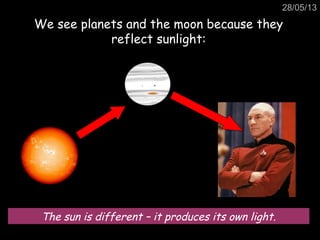
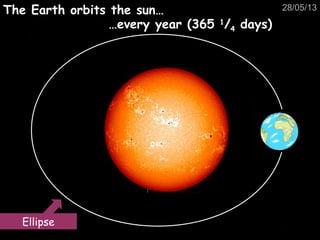
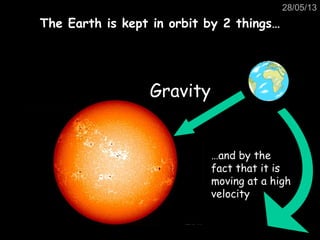
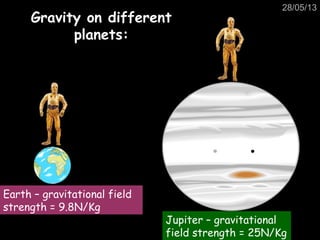
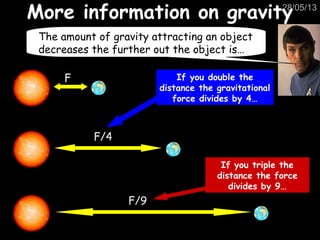
This document provides information about the solar system and beyond. It discusses the nine planets in our solar system and how we see planets and the moon because they reflect sunlight, unlike the sun which produces its own light. It also summarizes that the Earth orbits the sun in an elliptical pattern every year and is kept in orbit by gravity and its high velocity. Additional topics covered include gravity, the moon's phases, comets, artificial satellites, galaxies and the universe, and evidence for the Big Bang theory.