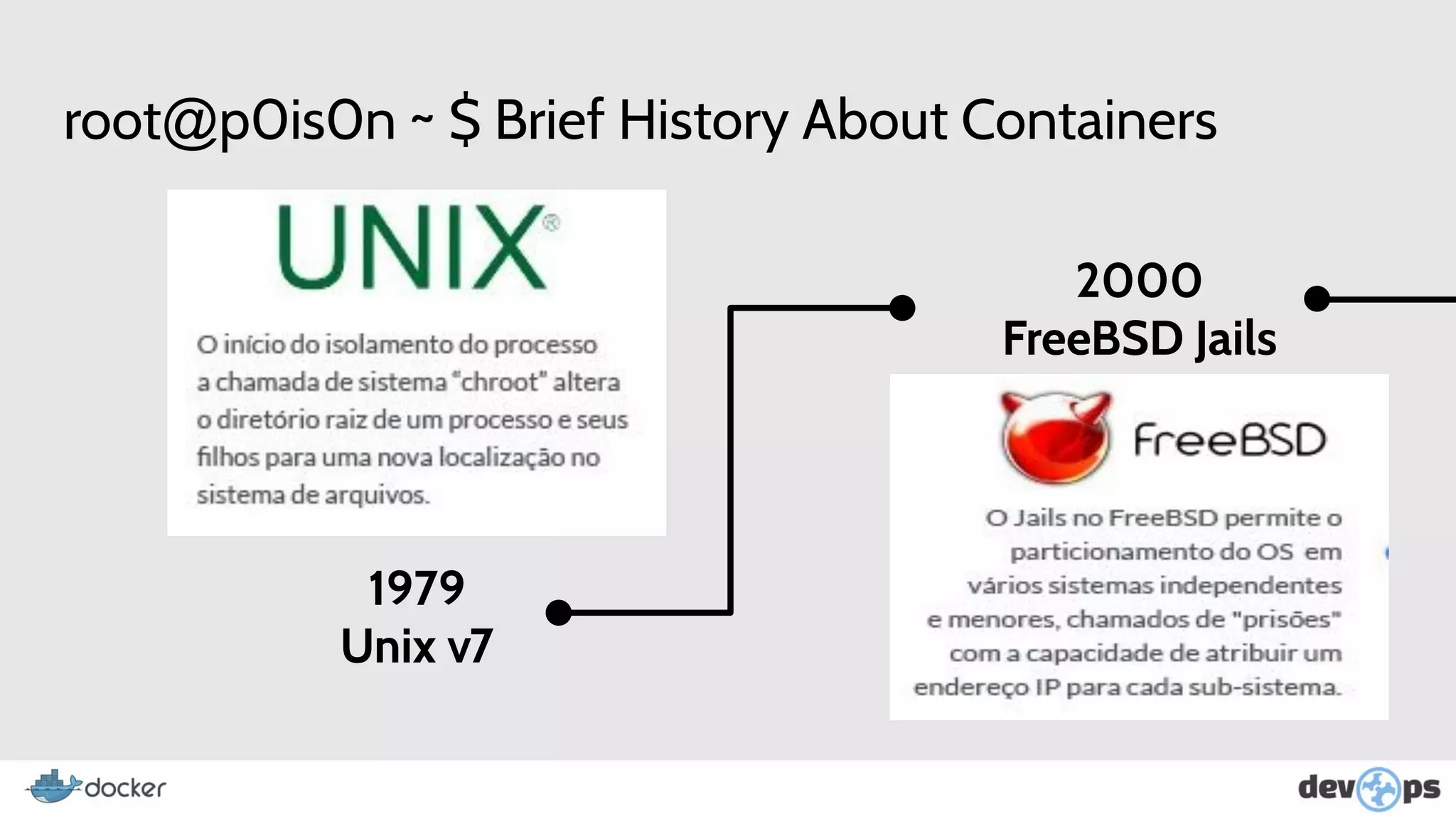
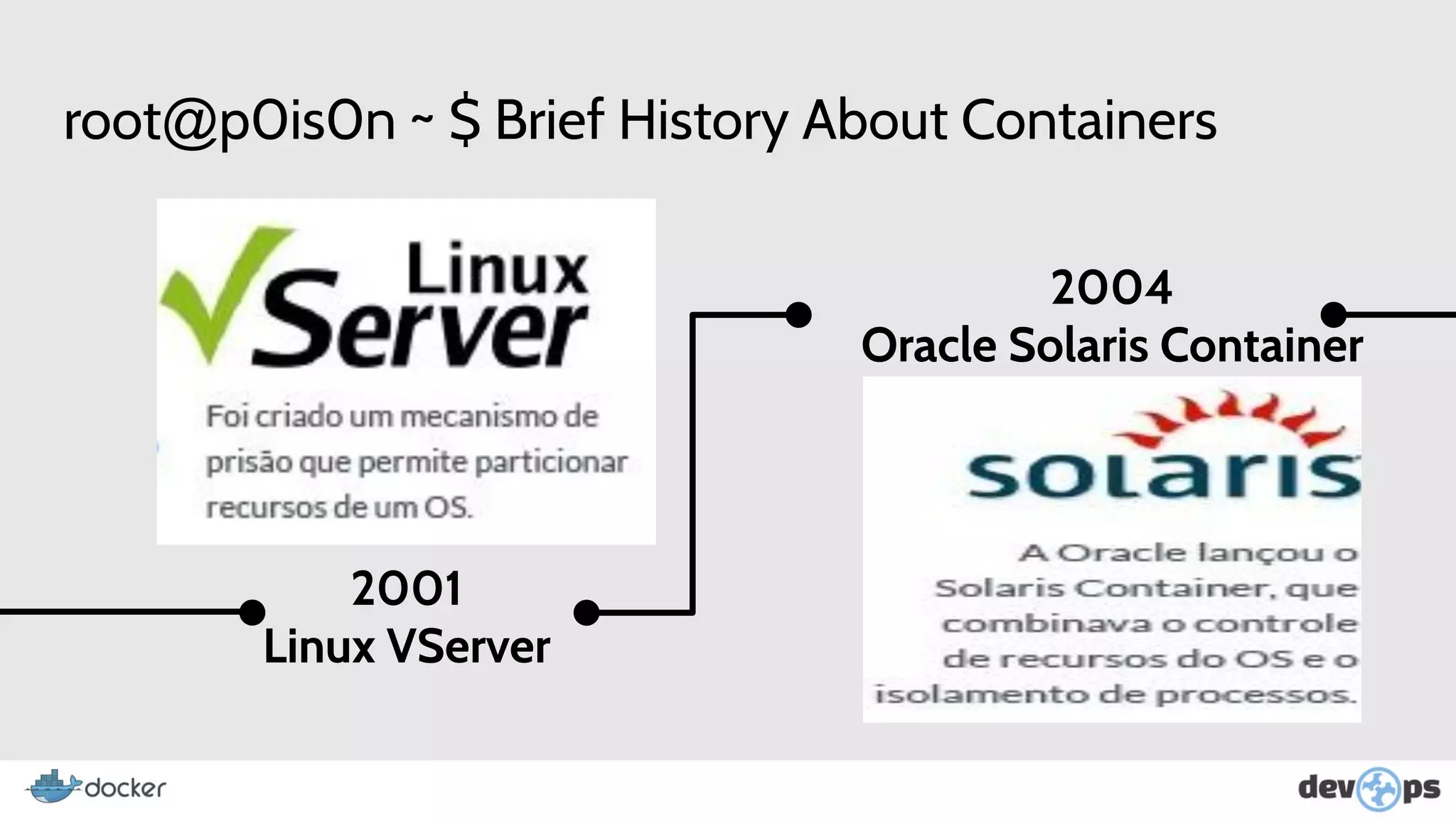
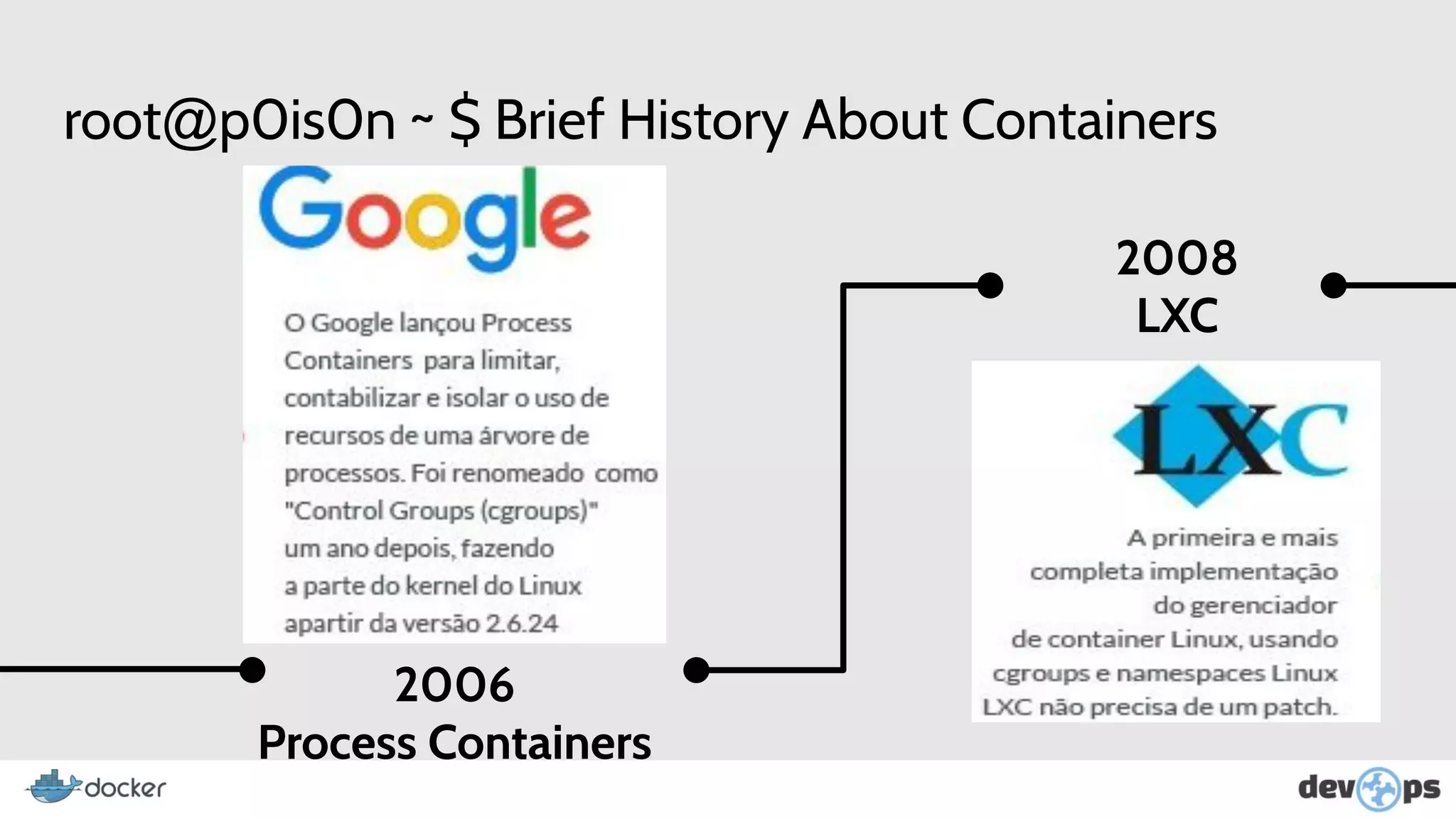
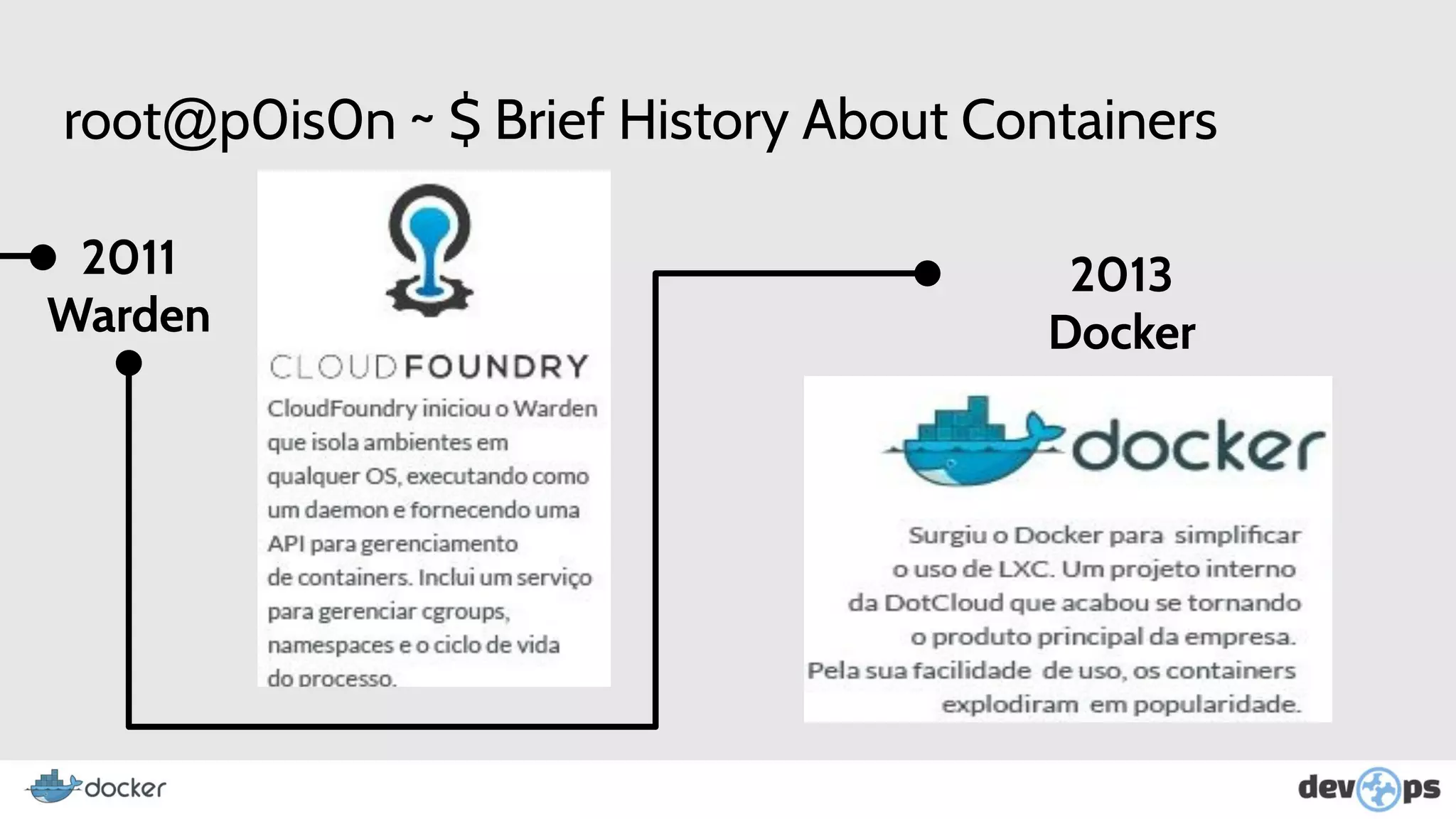
