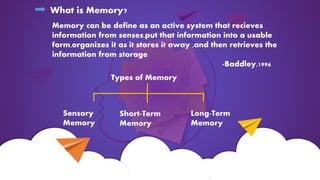
Long-term memory can be either implicit or explicit. Explicit memory, also called declarative memory, involves the conscious recollection of facts, experiences, and concepts. It has three processes: acquisition, consolidation, and retrieval. Explicit memory is further divided into semantic memory, which involves general knowledge and facts, and episodic memory, which involves autobiographical memories of personal experiences and events from one's life.