This document provides an introduction to Docker, including:
- A brief history of container technologies leading to the development of Docker in 2013.
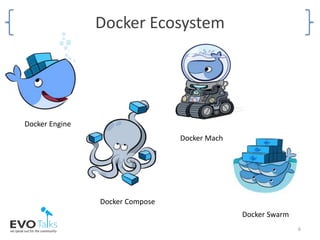
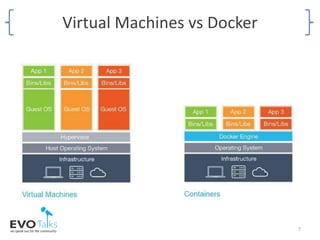
- An overview of the Docker ecosystem and how Docker compares to virtual machines.
- Common Docker commands for interacting with the Docker Engine to run, stop, inspect and manage containers.
- How to build Docker images using Dockerfiles to automate the image creation process.
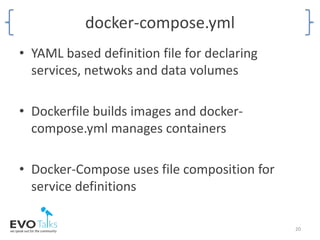
- How Docker Compose can be used to manage multiple containers through a YAML configuration file.
- Some advantages and disadvantages of using Docker for application deployment.






![Common Docker Commands
• docker run [image_name]
• docker start [container_id]
• docker stop [container_id]
• docker ps
• docker exec --ti [container_id] bash
• docker inspect [container_id]
• docker top [container_id]
11](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/evotalksdockerpresentation-161217155024/85/Evotalks-Docker-Presentation-11-320.jpg)


![Working With Images
• docker images
• docker pull/push [image_name]
• docker rmi [image_name/image_id]
17](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/evotalksdockerpresentation-161217155024/85/Evotalks-Docker-Presentation-17-320.jpg)