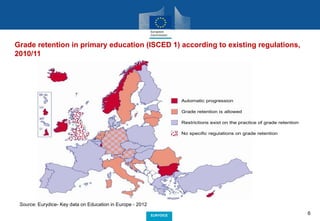
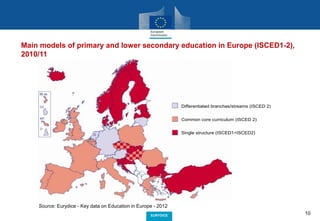
The document outlines the mission and contributions of Eurydice, a network that provides European-level analyses and information to assist education policy-making. It includes key data and reports about compulsory schooling, grade retention, parental choice in education, and various aspects of teacher and school leadership across Europe. The overarching goal is to improve the quality and efficiency of education and training, contributing to societal participation and economic success.