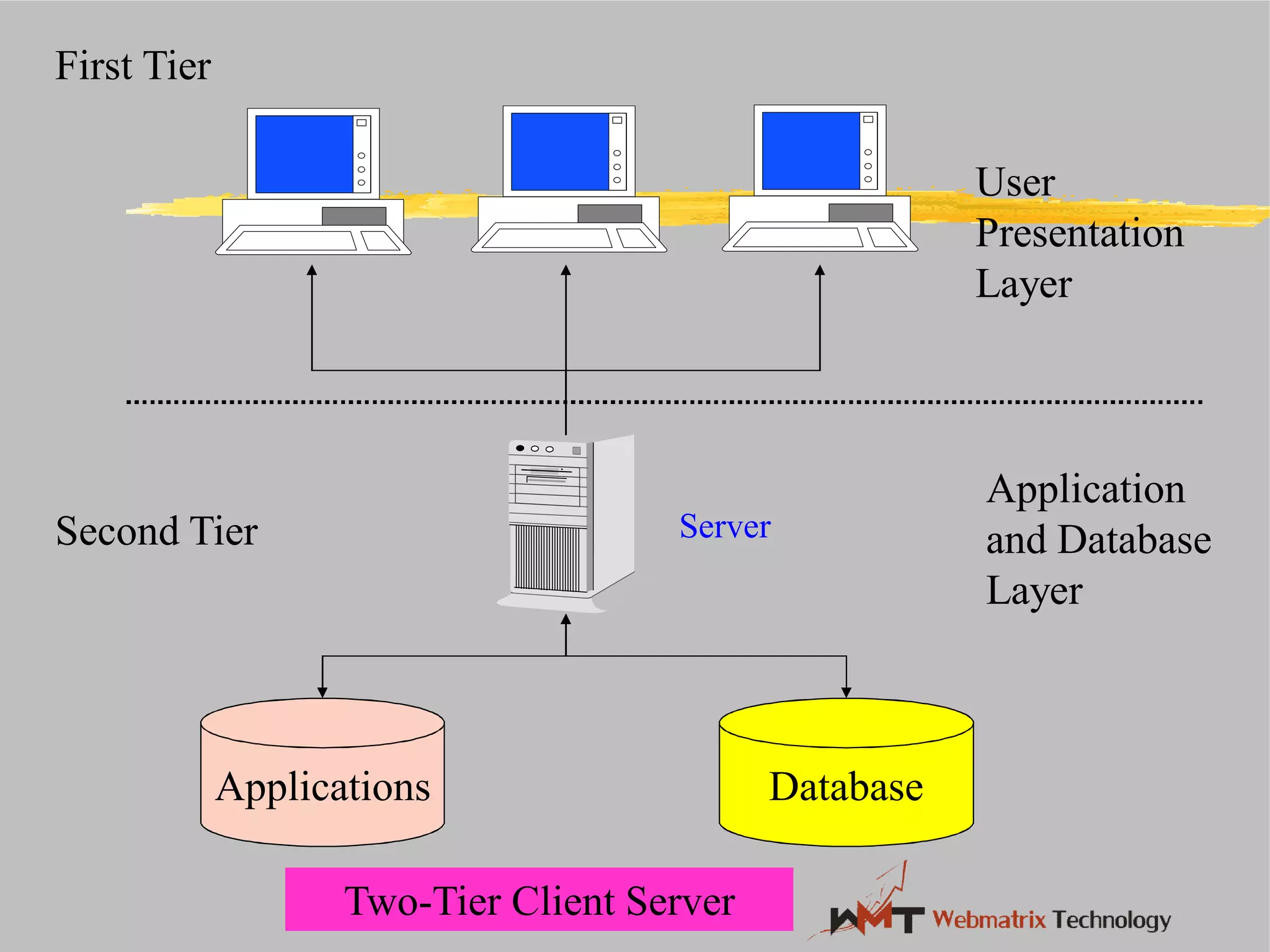
