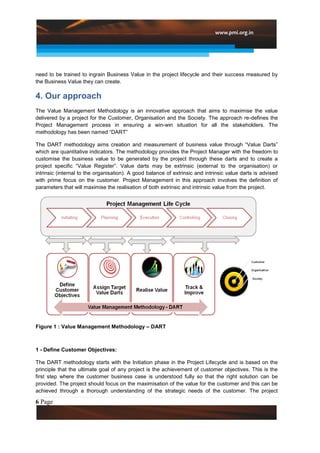
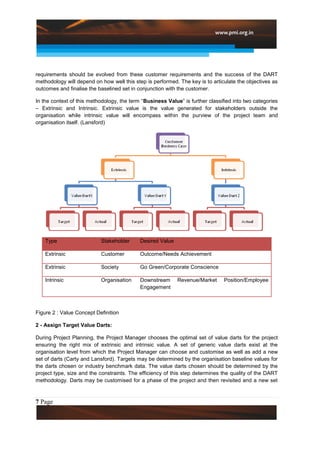
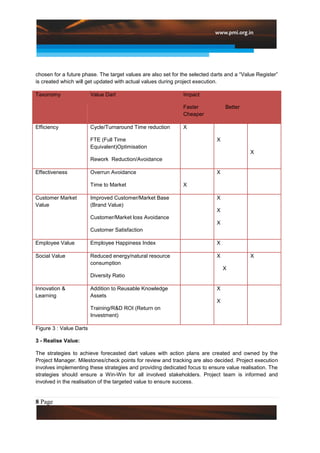
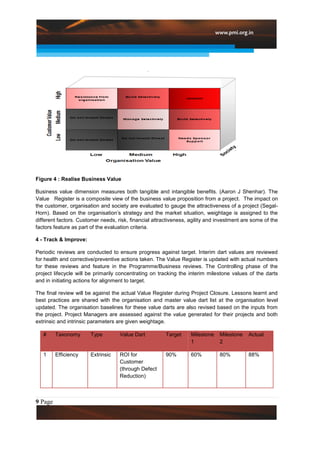
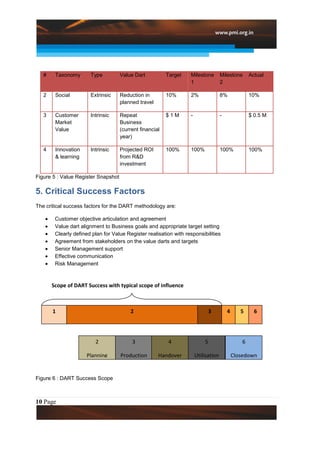
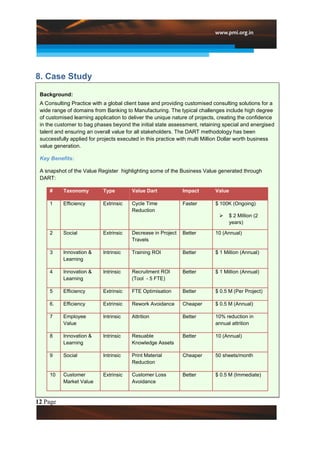
This document introduces a new approach called the "Value Diamond" that adds a fourth dimension of "Business Value" to traditional project management. It discusses the DART methodology for implementing this approach, which focuses on defining customer objectives, assigning target "value darts" to measure business value, realizing that value during project execution, and tracking/improving value realization. The approach has resulted in millions of dollars in quantified benefits for customers and businesses. Key challenges to implementation include socializing the new approach and customizing it for varied projects.