This document provides an overview and introduction to Docker including:
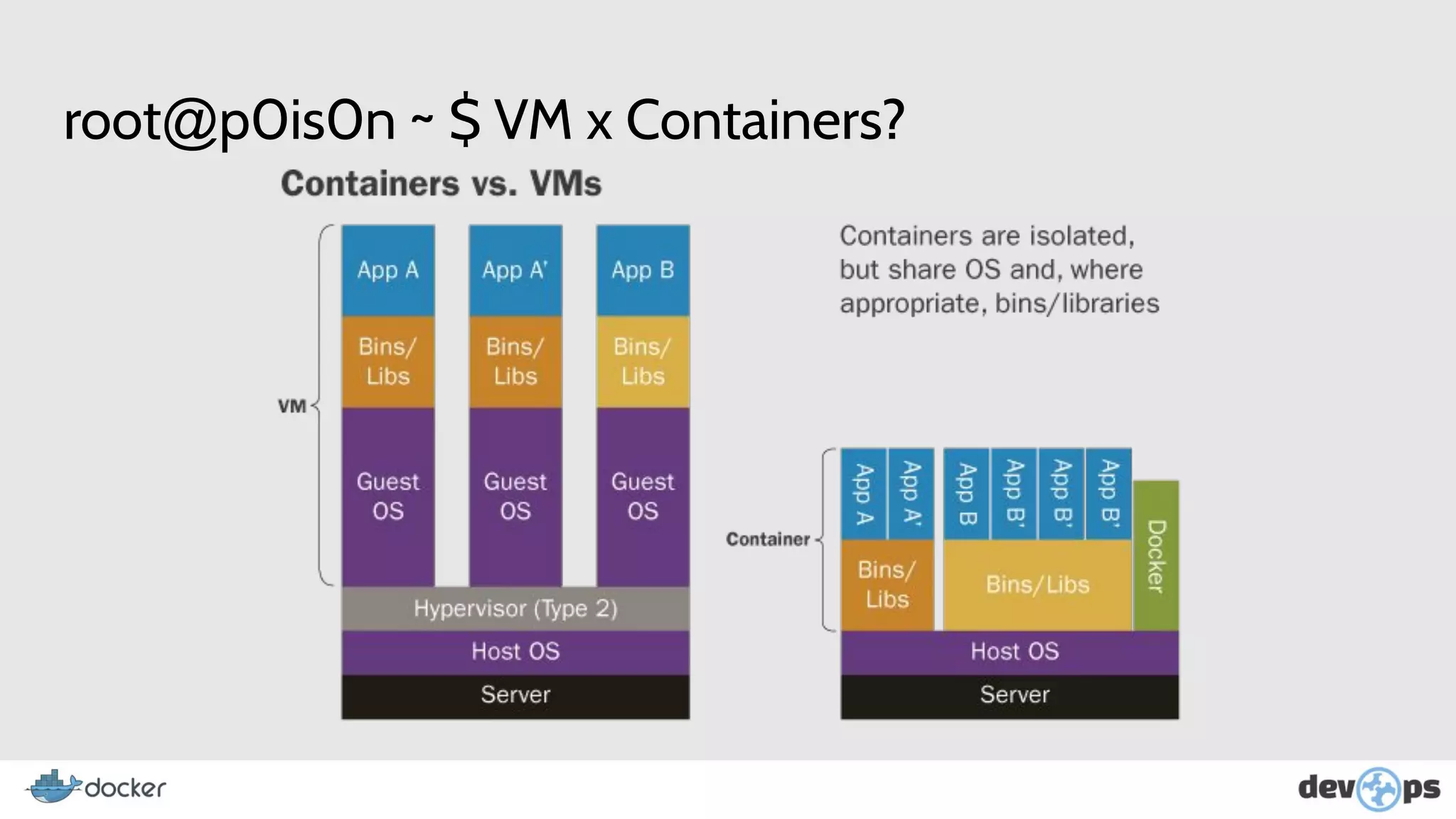
- Docker allows creating isolated environments called containers for running applications.