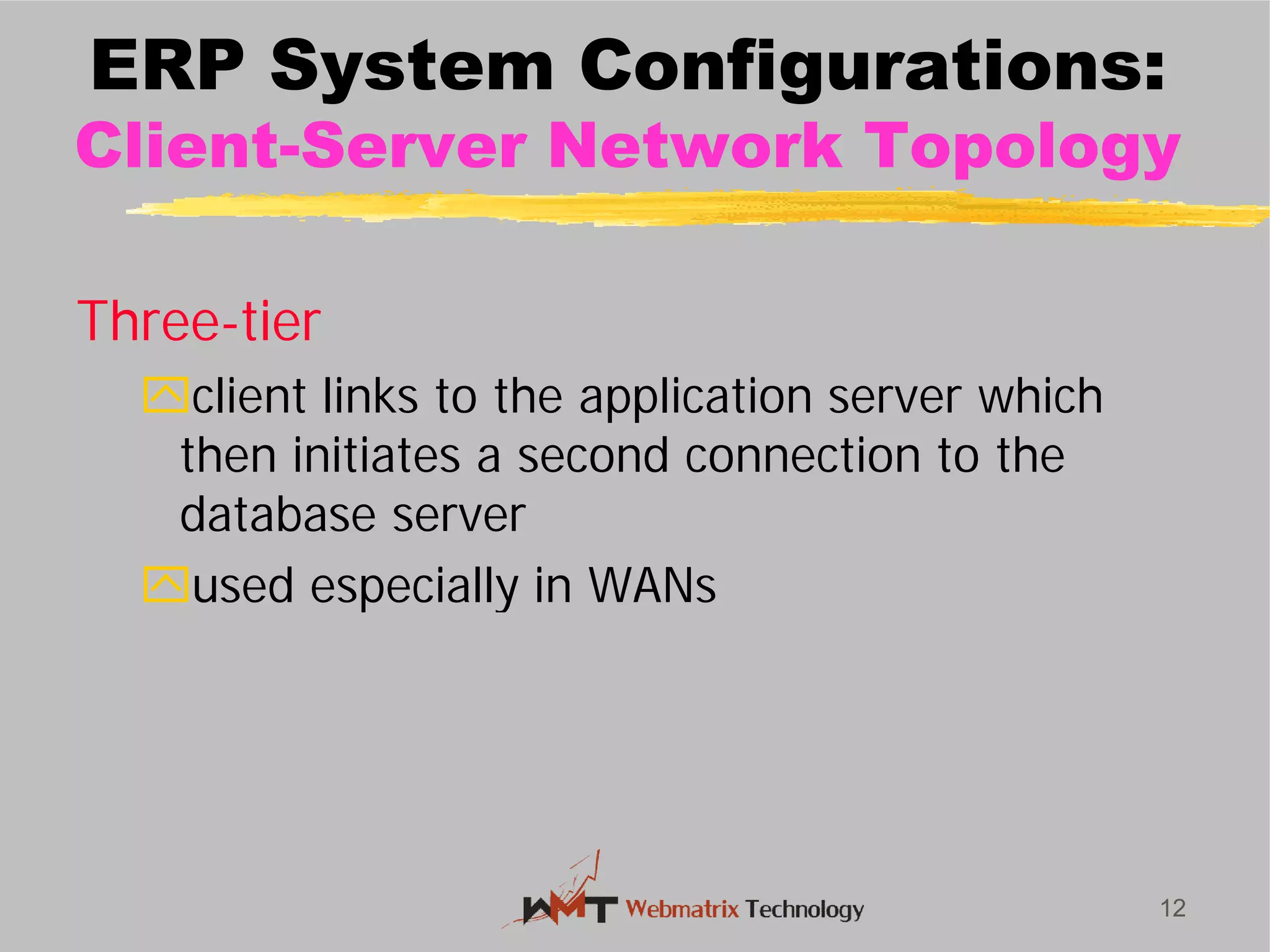
