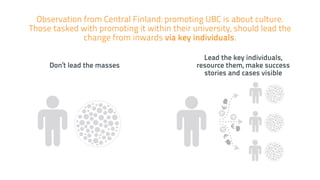
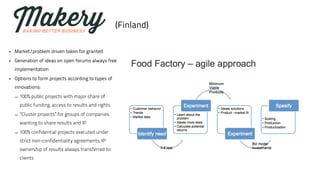
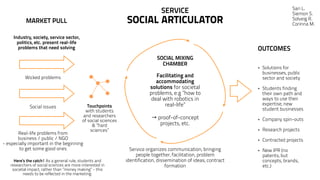
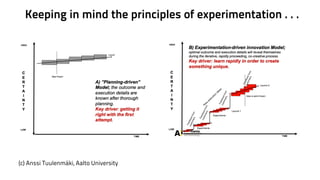
The EUBIC Learning Camp held in Porvoo, Finland from May 15-17, 2014, brought together experts to discuss university-business cooperation and aimed to extend discussions from benchmarking to benchlearning. Key observations included the need for better communication of commercialization efforts, the importance of project-based learning, and the evolving needs of the business world that challenge traditional education models. The document outlines various innovative approaches and models discussed, including the Startup Sauna and Prototron, which focus on fostering entrepreneurship and collaboration between universities and businesses.