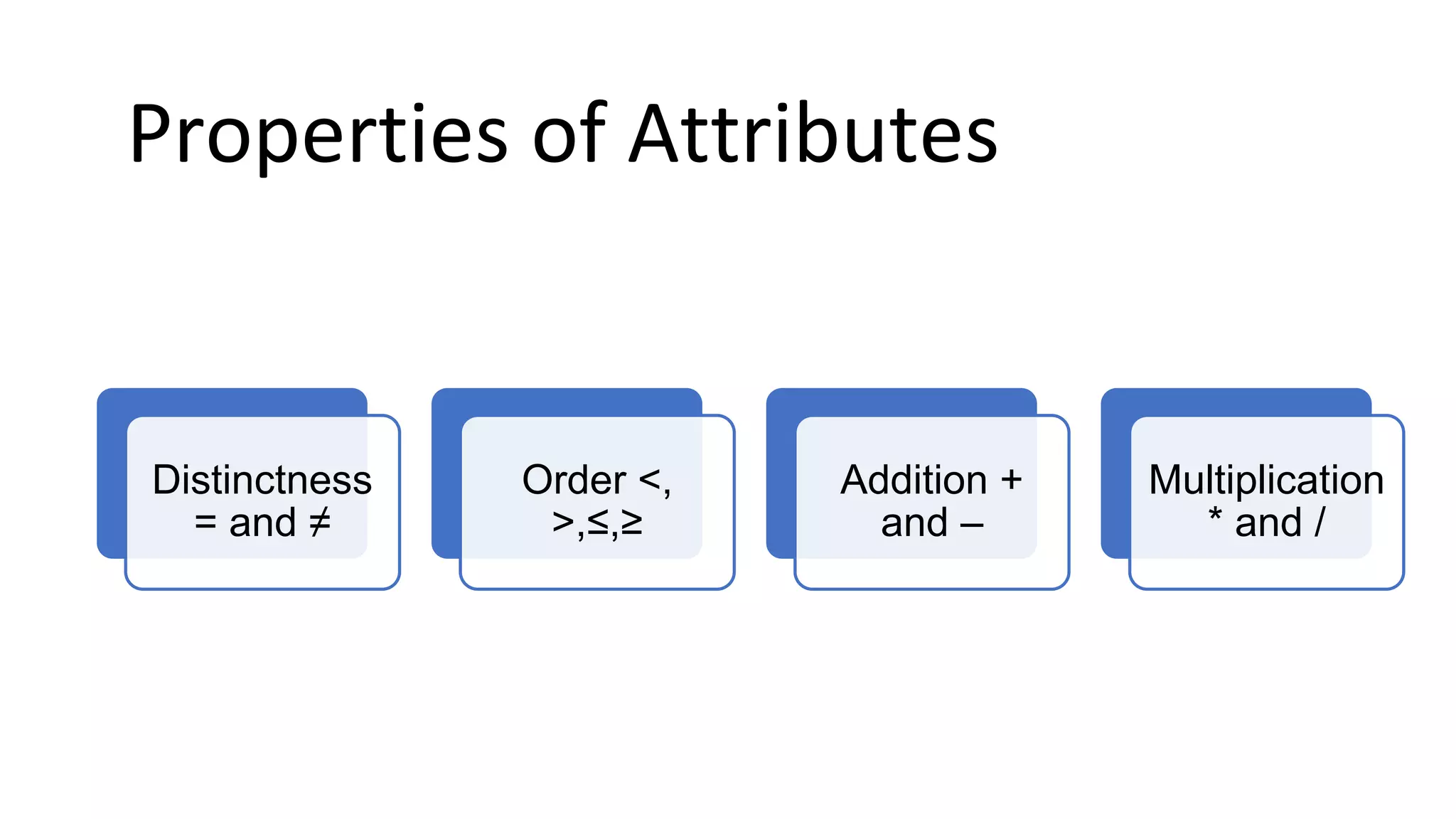
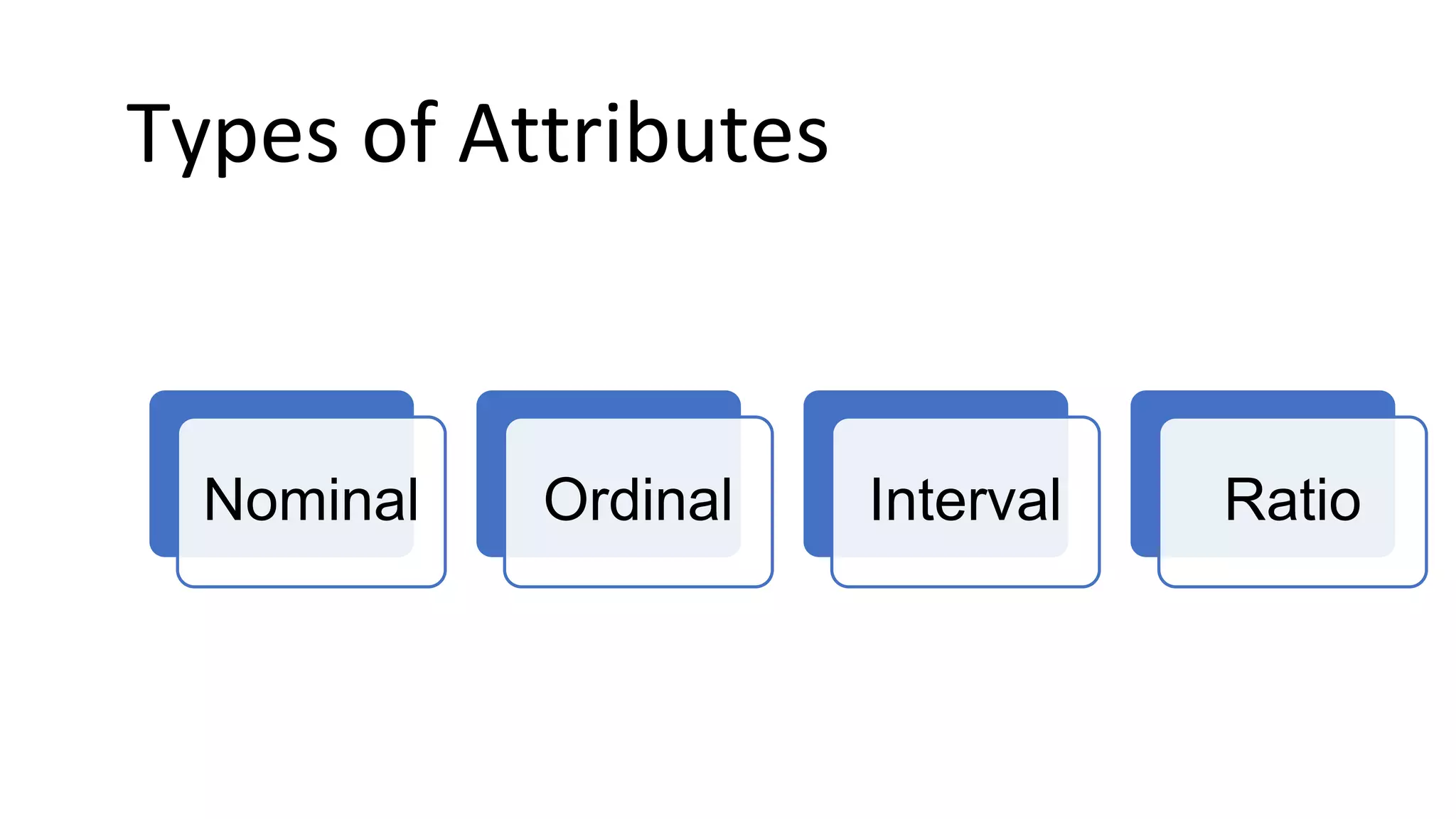
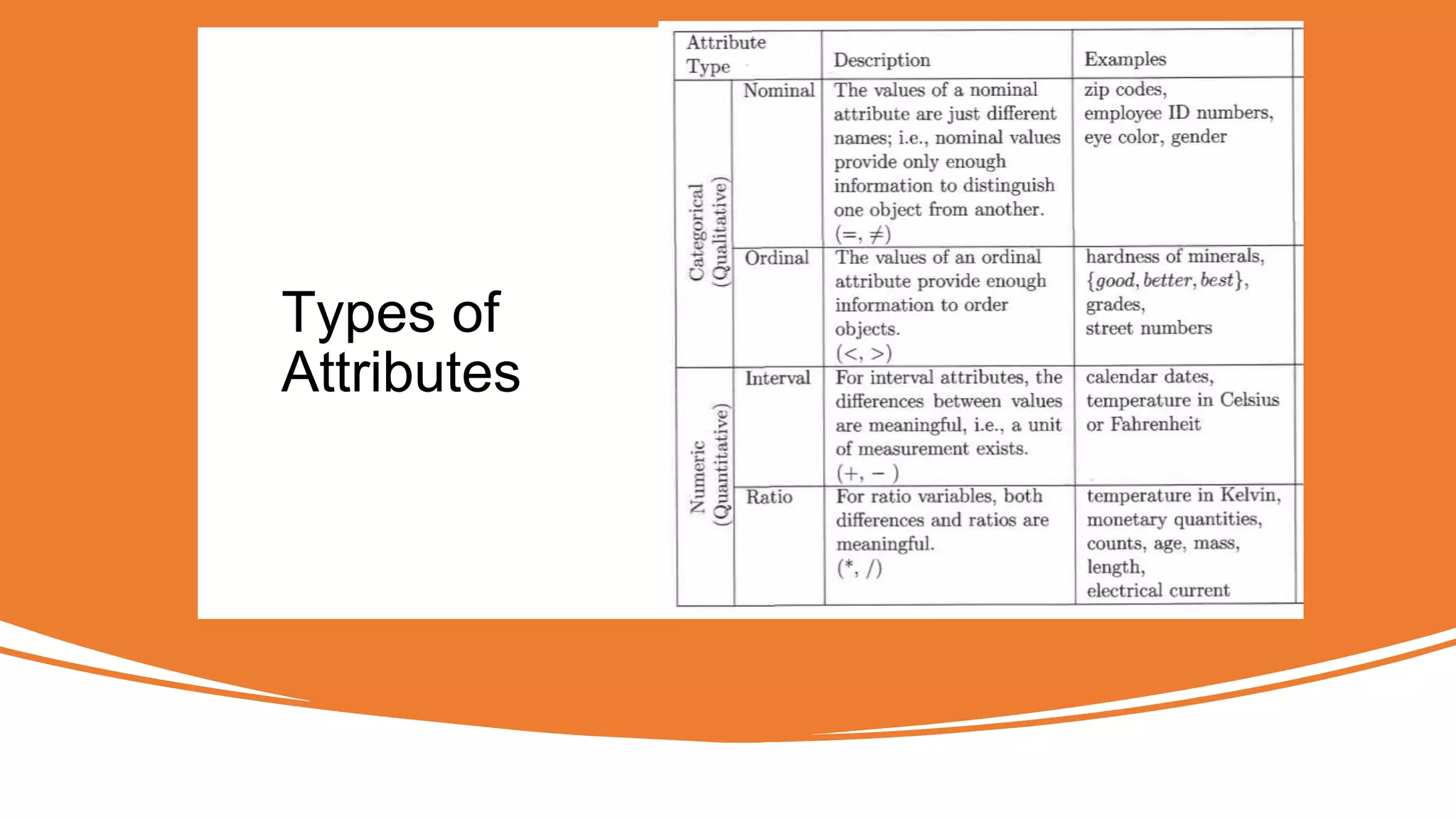