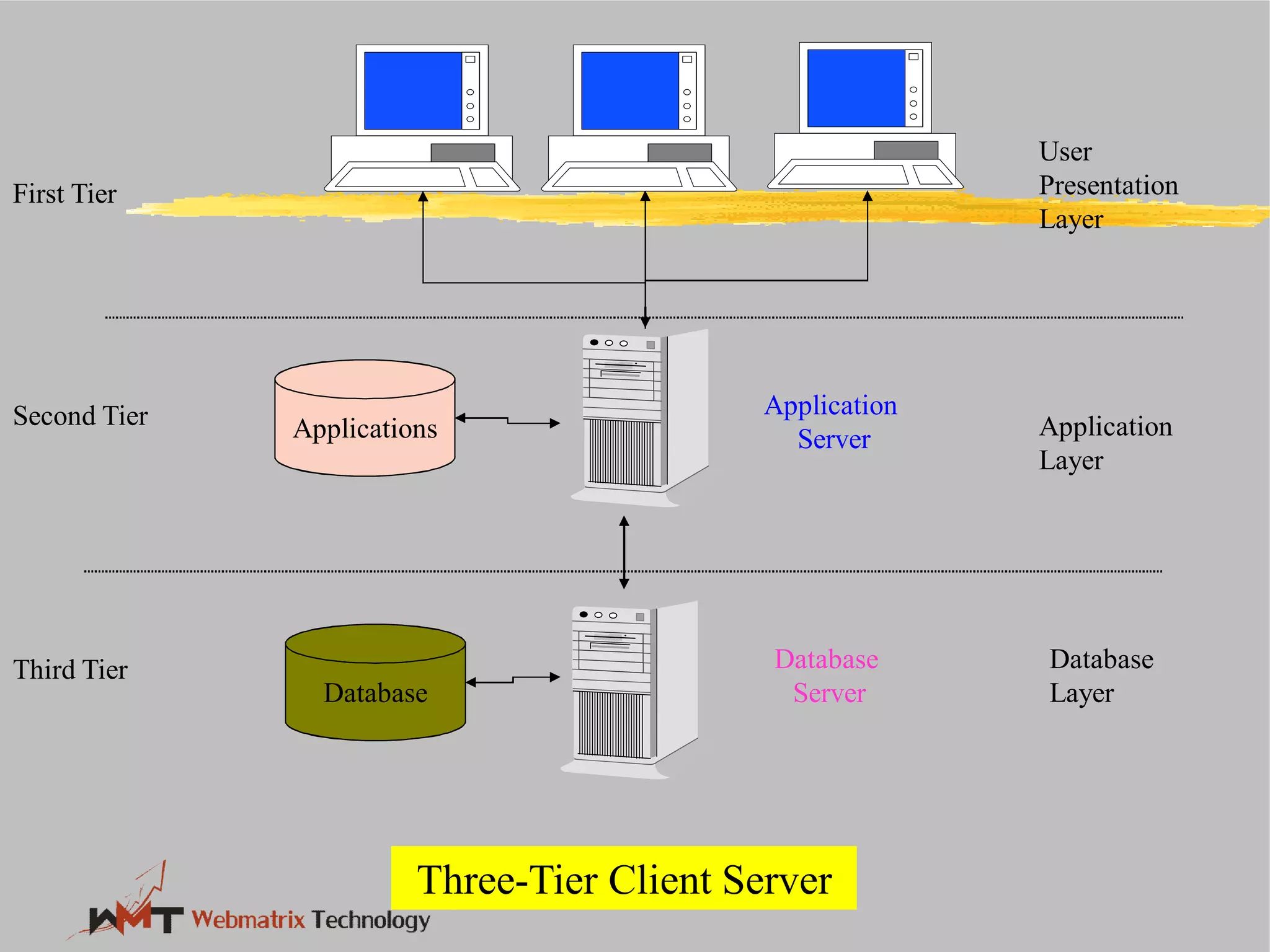