- Containers provide greater efficiency than virtual machines by sharing the host operating system kernel.
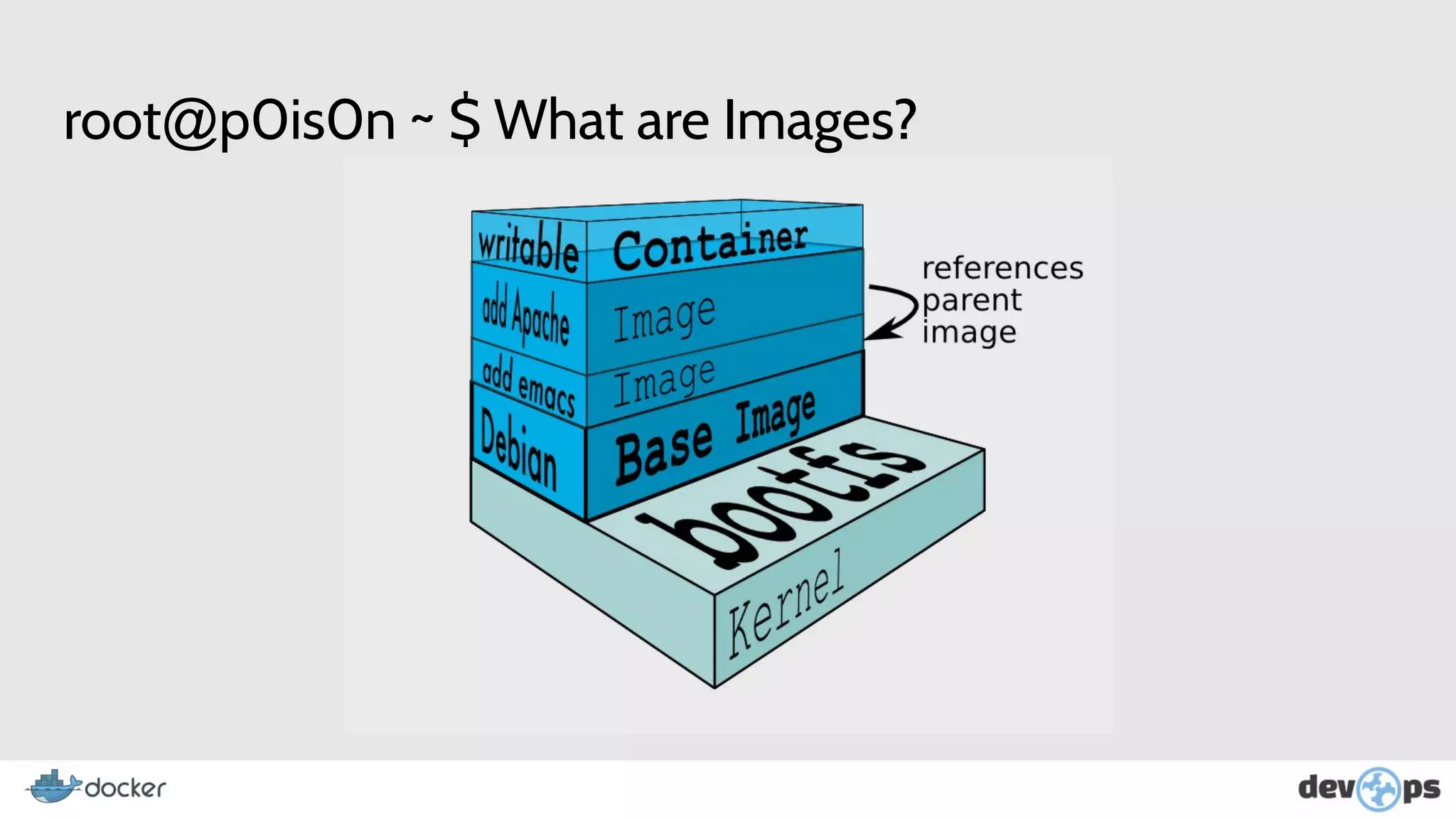
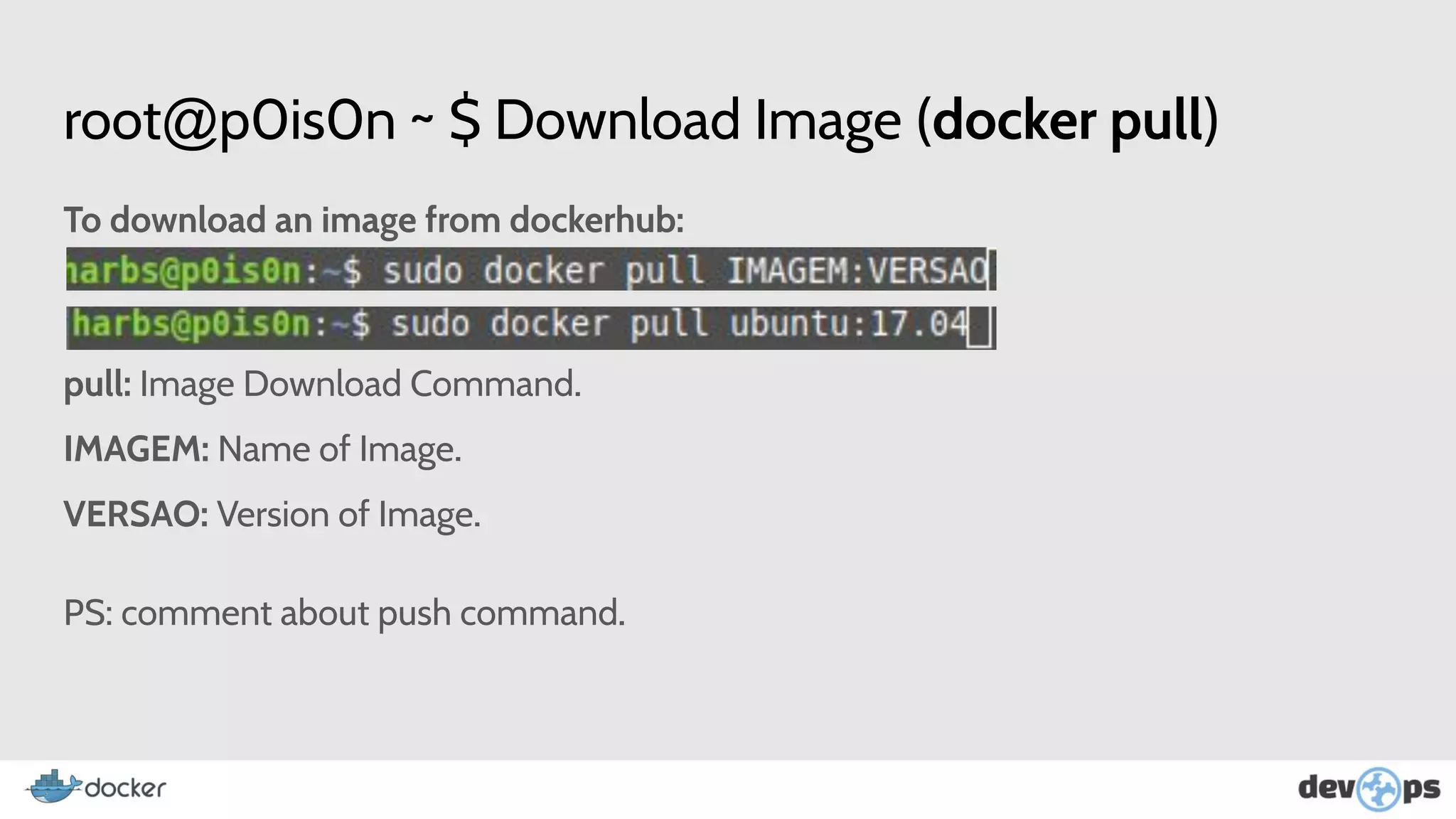
