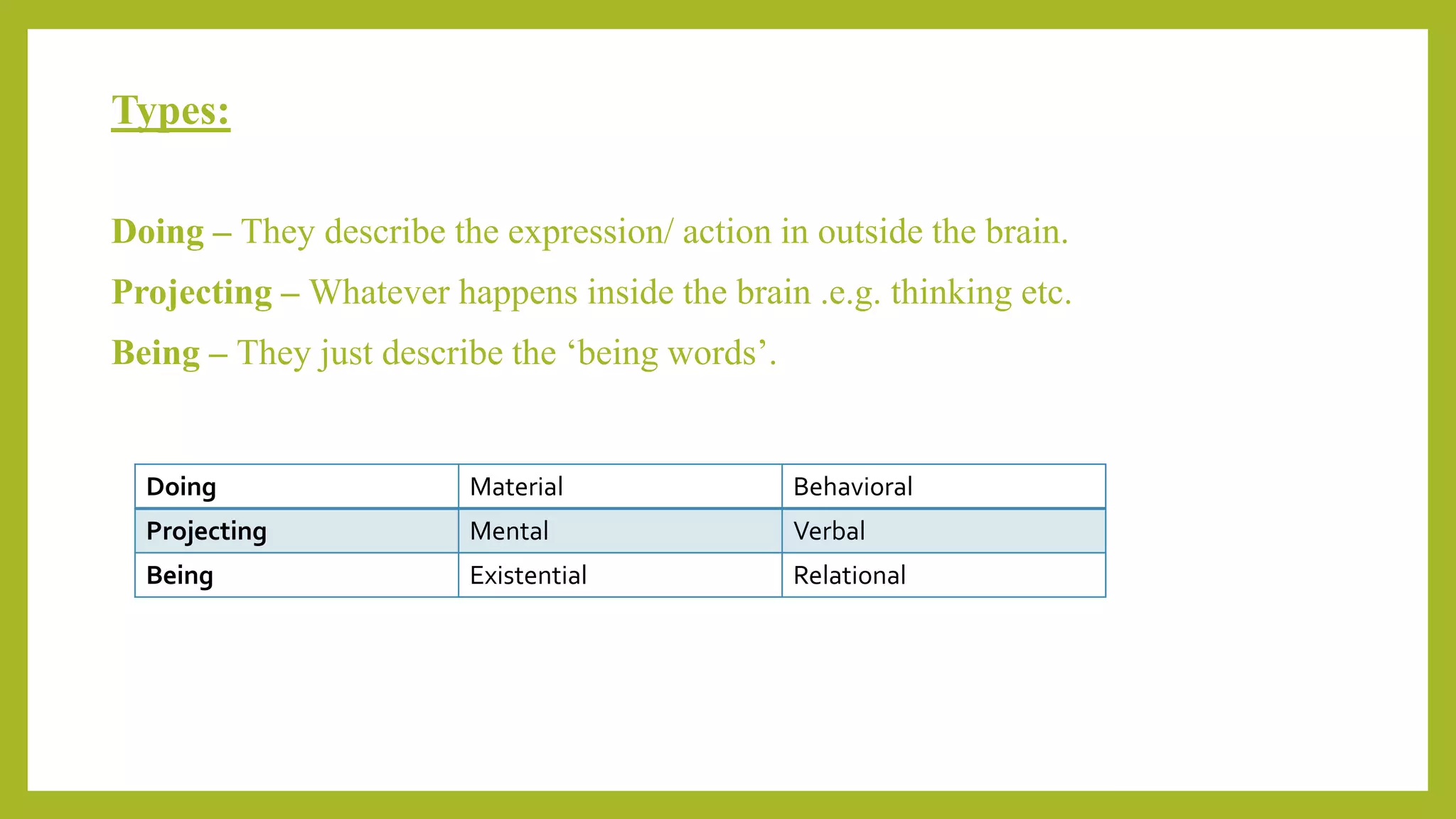
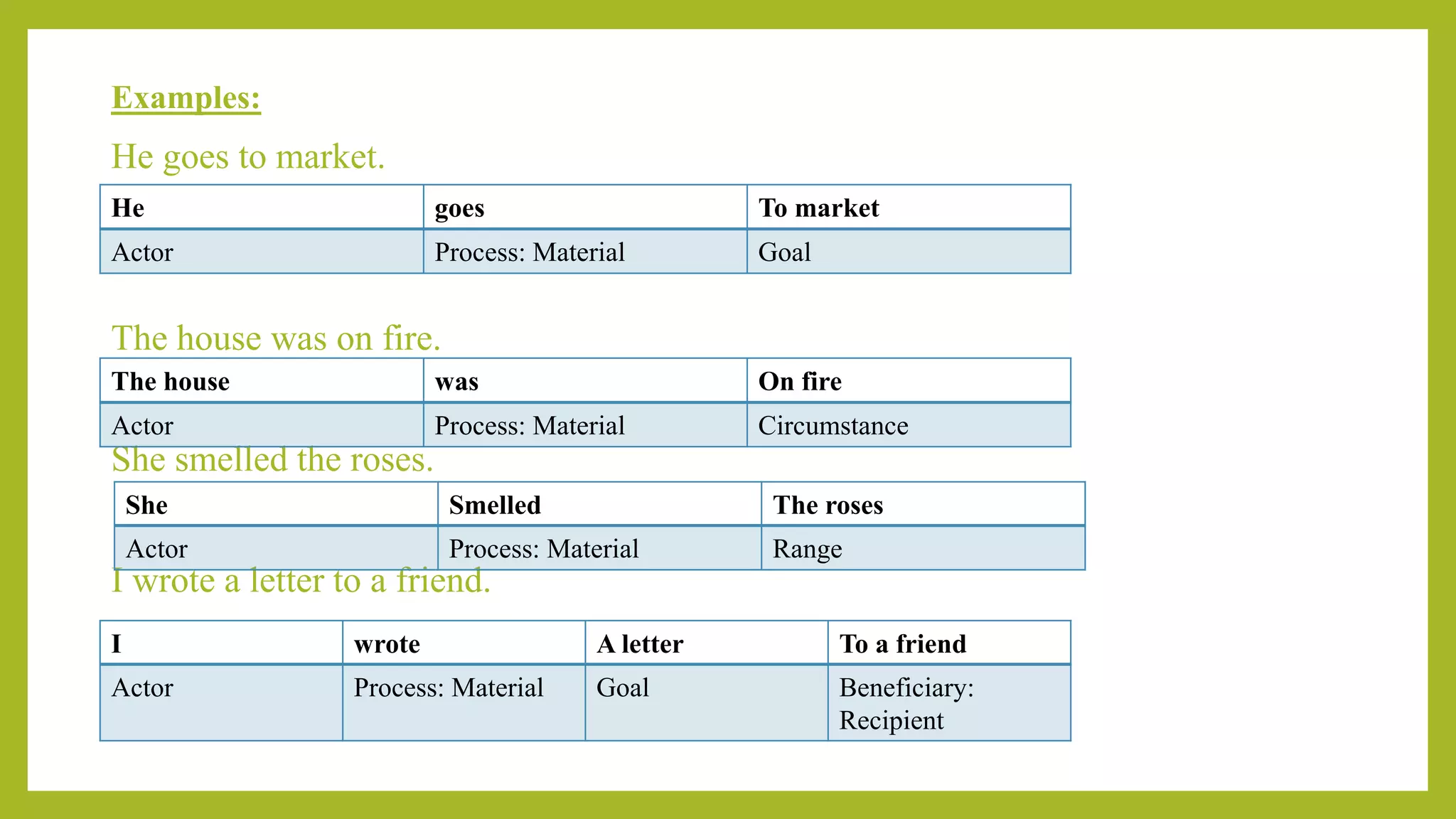
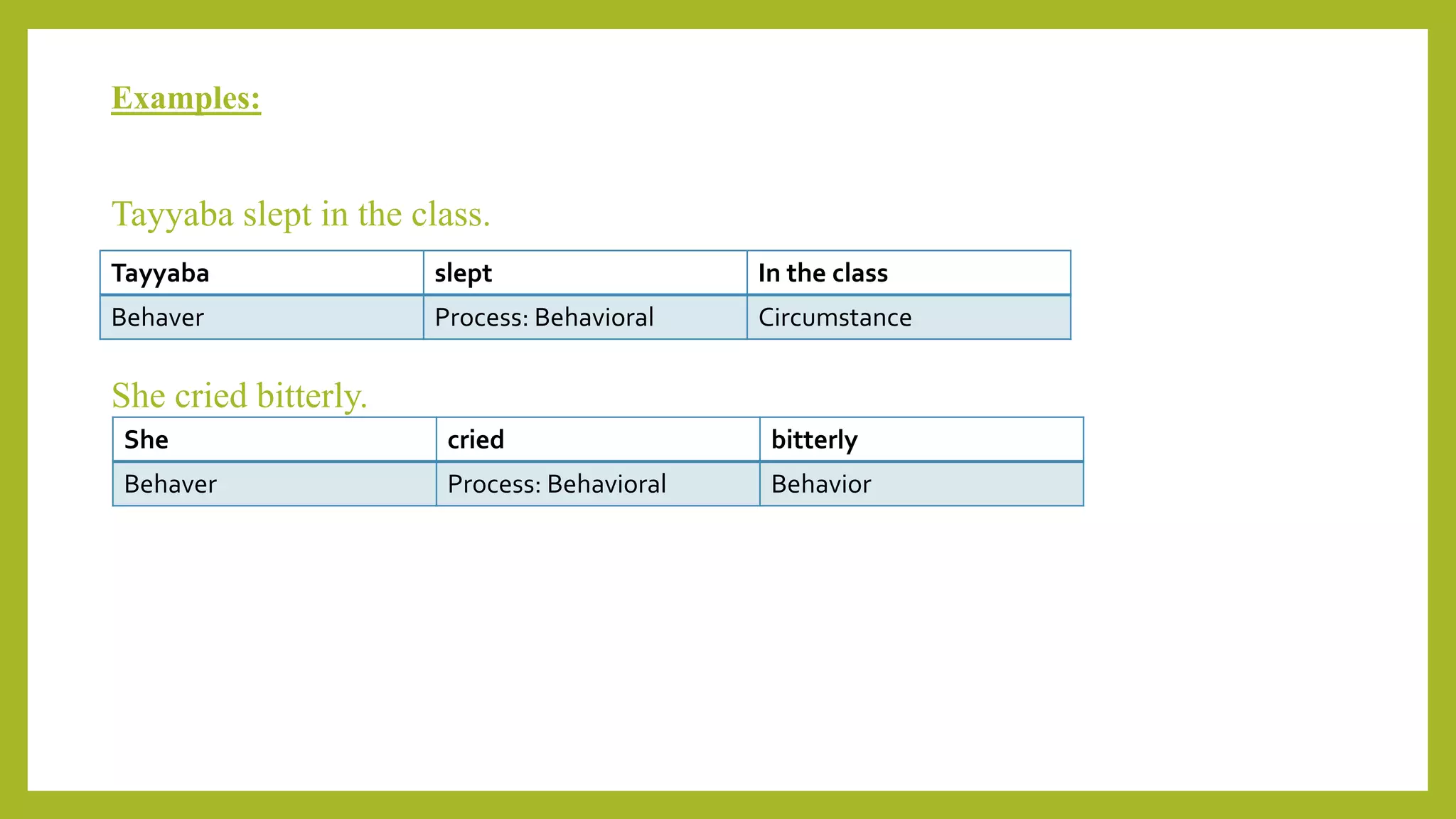
