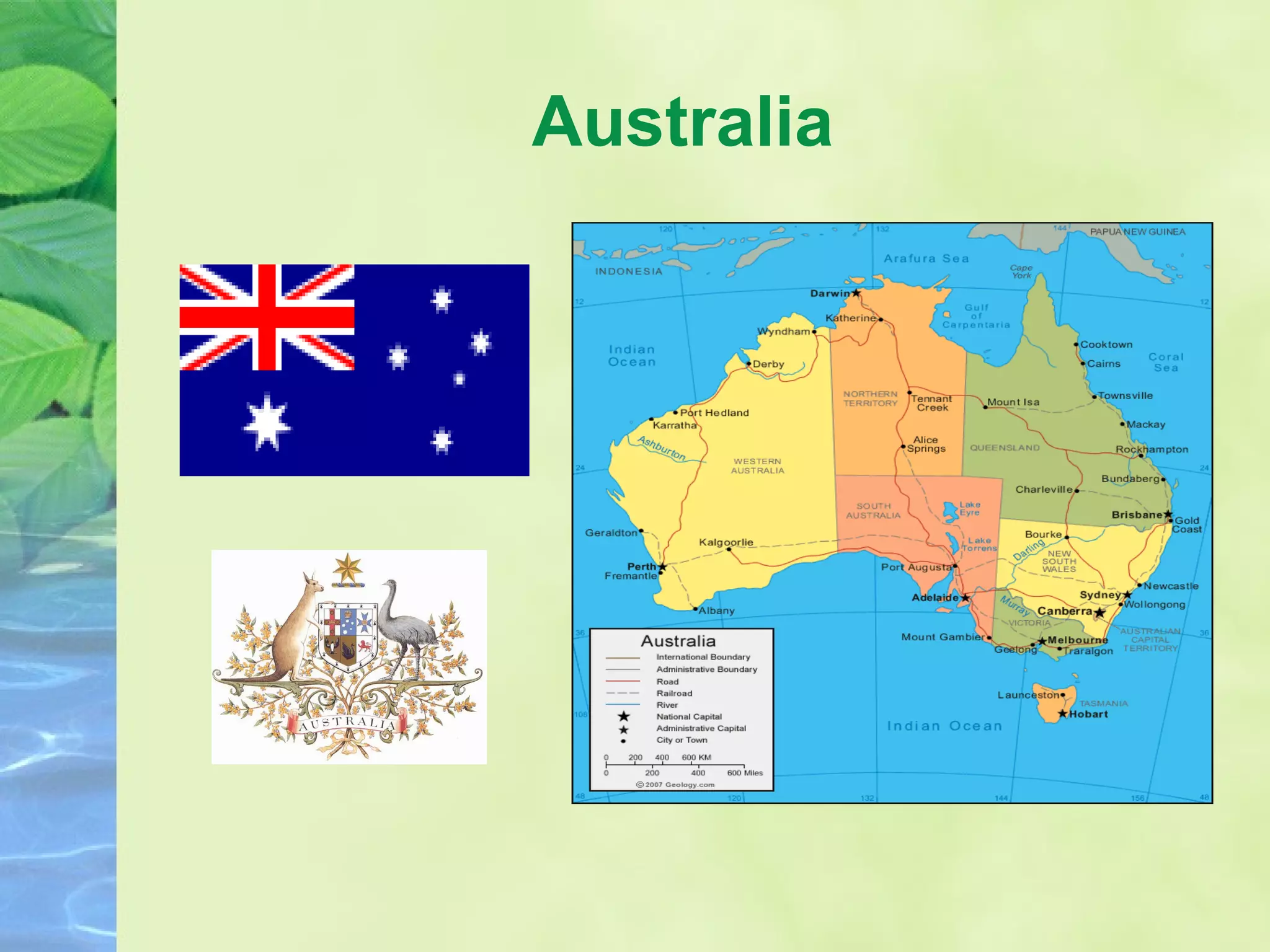
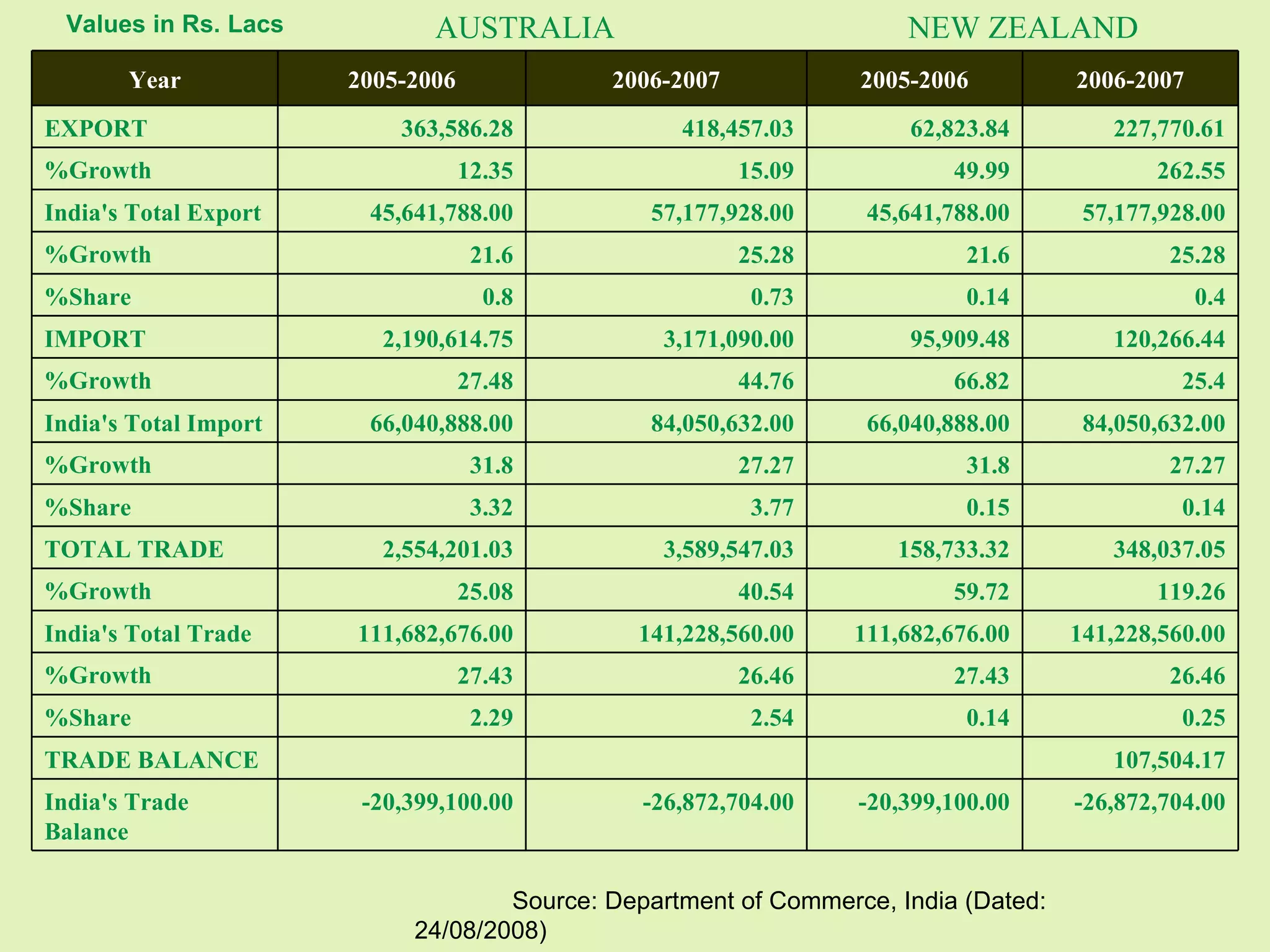
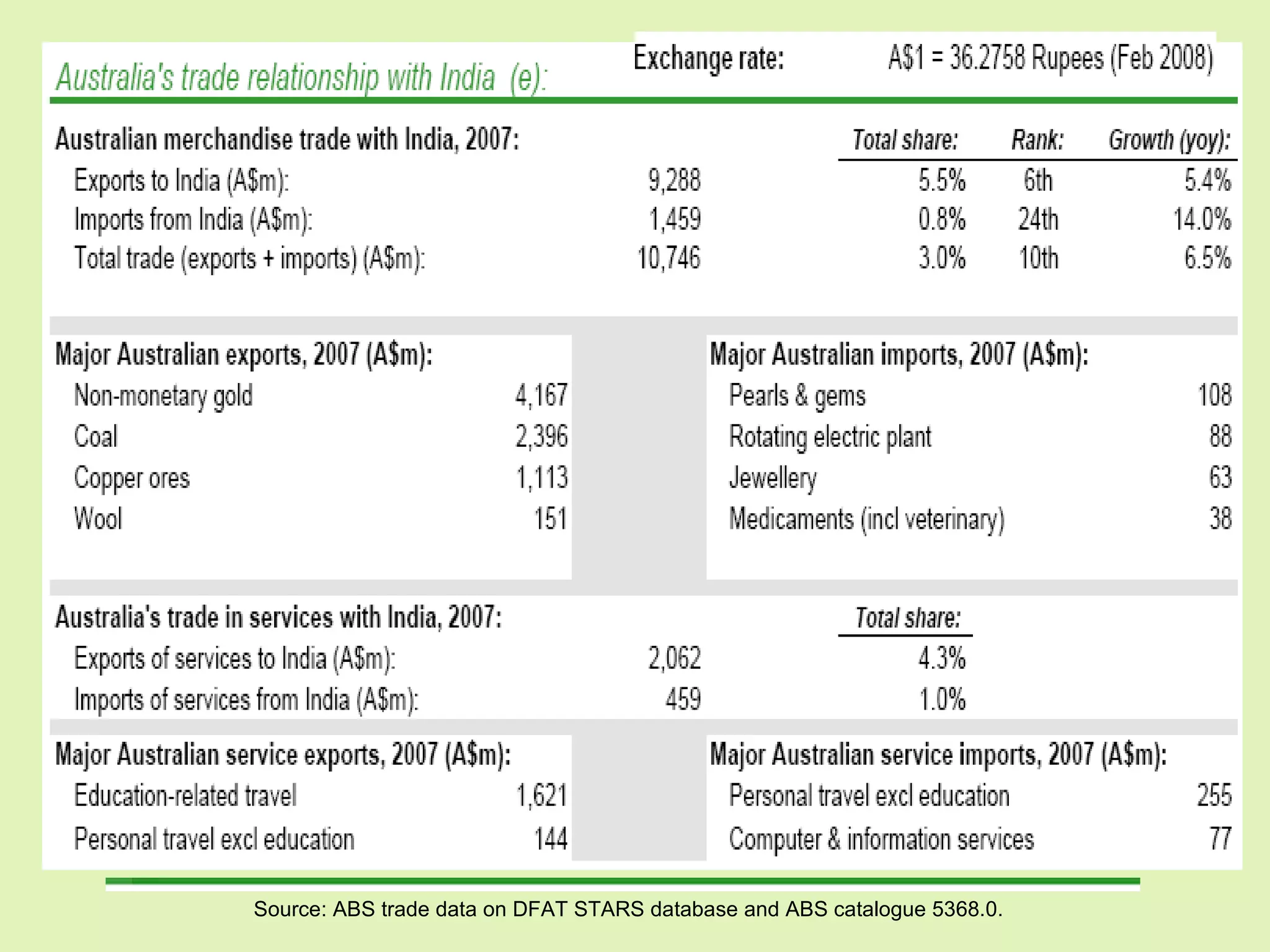
