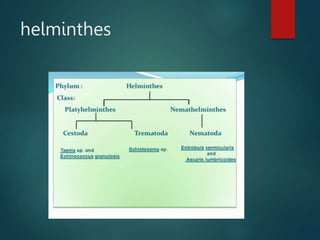
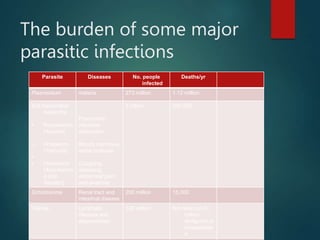
Medical parasitology deals with parasites that infect humans, the diseases they cause, their diagnosis, treatment and prevention. Parasites include protozoa like amoebas and plasmodium, and helminths like tapeworms, flukes and roundworms. They are transmitted through various routes like contaminated food or water, contact with infected individuals, or vectors. Common parasitic infections are caused by malaria, soil-transmitted helminths and schistosomiasis, affecting billions of people worldwide and causing deaths. Their diagnosis involves clinical and laboratory methods while treatment consists of chemotherapy, surgery and improving nutrition. Prevention relies on education, reducing sources of infection, and controlling vectors and reservoir hosts.