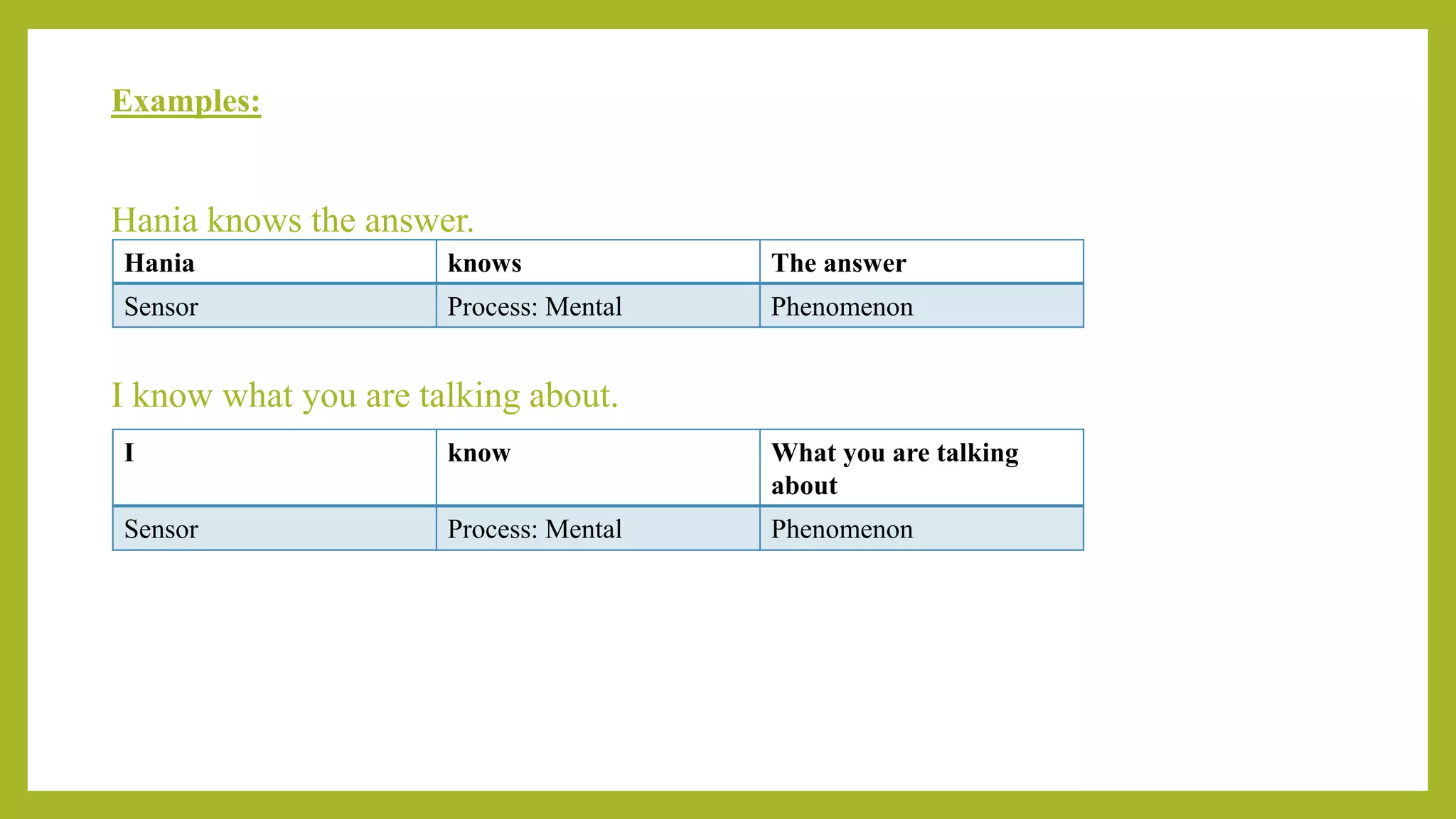
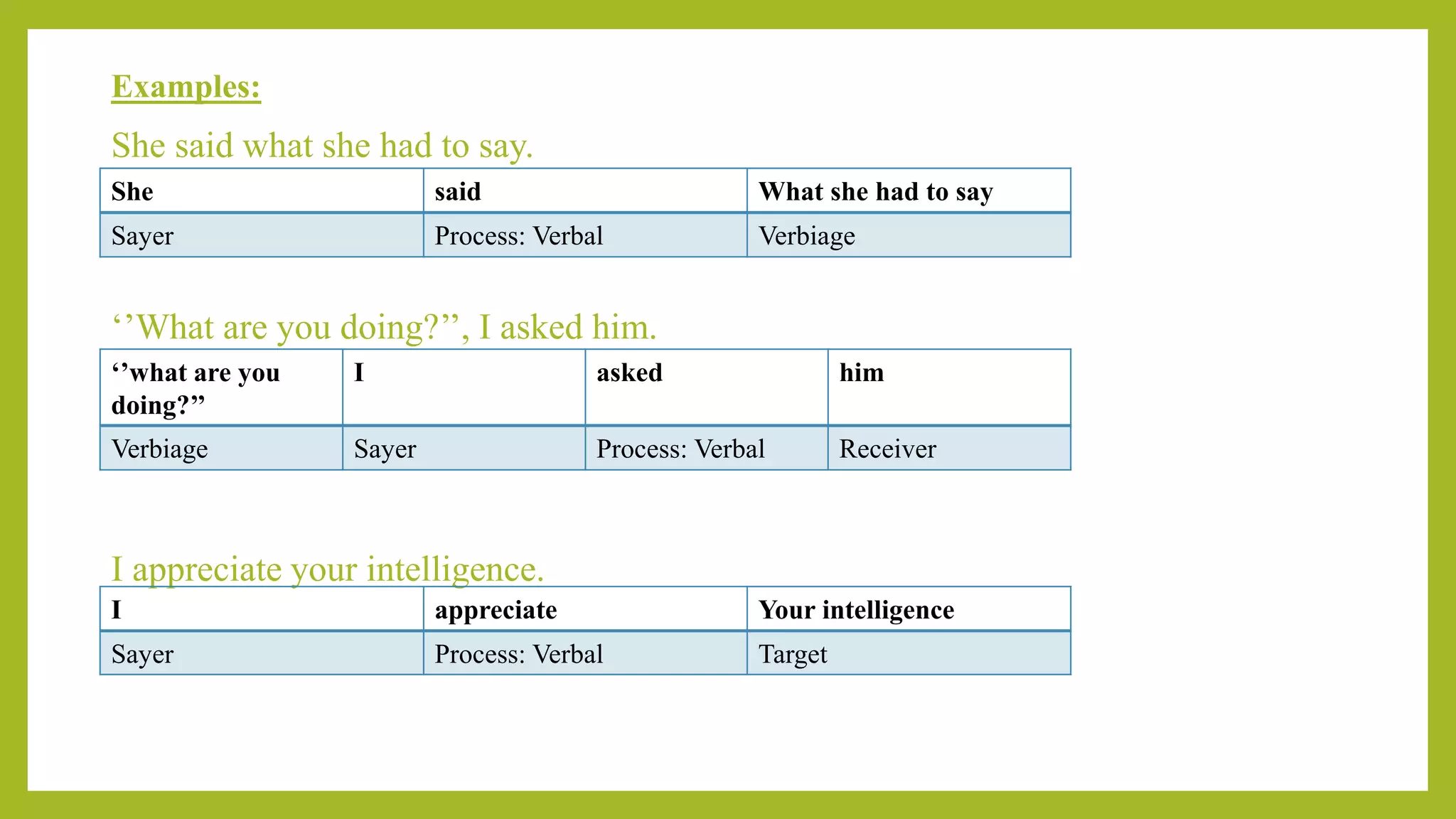
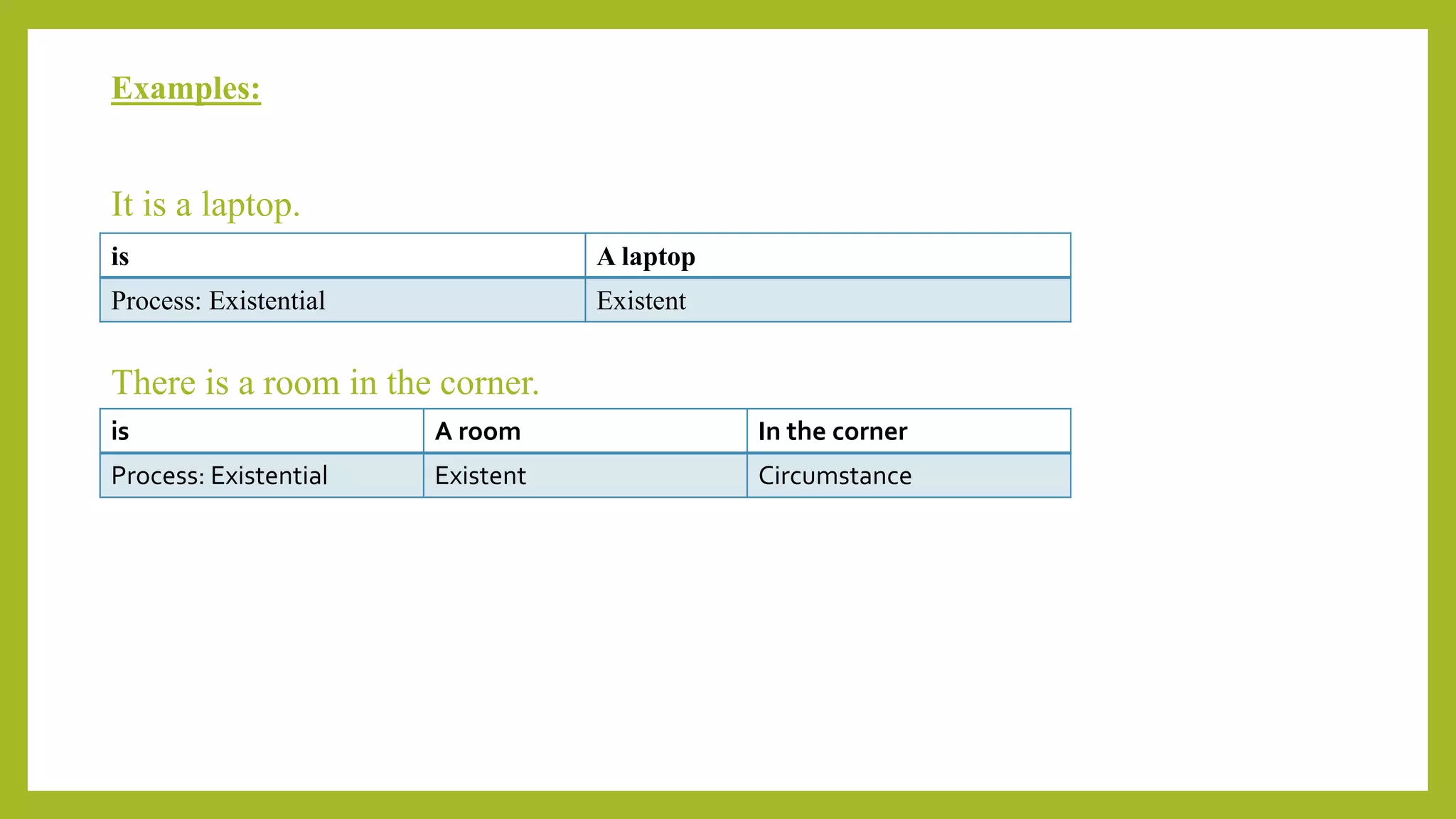
