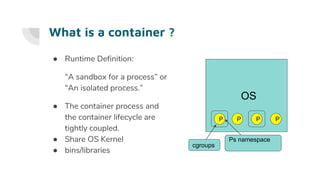
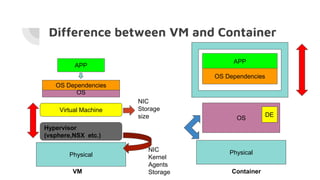
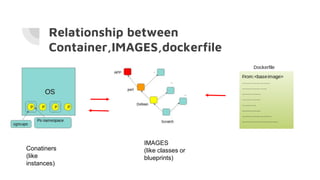
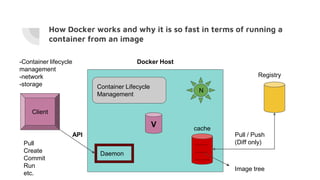
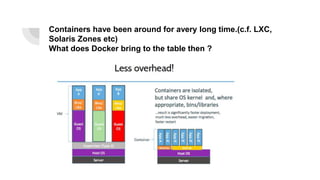
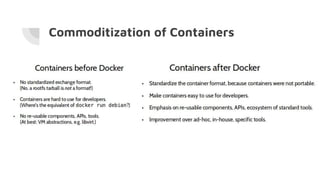
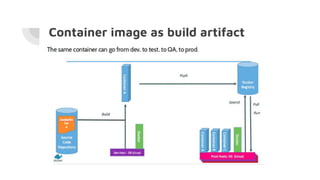
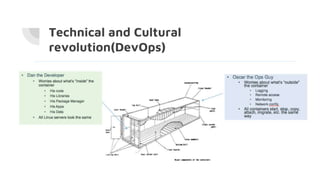
Docker allows users to run isolated processes called containers. Containers leverage features of the host operating system like namespaces and cgroups to isolate resources and run multiple containers on a single host. Docker uses images which are read-only templates used to create containers. Images are composed of layered filesystems. The Dockerfile defines how to build an image. Docker provides tools to manage the entire container lifecycle from image management to container runs. It standardizes the package and distribution of applications as container images. This helped drive adoption of containers and microservices architectures in DevOps workflows.