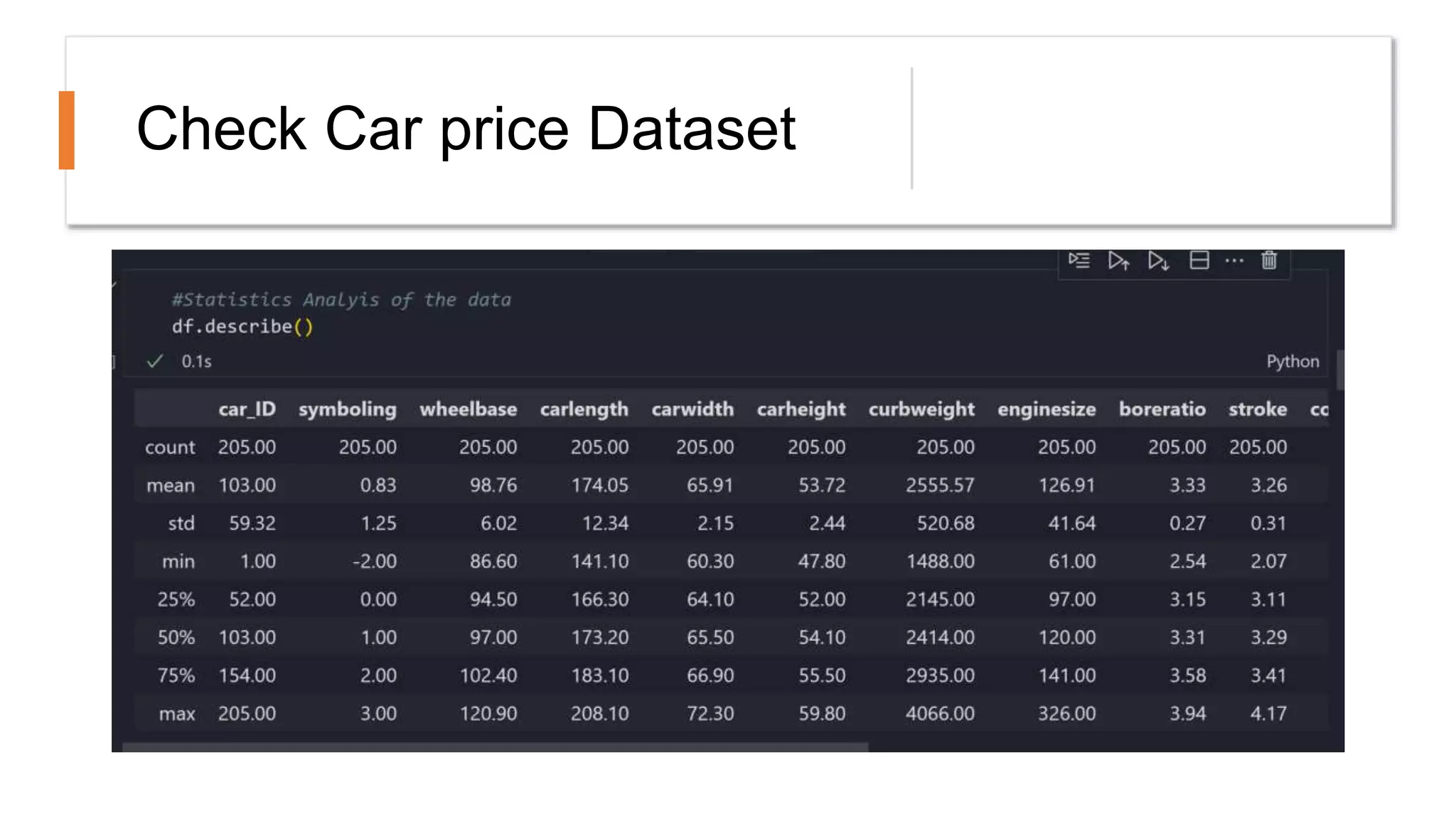
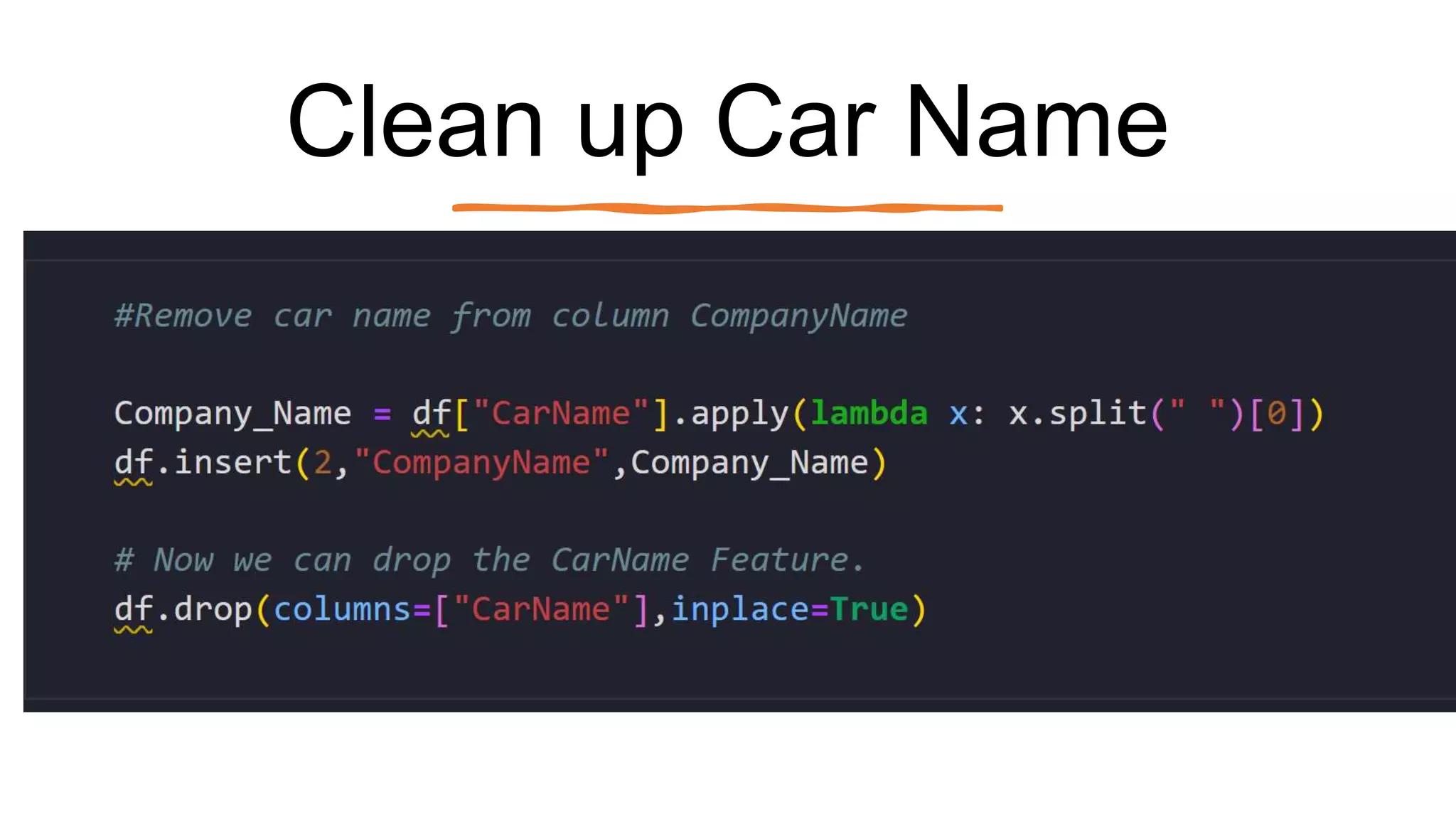
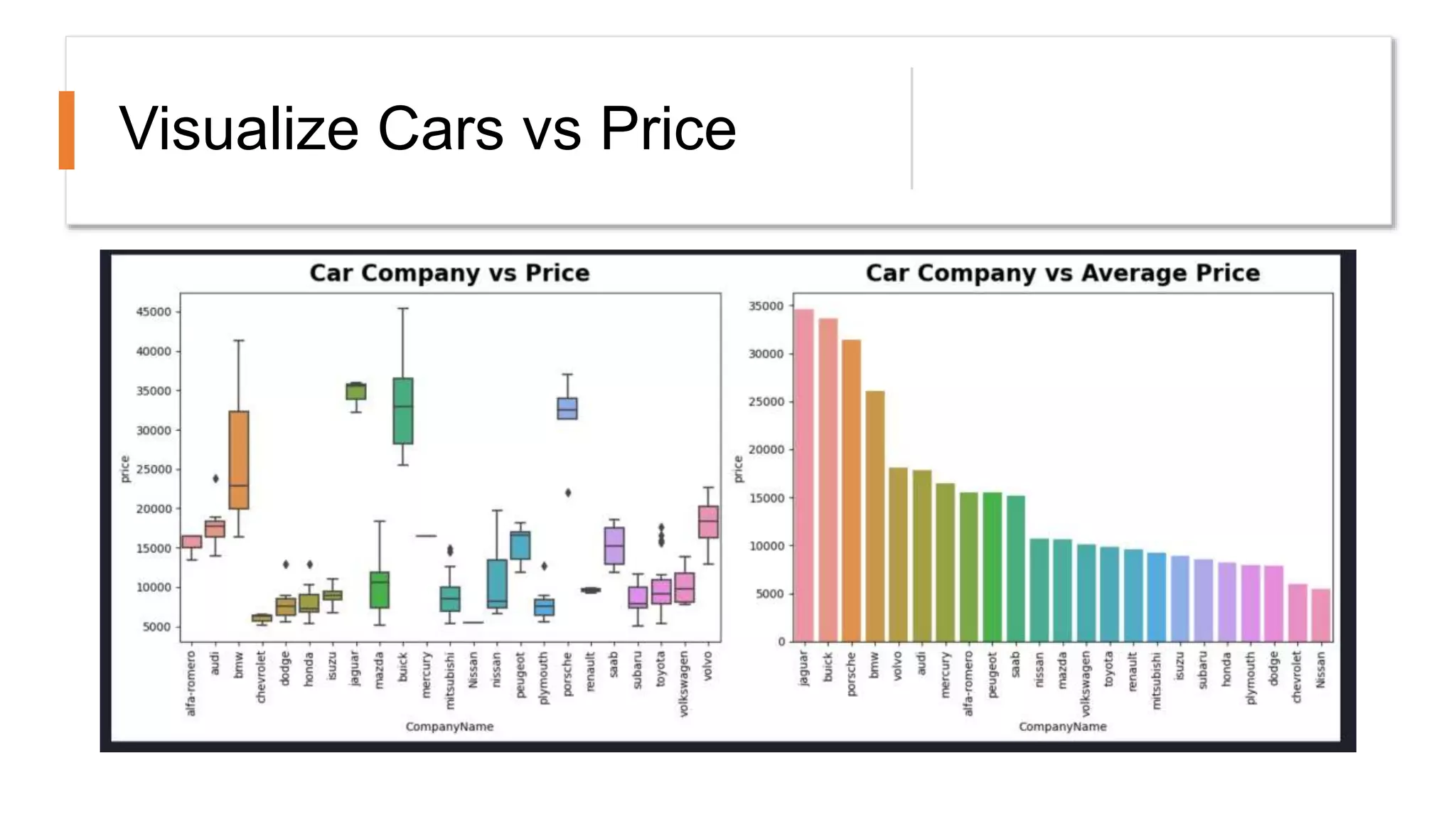
