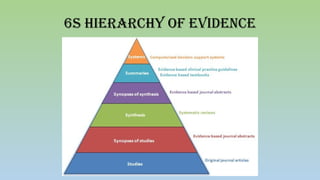
Evidence-based practice (EBP) in nursing is defined as a process that integrates the best evidence from literature, clinical expertise, and patient preferences to enhance nursing care quality. The EBP process involves formulating clinical questions, acquiring and appraising evidence, and applying findings to practice, ultimately aiming for better patient outcomes. However, various challenges such as lack of research skills, time constraints, and resistance to change hinder the adoption of EBP among nurses.