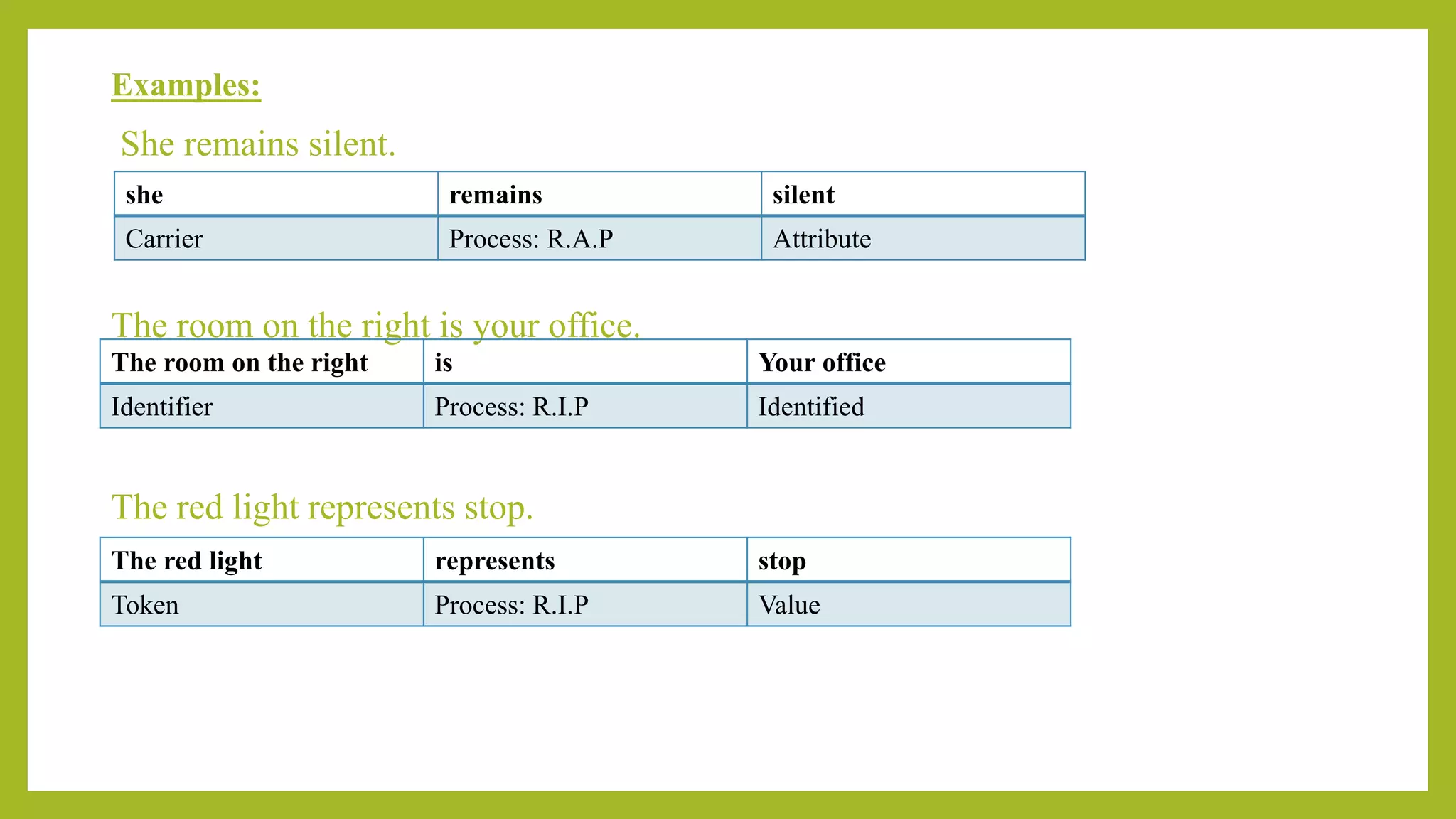
This document discusses experiential meta-functions which are used to encode experiences. There are three main types: doing, projecting, and being. Doing describes external actions, projecting describes internal thoughts and feelings, and being describes states of existence. Within these types are subcategories like material, behavioral, mental, verbal, existential, and relational processes. Each process involves participants and can be used to construct clauses that describe who did what to whom and in what circumstances. Examples are provided to illustrate the different processes and participant roles.