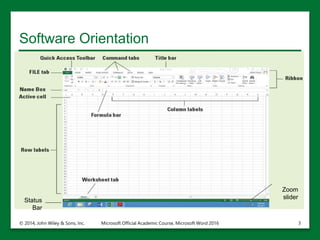
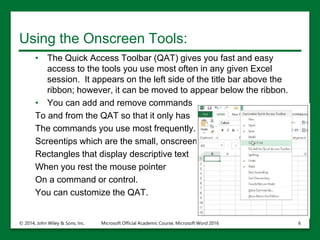
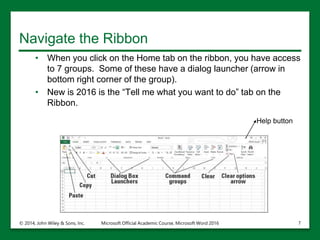
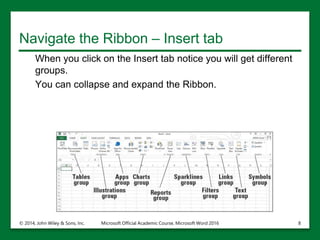
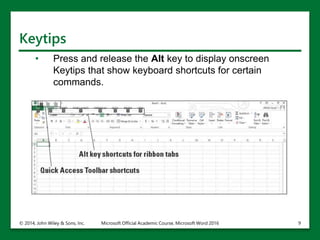
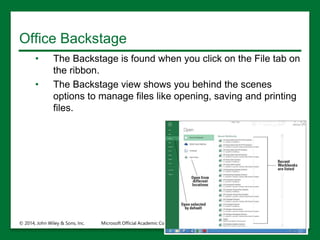
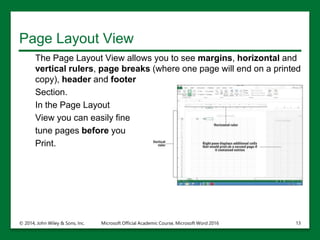
The document provides an overview of Microsoft Excel 2016, highlighting its key features such as the worksheet structure made of cells, rows, and columns, as well as the command ribbon and toolbar for user navigation. It covers essential tasks such as starting Excel, managing workbooks, navigating worksheets, and using the help system for assistance. Additionally, it explains the importance of descriptive file names and Cloud storage options like Skydrive for efficient file management.