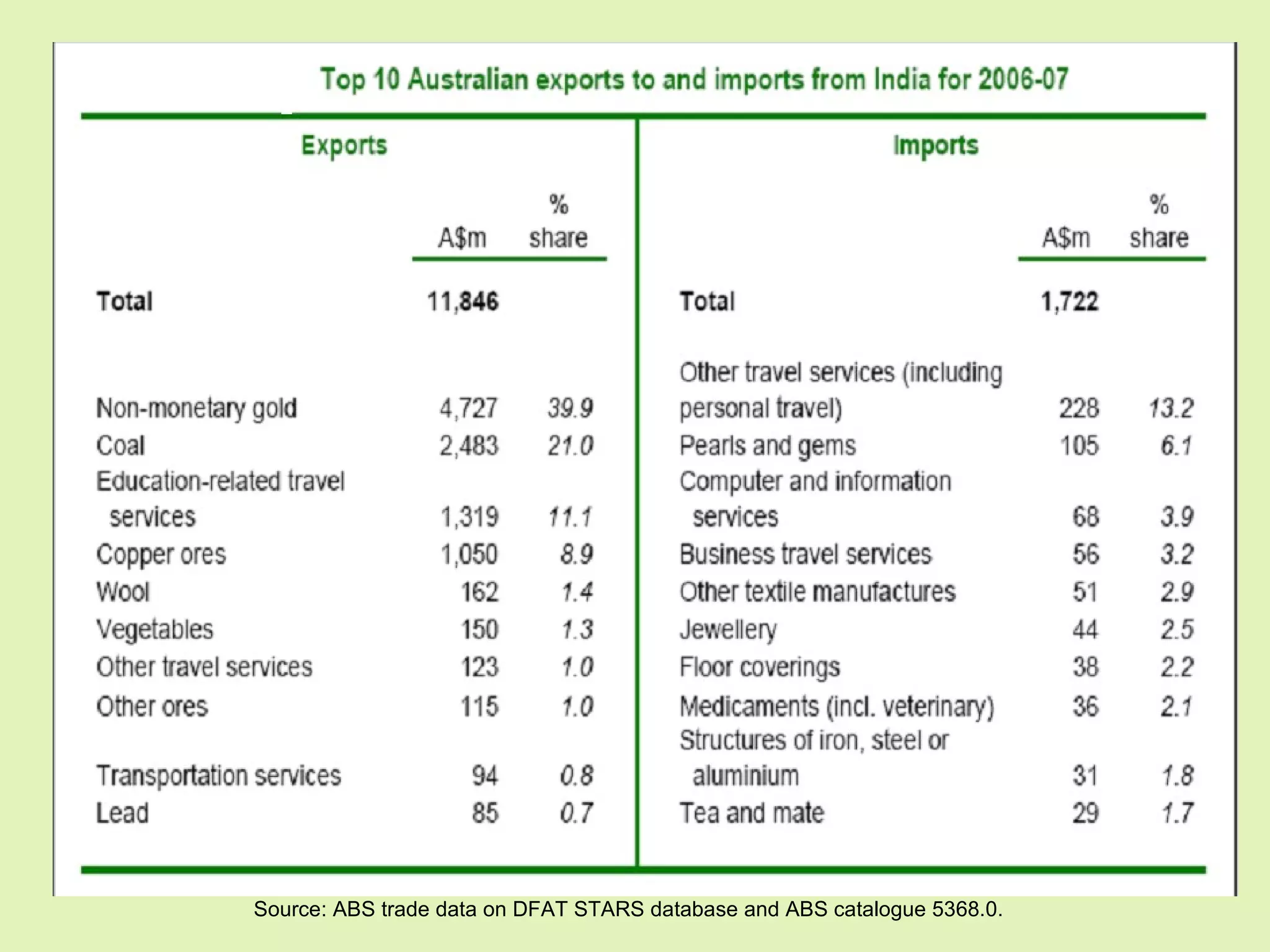
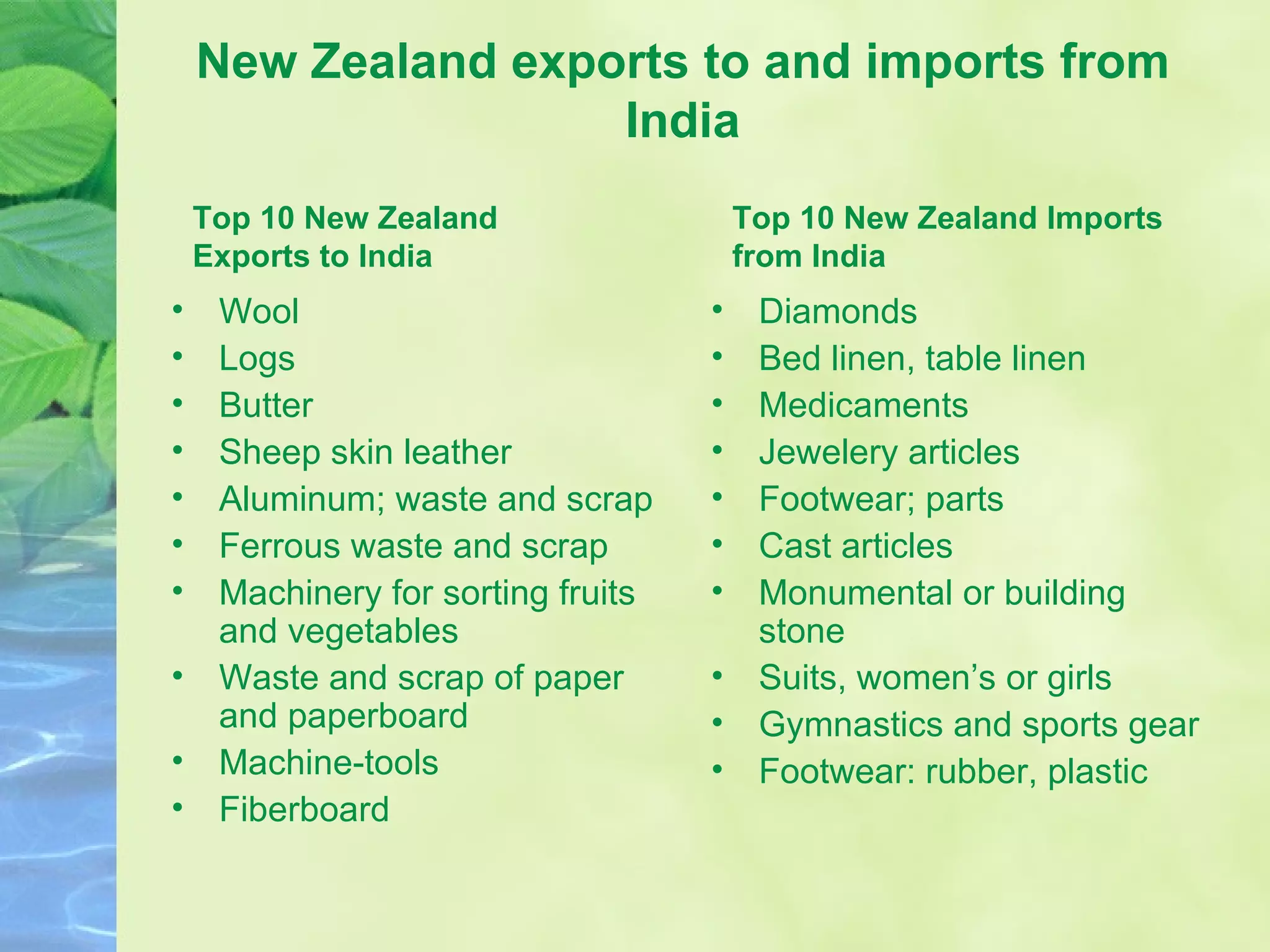
The document provides background information on Oceania and its subregions, including details about Australasia. It then discusses Australia and New Zealand, outlining each country's geography, climate, population, government, and economy. Key facts are given about bilateral relations between Australia, New Zealand, and India.