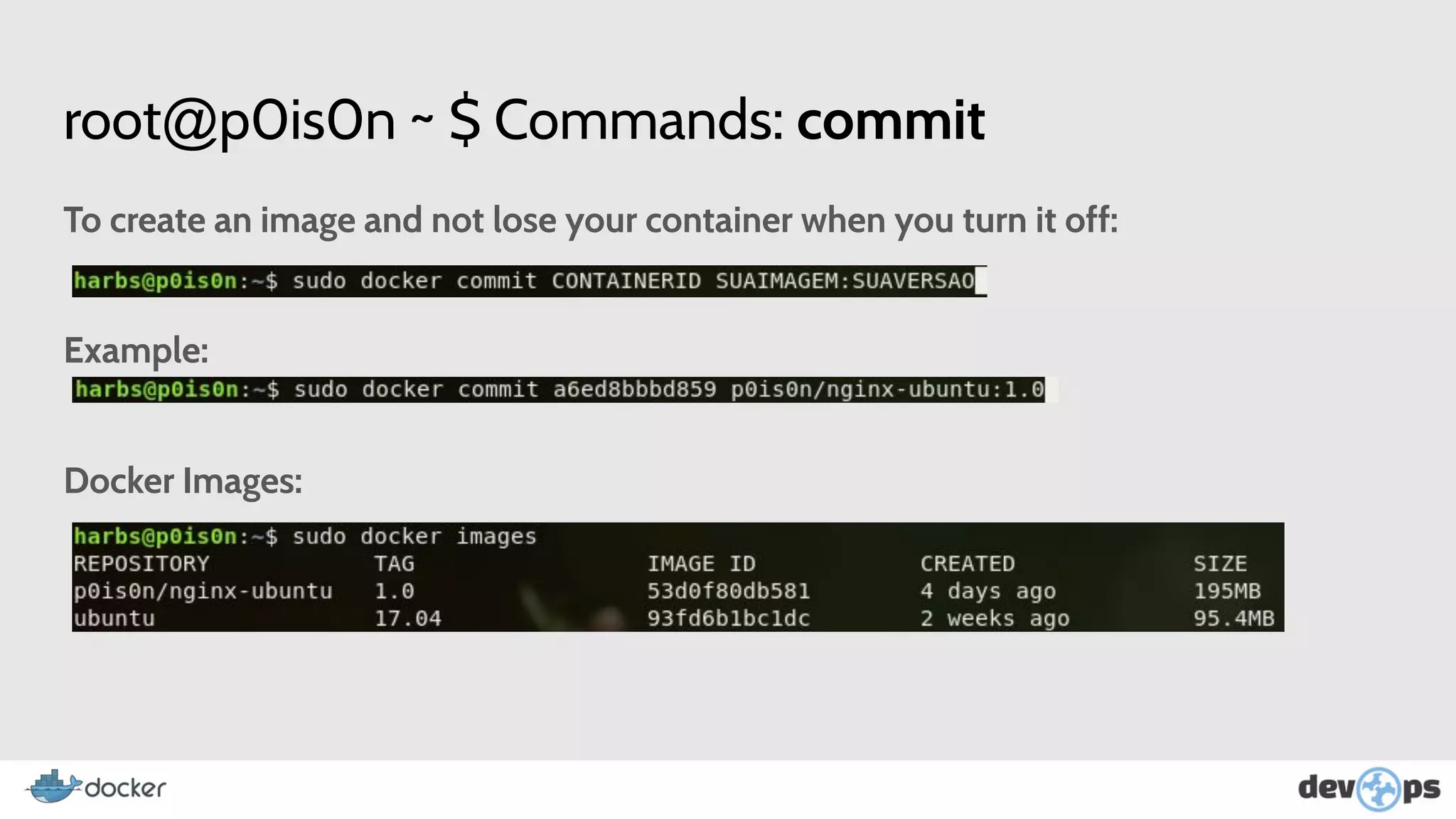
- Docker images contain the files, dependencies, and configuration for an application. Containers are based on images.
