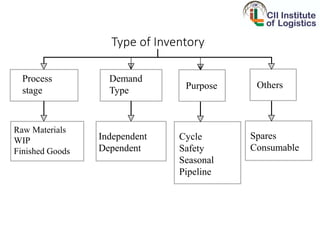
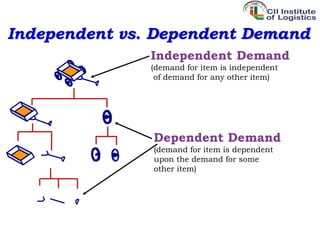
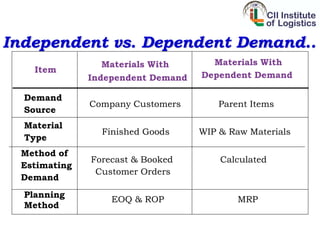
Inventory management aims to ensure organizations hold the lowest possible inventory costs while ensuring adequate supplies. It can reduce costs, improve quality of service, enhance product availability, and ensure customer satisfaction. The objectives of inventory management are optimum inventory levels, lowest costs, ensuring delivery lead times, customer satisfaction, loyalty, and repeat purchases. Inventory management classifications include VED, HML, FSN, SOS, SDE, GOLF, and XYZ. Customer satisfaction, loyalty, and repeat purchases are important outcomes of effective inventory management.