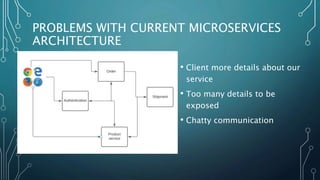
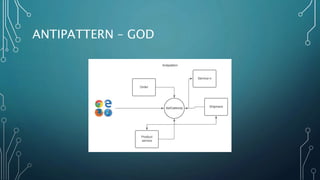
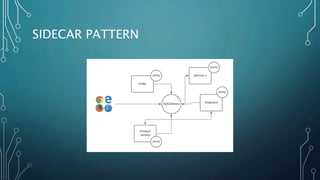
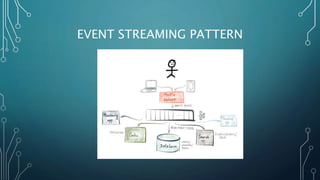
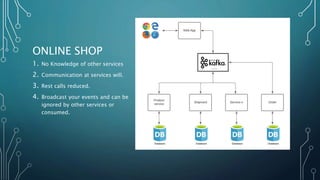
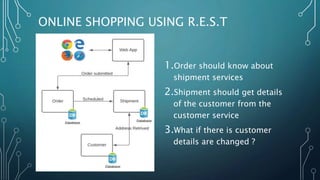
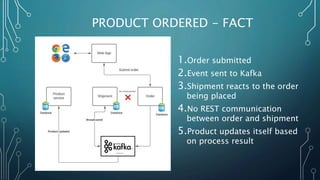
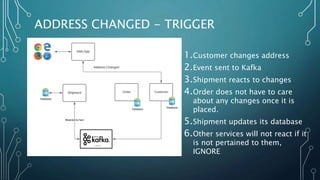
The document discusses event streaming architecture, emphasizing its advantages for real-time processing and analytics over traditional ETL and microservices methods. It explores how event-driven communication reduces dependencies between services, illustrated through an online shopping scenario. Key concepts include events as immutable facts, stream joins for data analysis, and practical insights into utilizing Azure Event Hubs for anomaly detection.