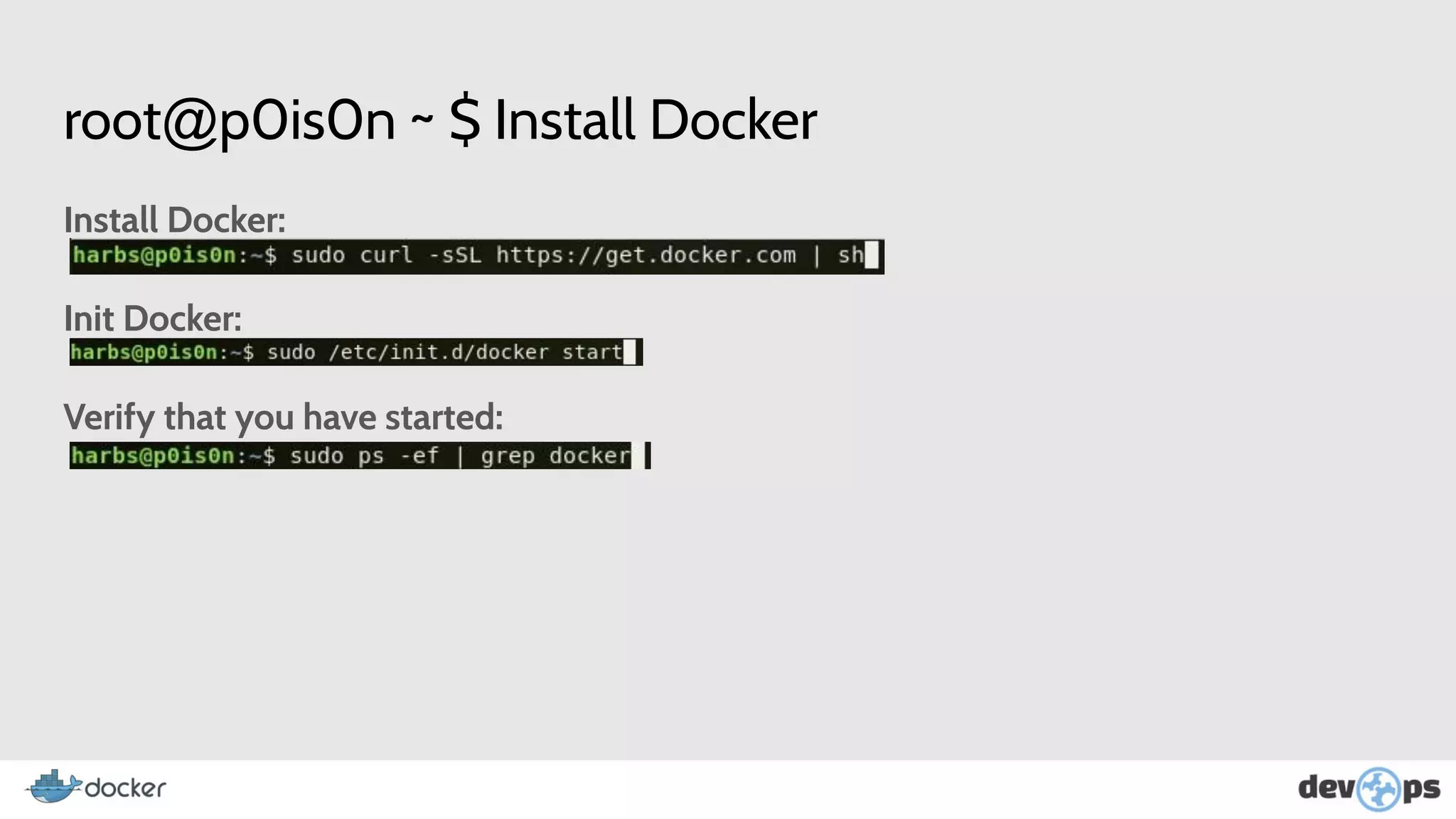
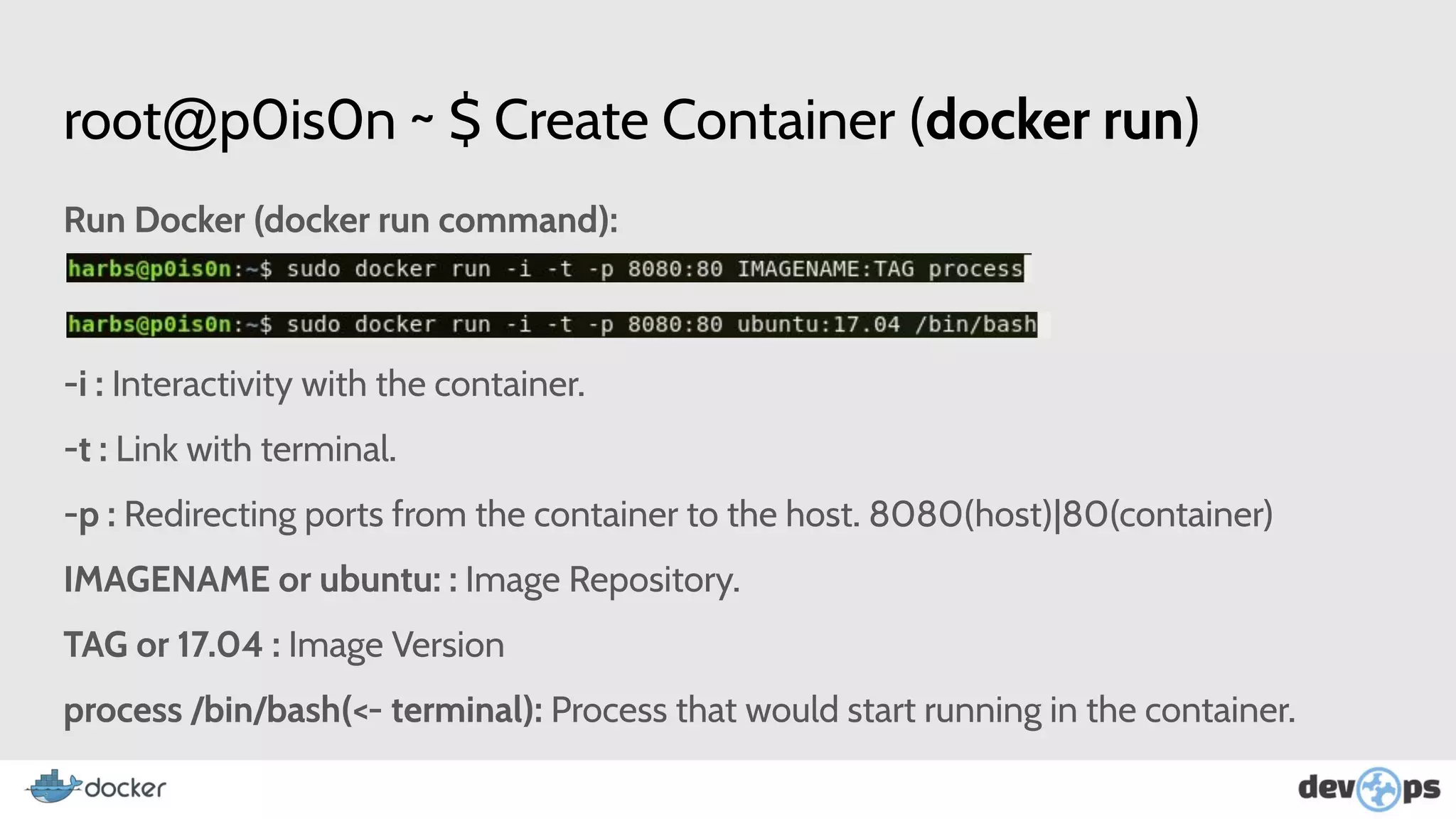
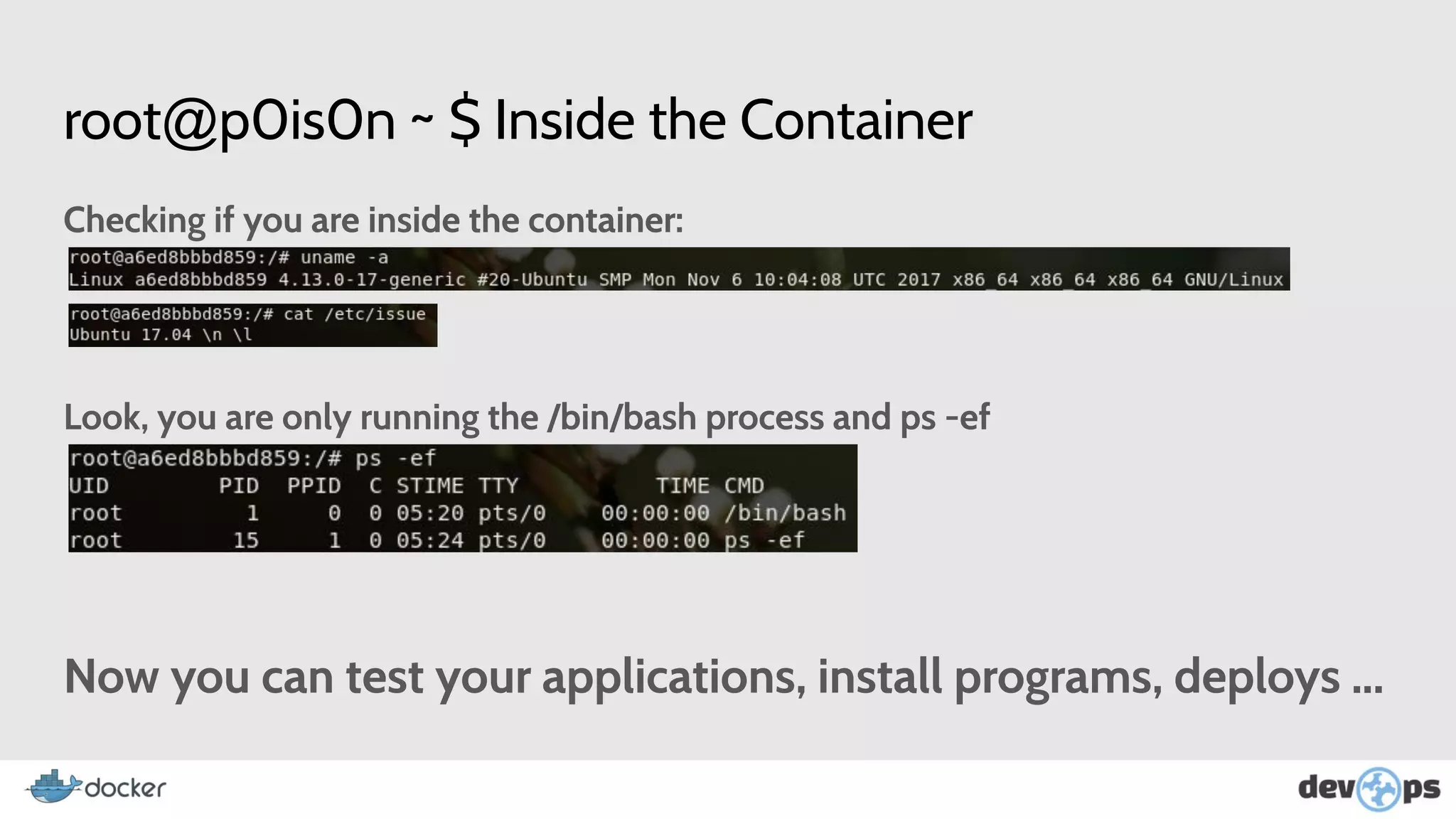
