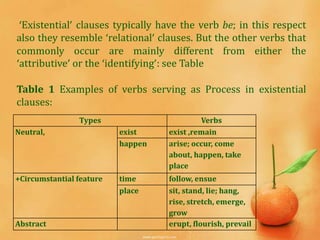
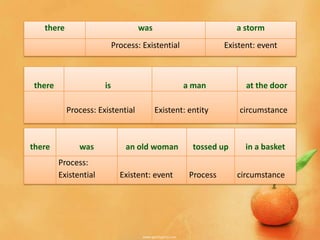
Existential processes represent that something exists or happens using the word "there" as the subject. Existential clauses typically use the verb "be" and represent a neutral existence or one with circumstantial features like time or place. The entity or event said to exist is called the "existent" and can be things, actions, events, or abstractions. Examples show "there" used with verbs like "was," "is," representing the process of existing, along with the existent and any circumstances.