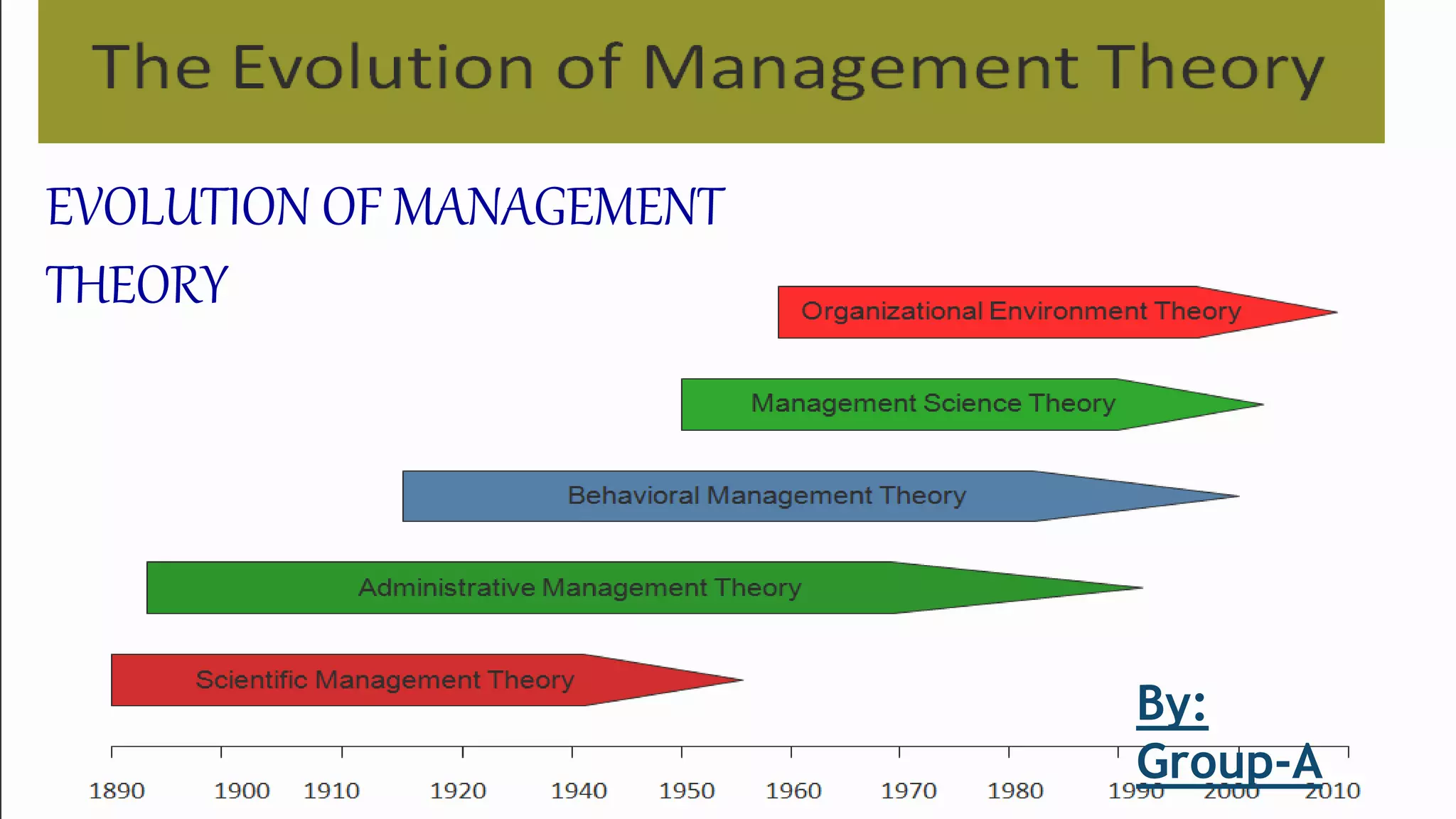
The document outlines the evolution of management theory, detailing various approaches including scientific management by Frederick Winslow Taylor, administrative management by Henry Fayol, and behavior science theory, among others. Each theory has its contributions and limitations, emphasizing aspects such as efficiency, human relations, and decision-making processes. The document also highlights the contingency theory, which suggests there is no one best way to manage, acknowledging the influence of situational variables on management practices.