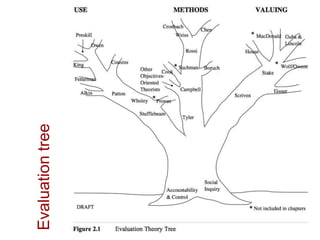
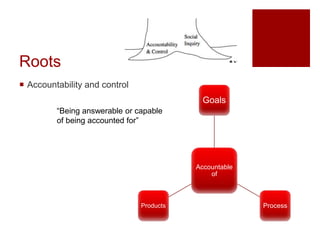
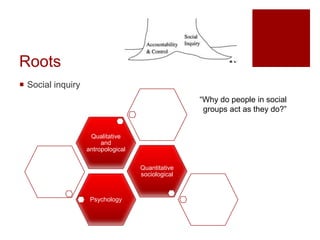
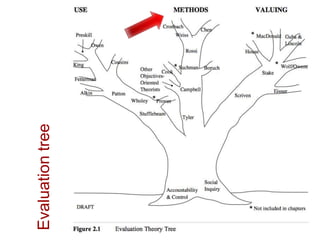
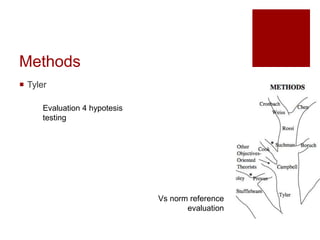
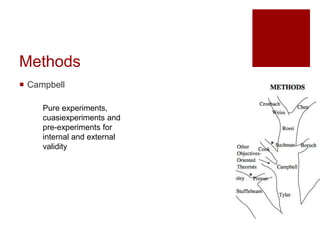
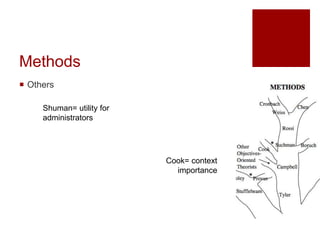
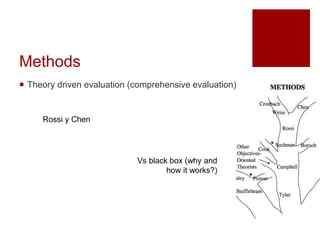
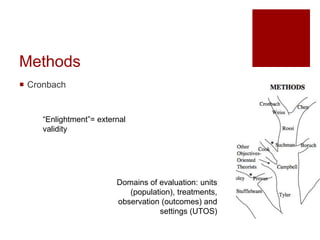
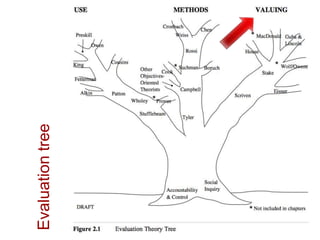
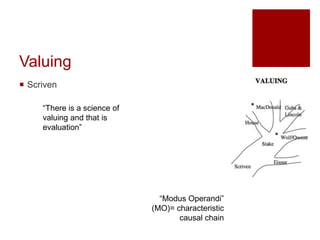
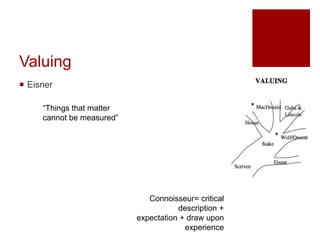
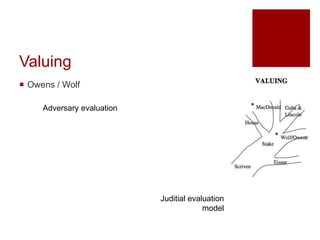
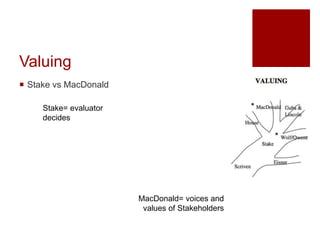
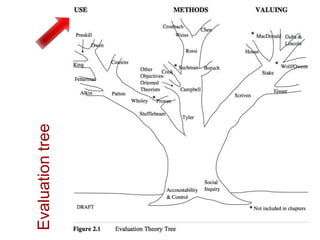
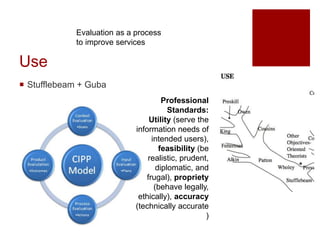
This document presents an "evaluation theory tree" that traces the development of evaluation theories and influences among prominent evaluation theorists. The tree has roots in accountability/control and social inquiry. It outlines key theorist perspectives on evaluation methods including Tyler, Campbell, Scriven, Cronbach, and others. It also outlines theorist perspectives in the areas of valuing evaluations including Eisner, Owens/Wolf, Stake, MacDonald, and House. Finally, it outlines theorist perspectives related to the use of evaluations including Stufflebeam/Guba, Wholey, Patton, Cousin, Preskill, Owen, and Fetterman. The tree is intended to map the evolution of evaluation theory across different branches