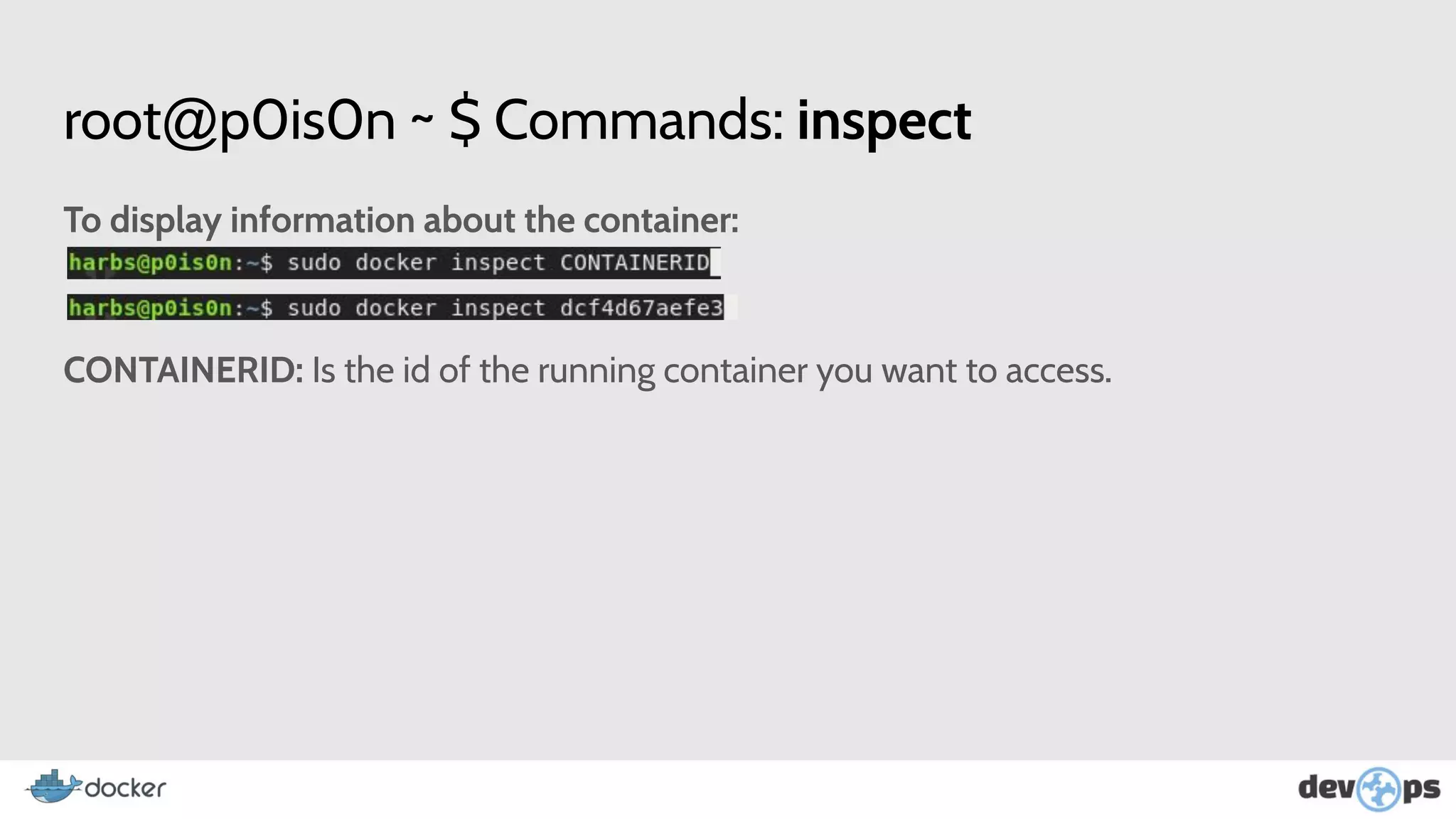
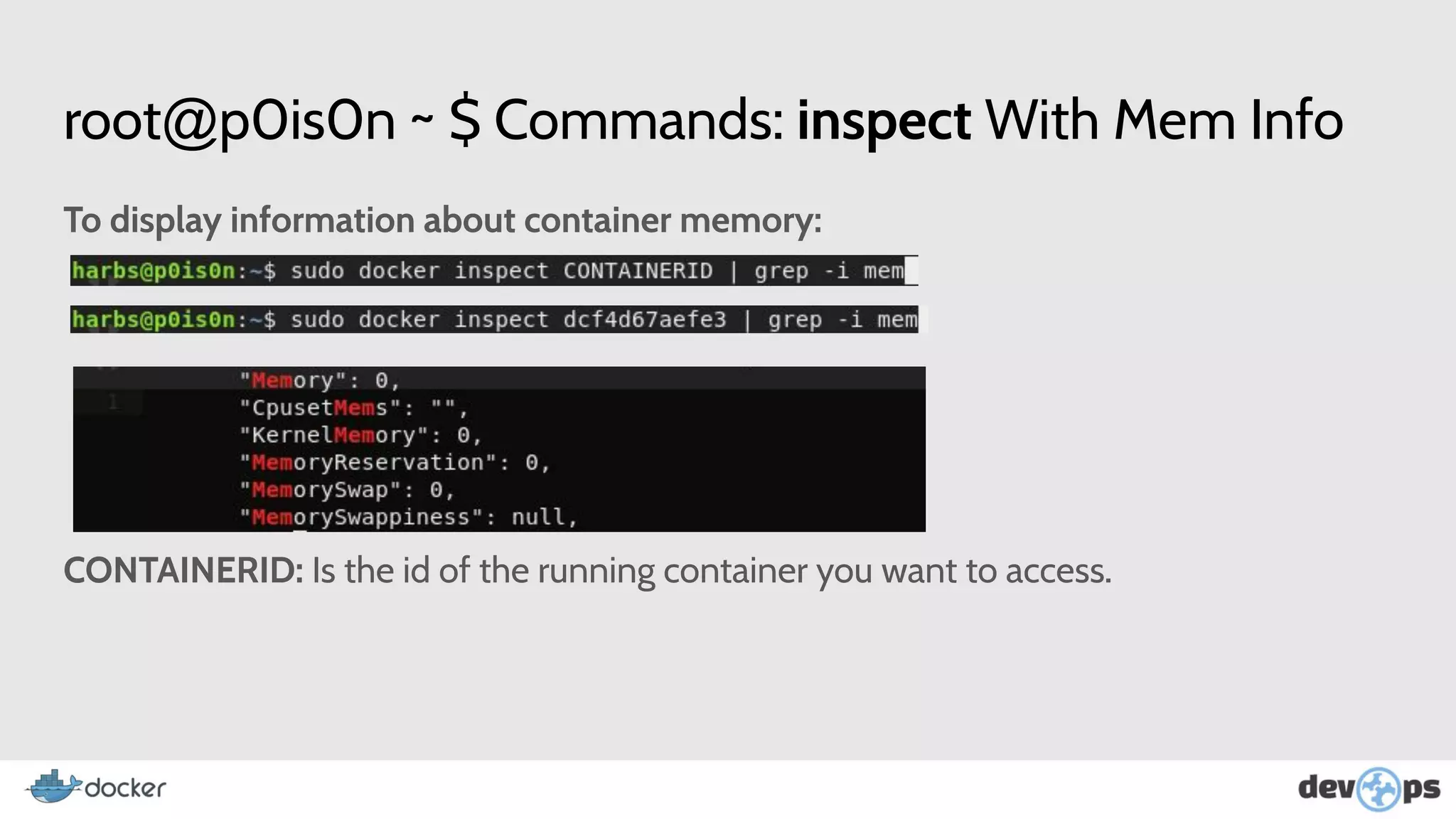
