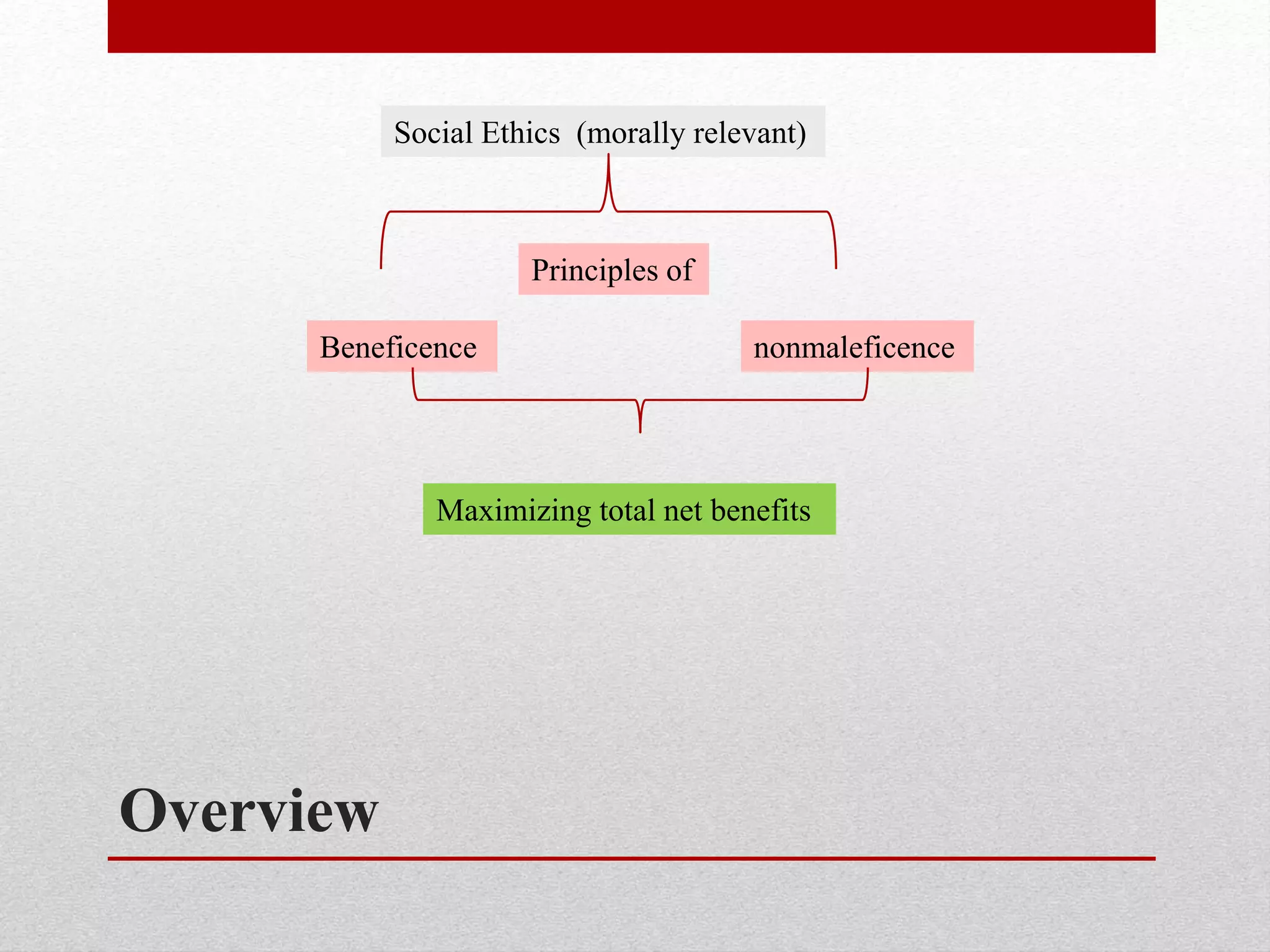
This document discusses ethical principles in pharmacology, including nonmaleficence, beneficence, justice, autonomy, veracity, fidelity, and avoidance of killing. It provides an overview of social ethics and principles of maximizing total net benefits. It also discusses how the principles of justice, autonomy, veracity, fidelity and avoidance of killing are more individual ethical concerns important in traditional clinical healthcare ethics when acting on one patient. Finally, it focuses on the principle of veracity, or dealing honestly with patients, and how various codes of ethics address the duty of pharmacists to tell patients the truth.