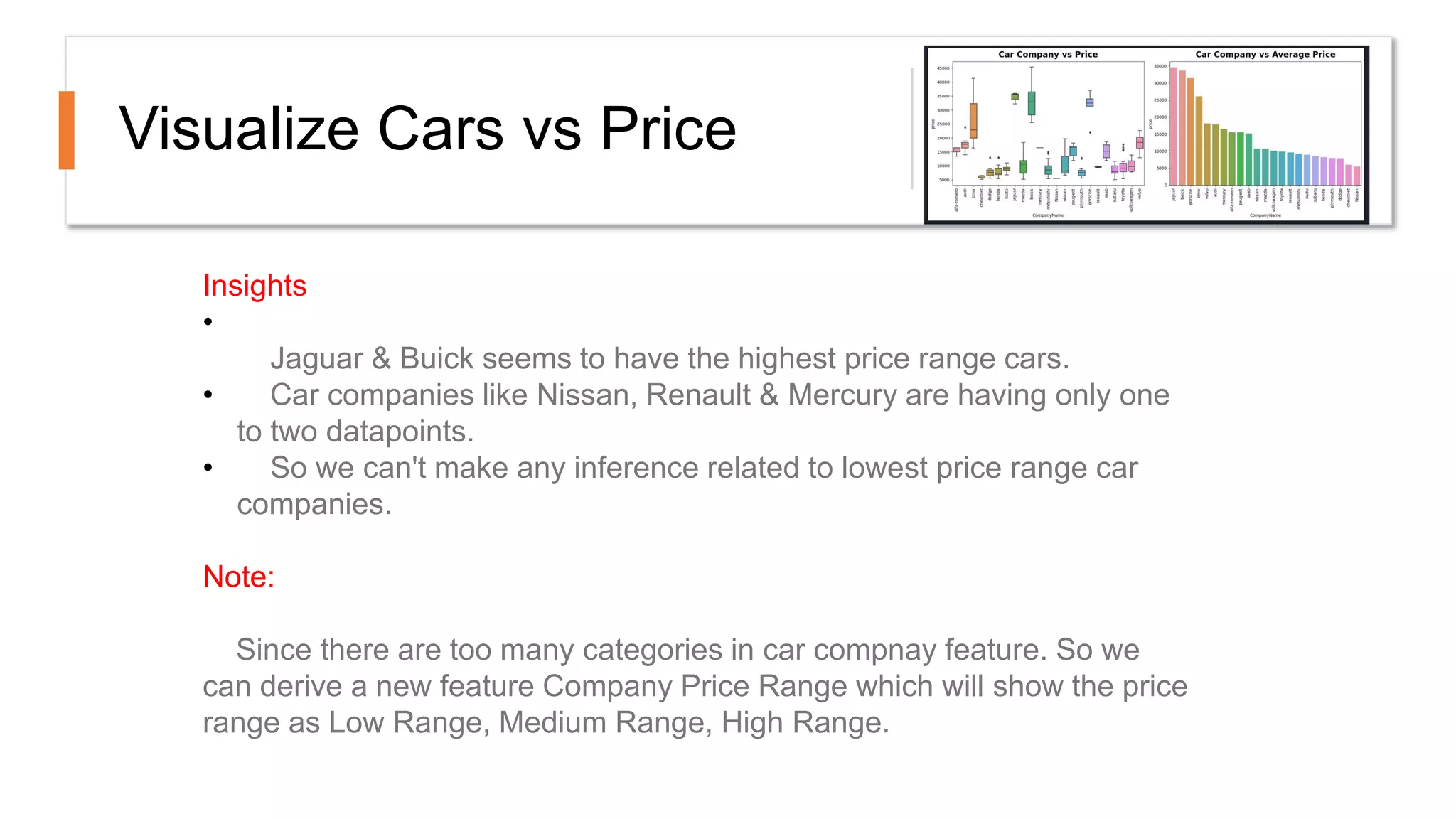
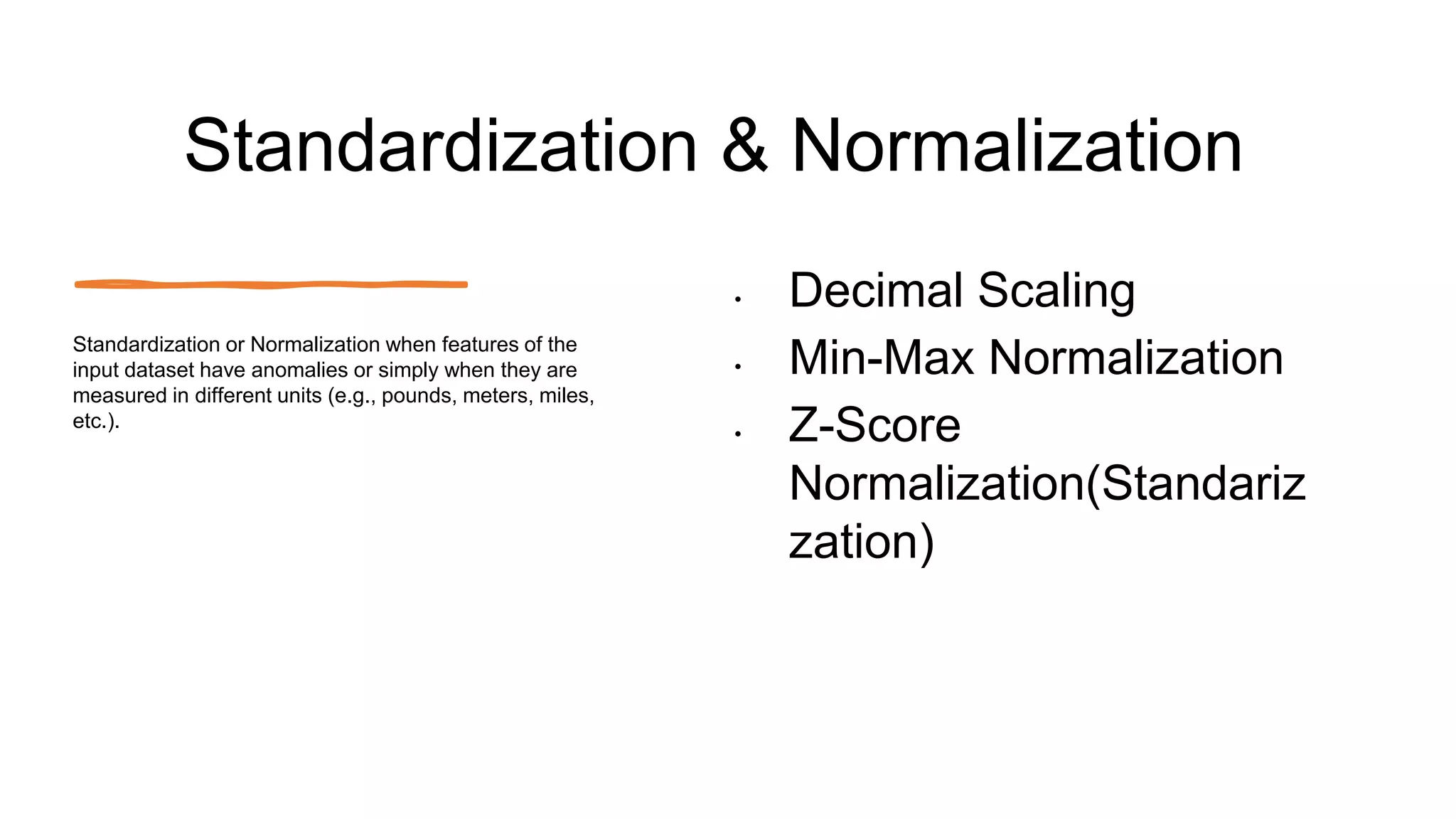
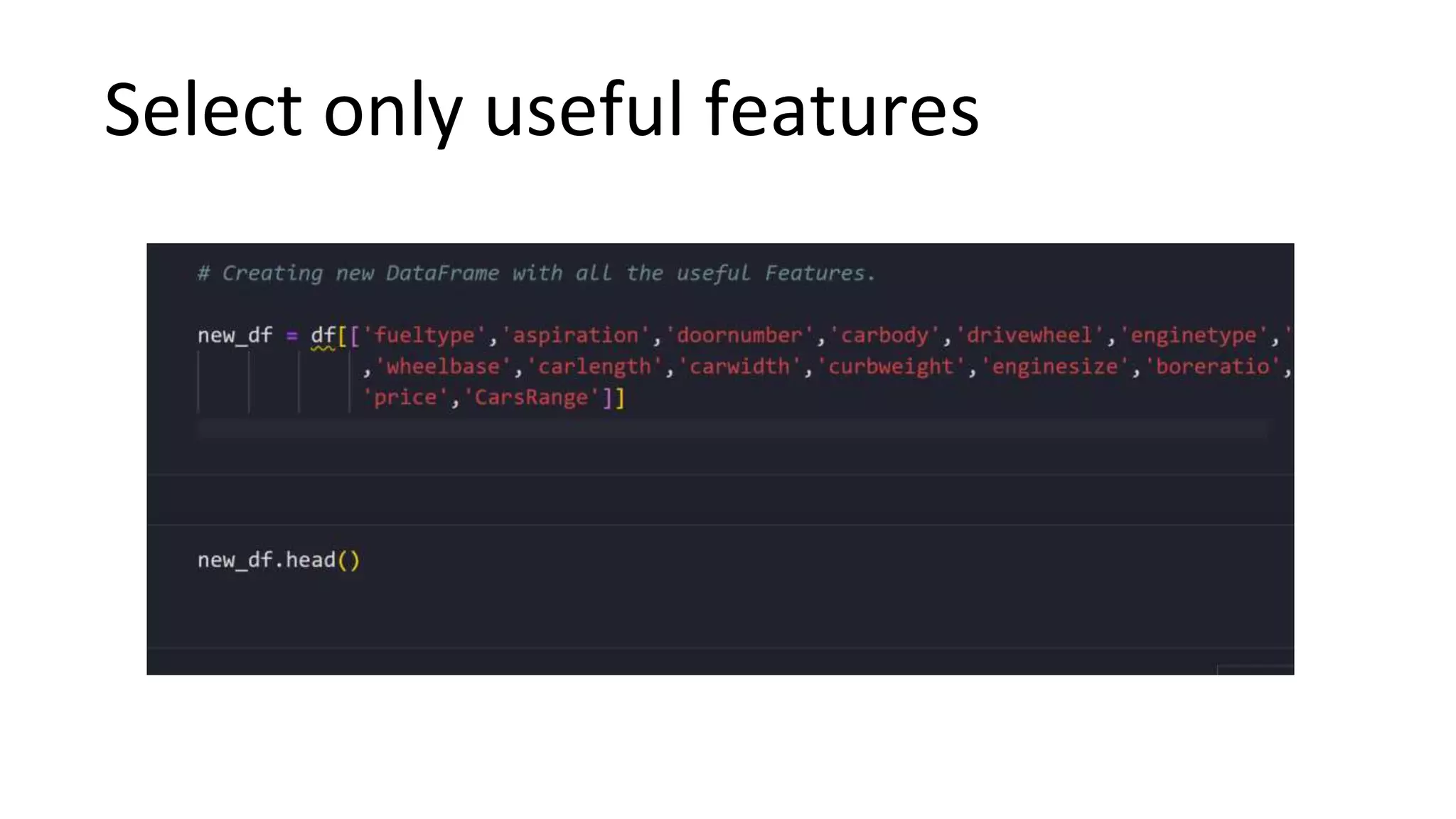
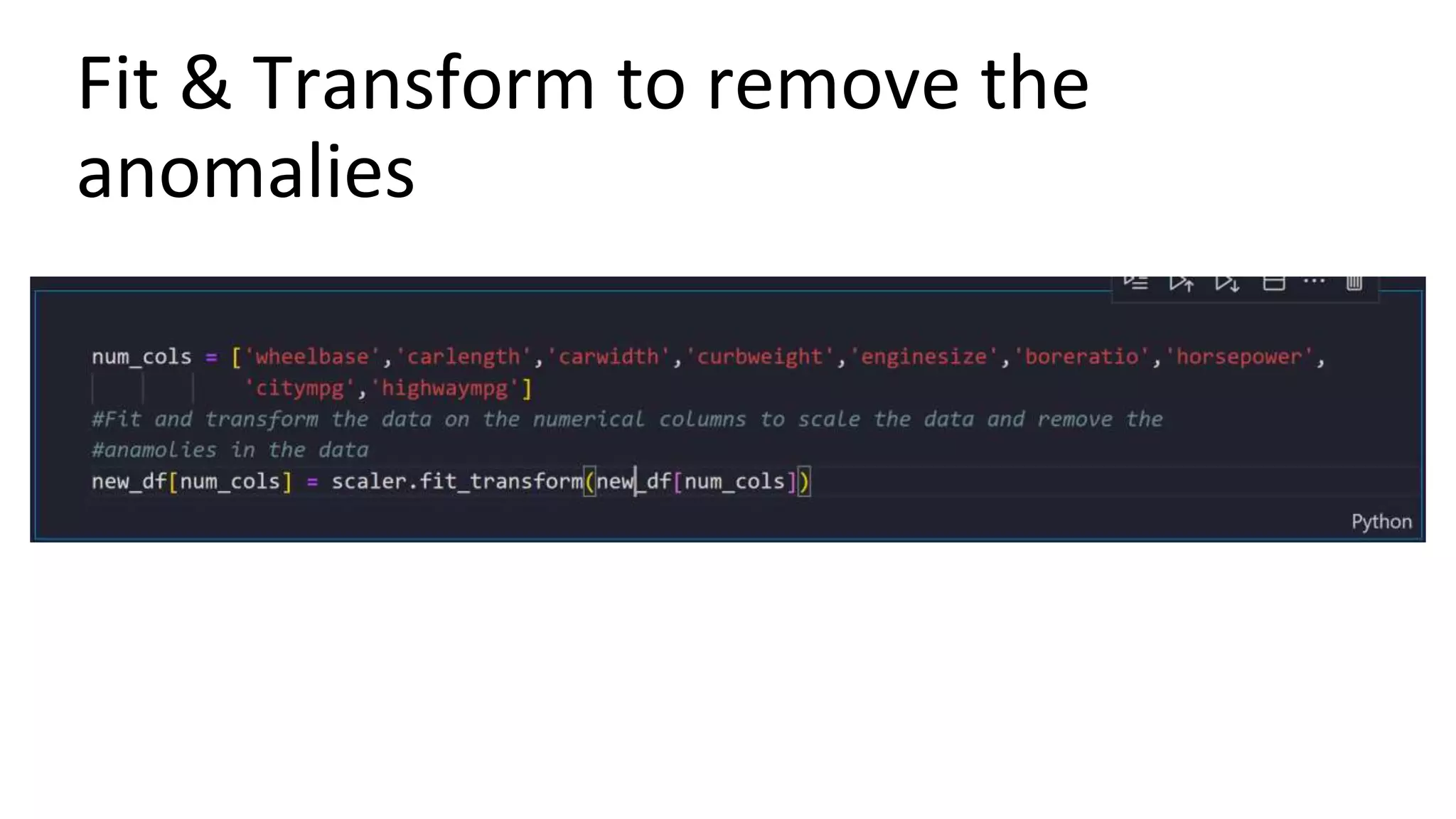