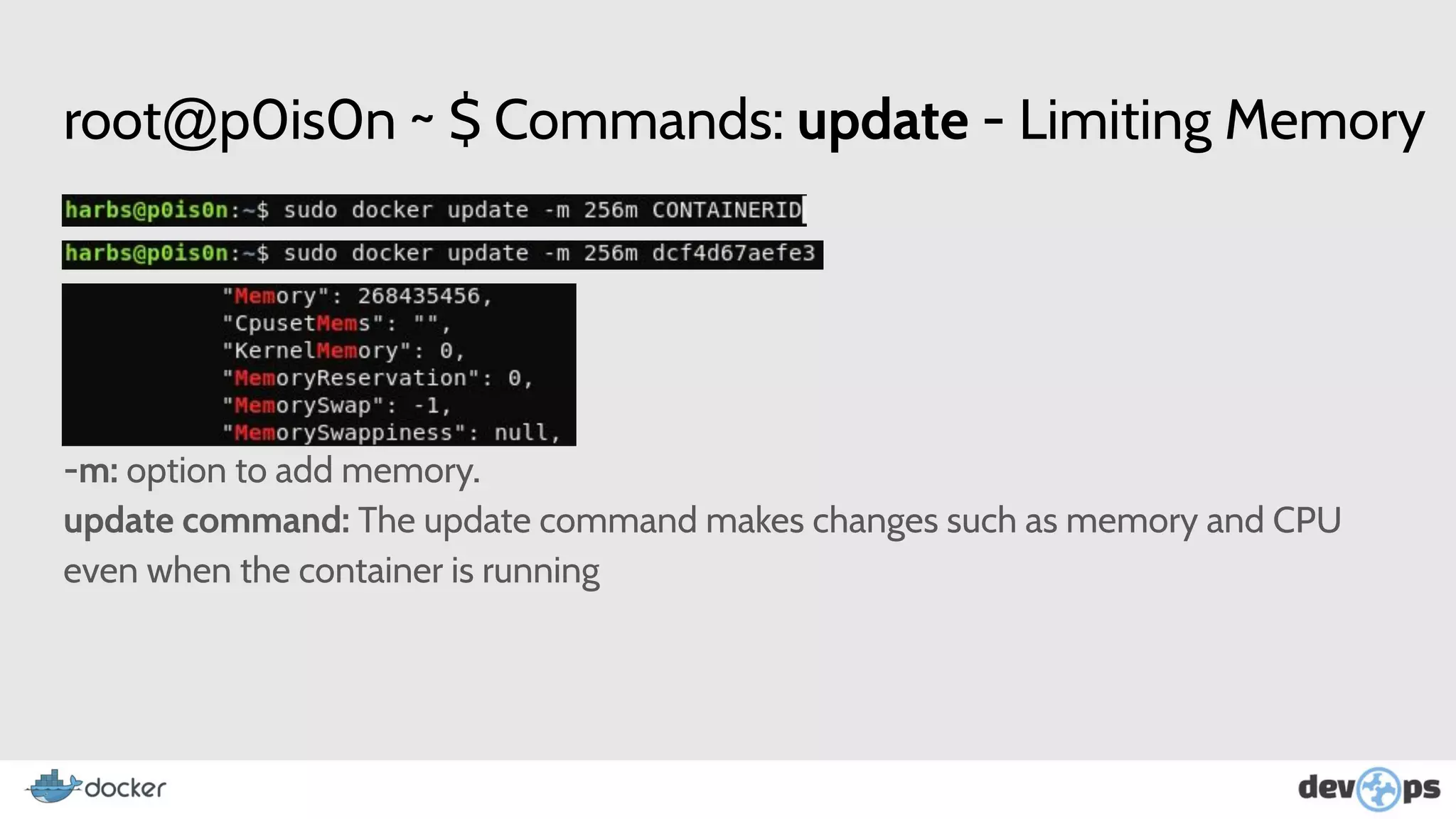
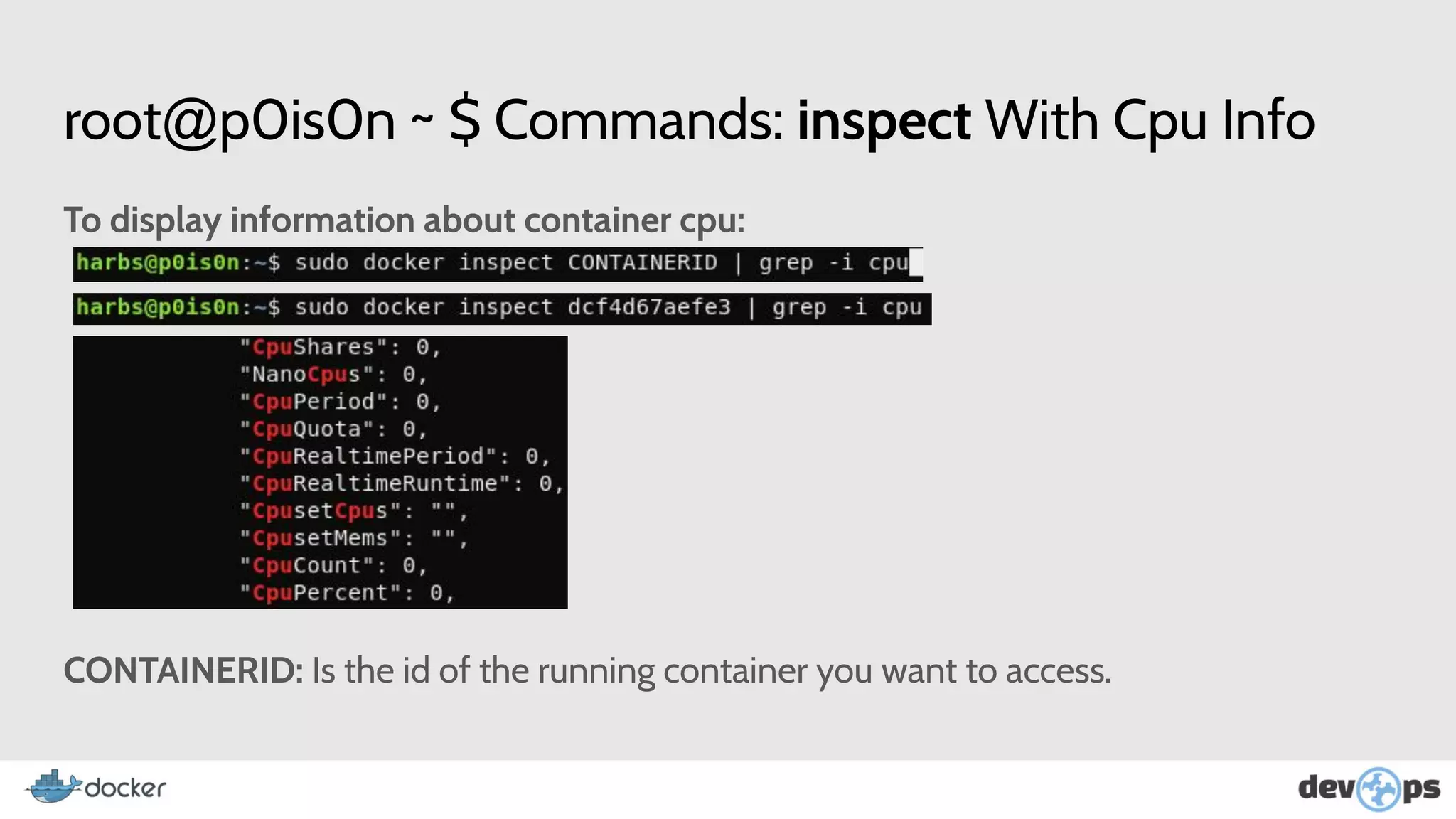
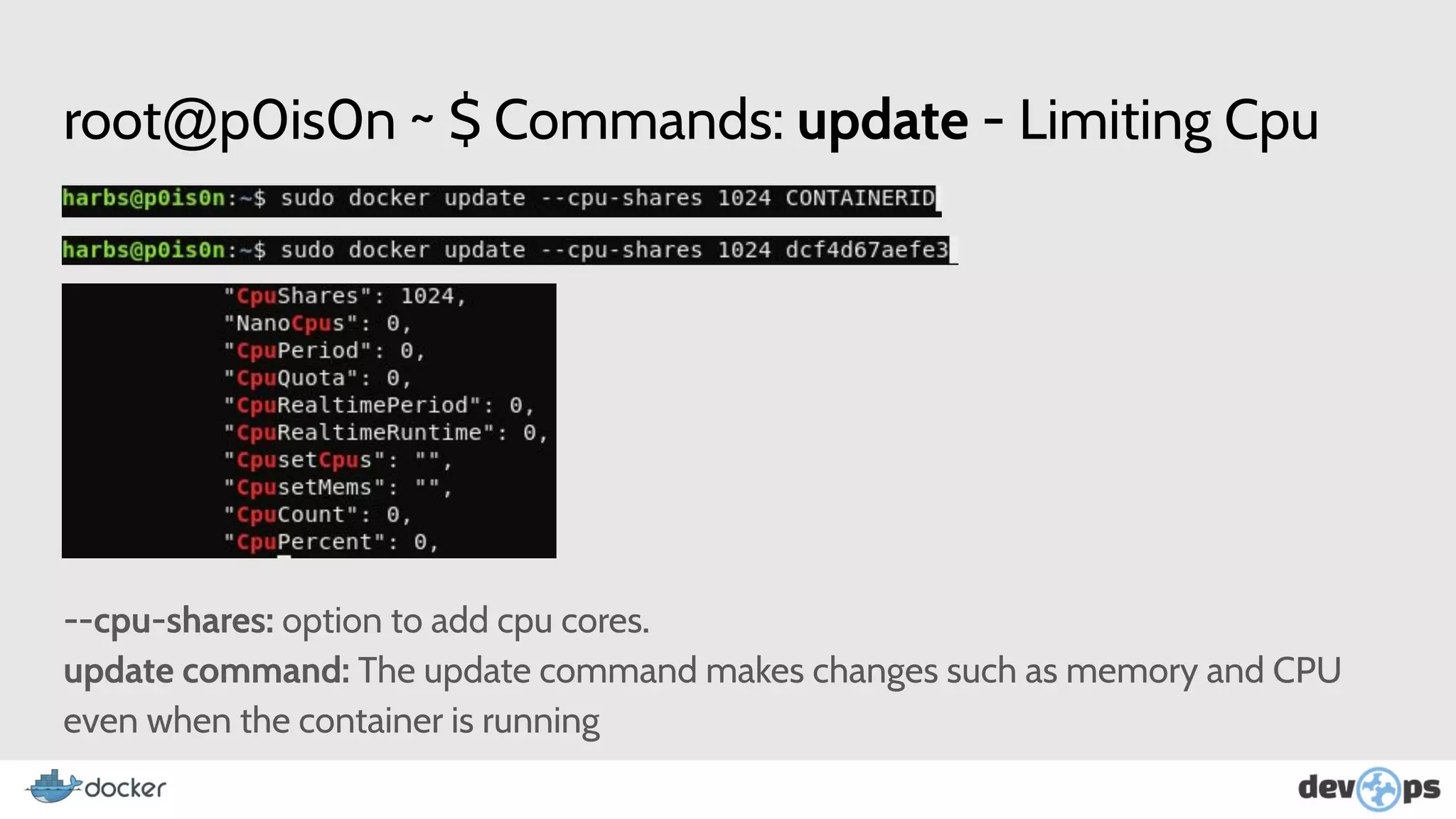
- The document then covers Docker commands for running, managing, and building containers and images.