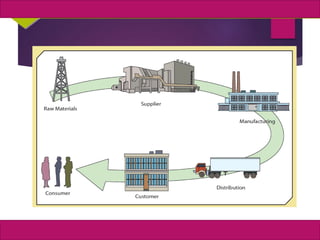
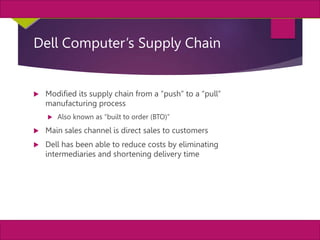
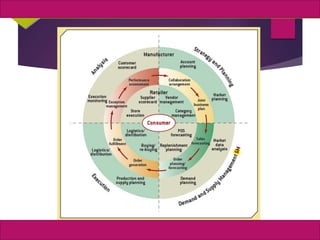
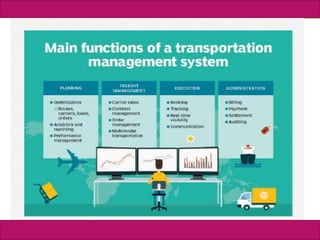
The document discusses supply chain management and enterprise systems. It describes how supply chain management coordinates procuring materials, transforming materials into products, and distributing products to customers. It also discusses key supply chain management decisions around location, inventory, production, and transportation. The document then covers technologies that support supply chain management like electronic data interchange and internet-enabled supply chain management systems. It provides examples of Dell Computer's supply chain and collaborative planning systems.