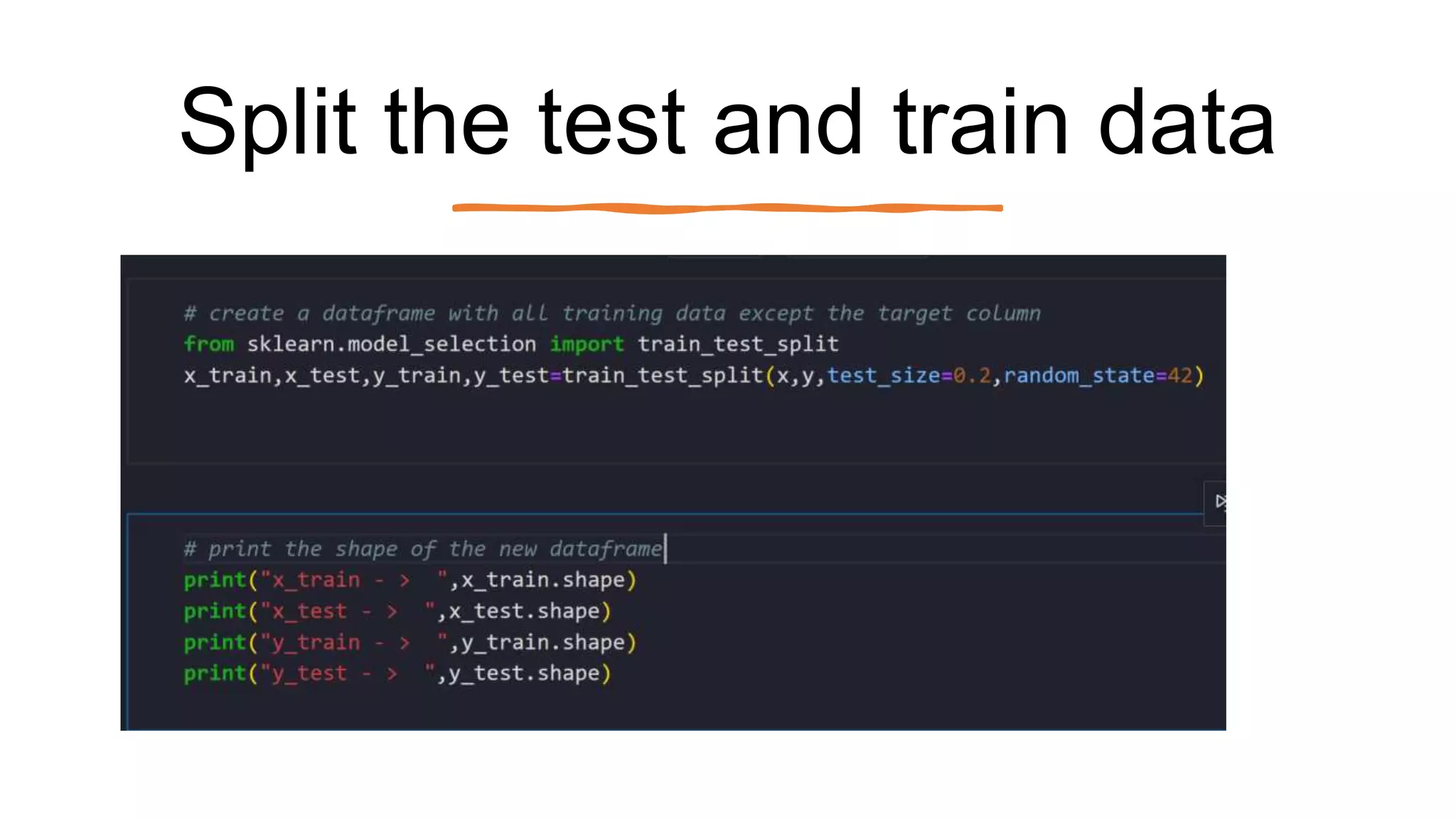
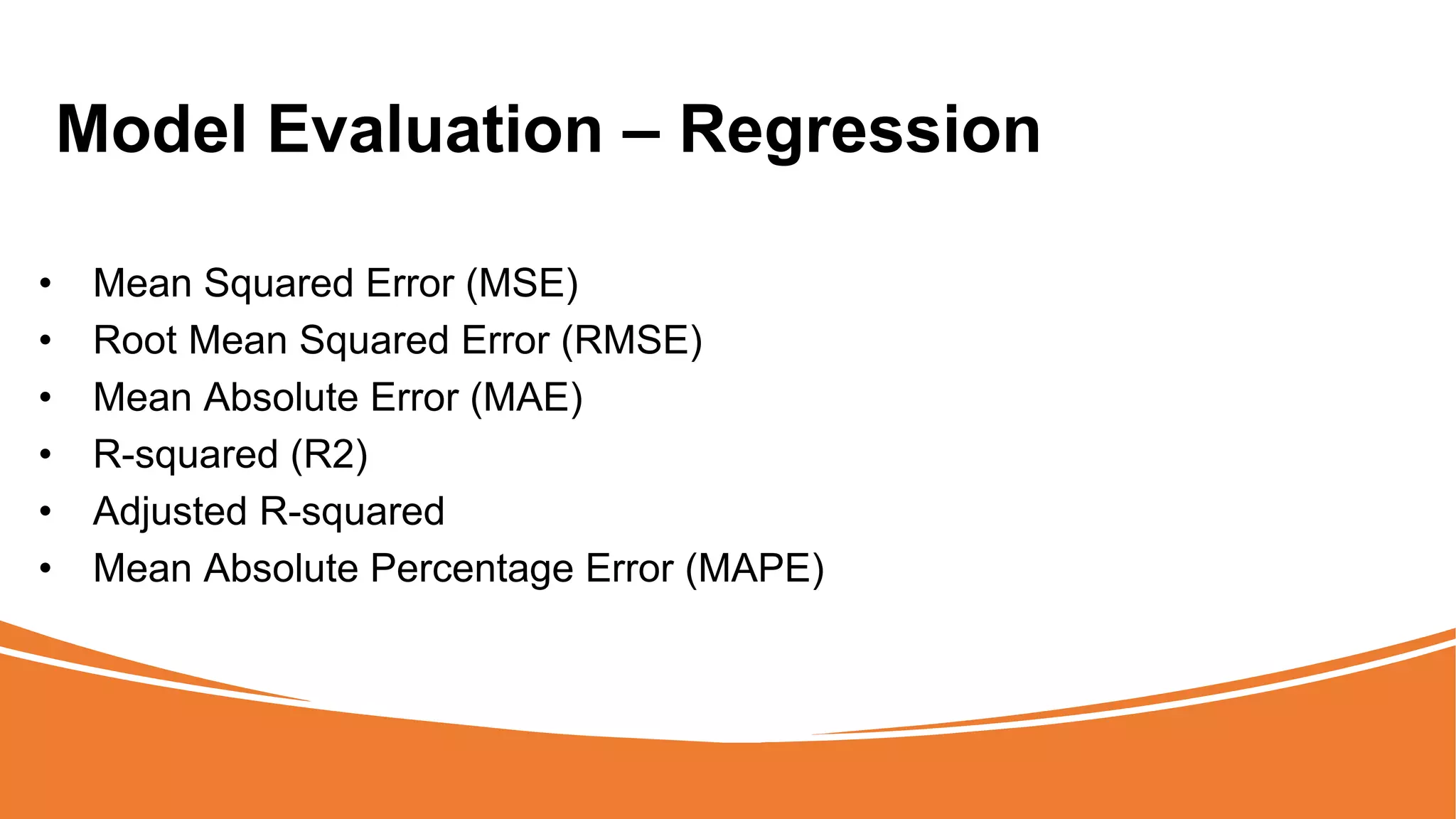
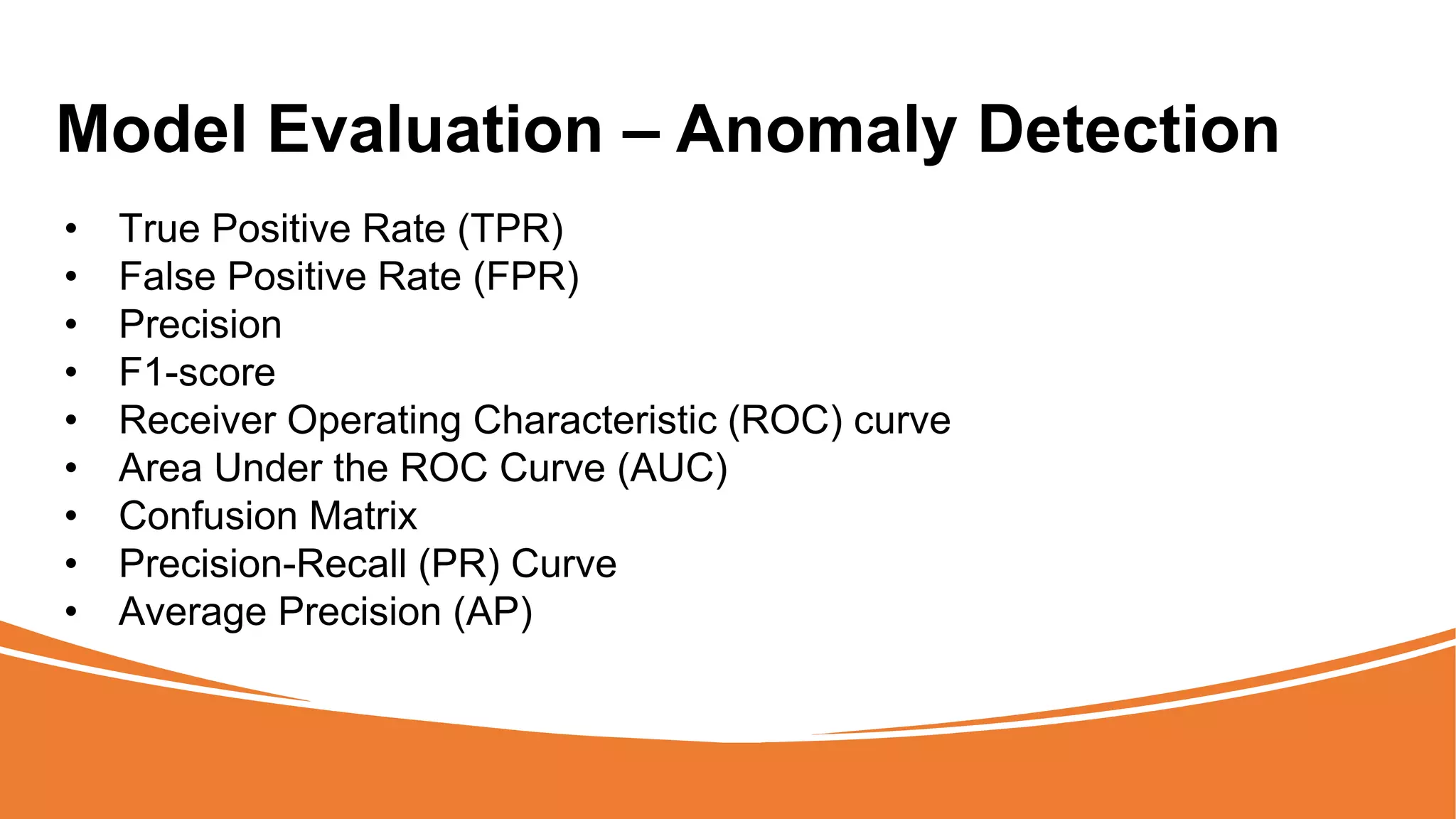
The document outlines a comprehensive workshop on data science, covering key topics such as data cleaning, exploratory data analysis, feature engineering, model selection, evaluation, and deployment. It provides practical prerequisites, tasks, and insights on analyzing car price datasets, including visualization techniques and feature transformations. Model evaluation metrics for regression, clustering, classification, and anomaly detection are also discussed to guide participants in assessing their data science models.