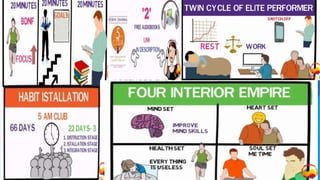
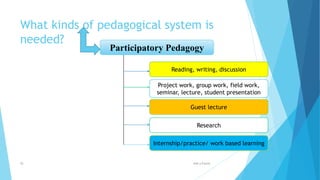
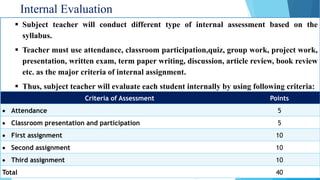
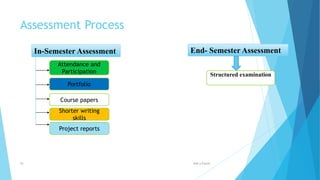
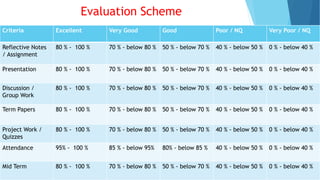
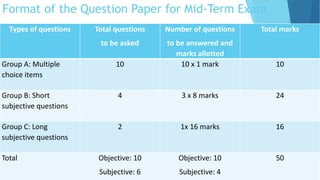
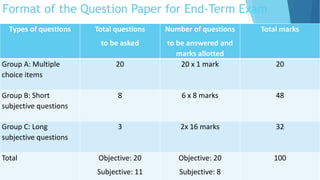
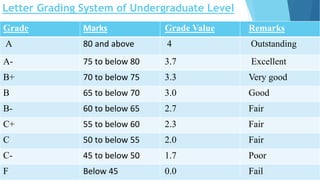
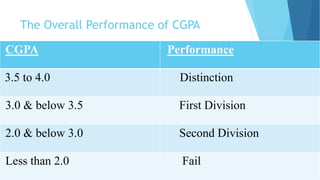
The document provides information about an induction program on evaluation criteria and procedures for a semester system. It discusses key features of a semester system including dividing the academic year into two six-month semesters, ongoing evaluation throughout each semester, developing regular study habits among students, and reducing examination burden. The document also outlines subjects offered in the first semester, evaluation methods like assignments, presentations, term papers and attendance tracking. Suggestions are provided for students and teachers to be engaged throughout each semester and actively participate in learning.