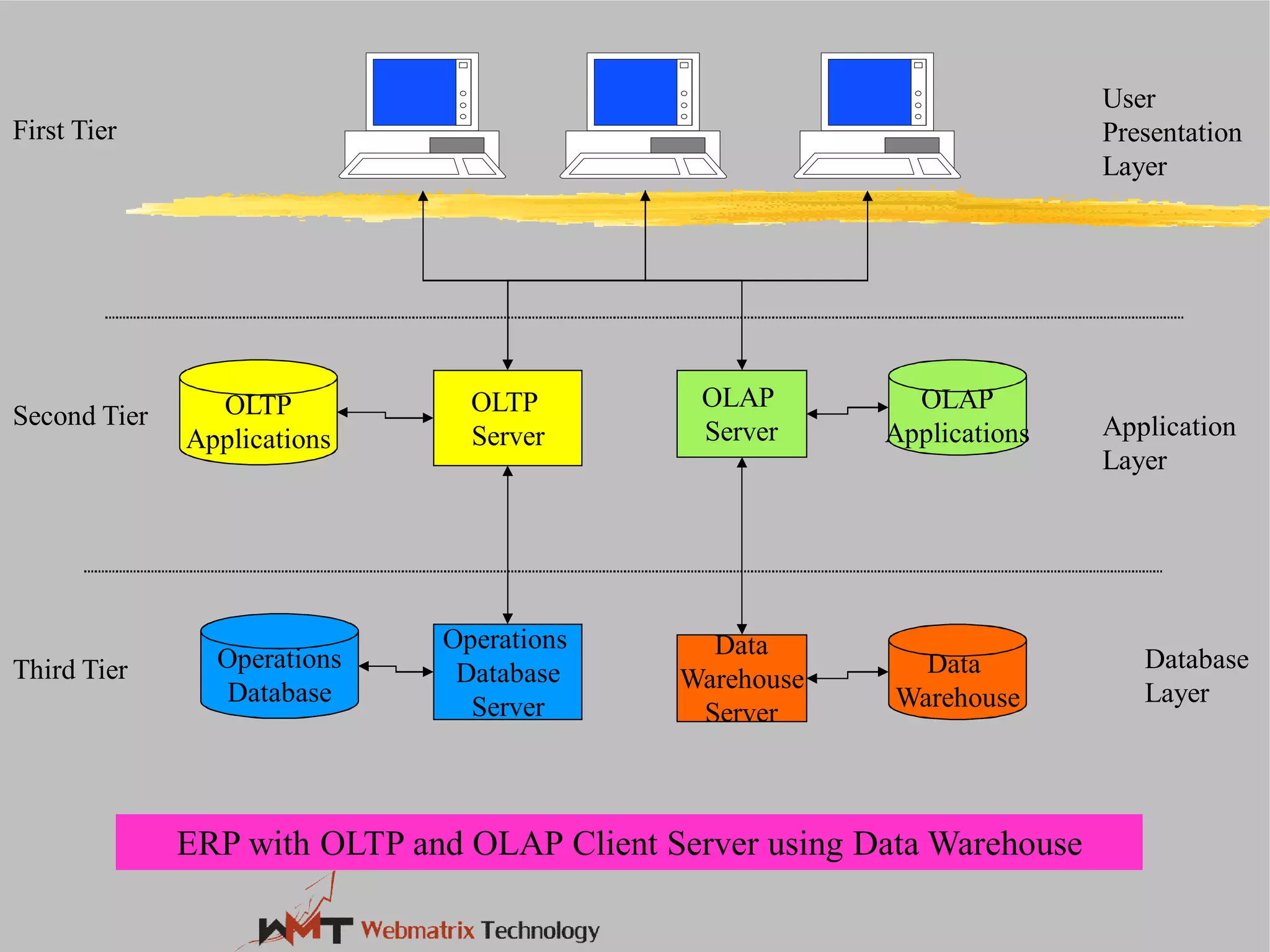
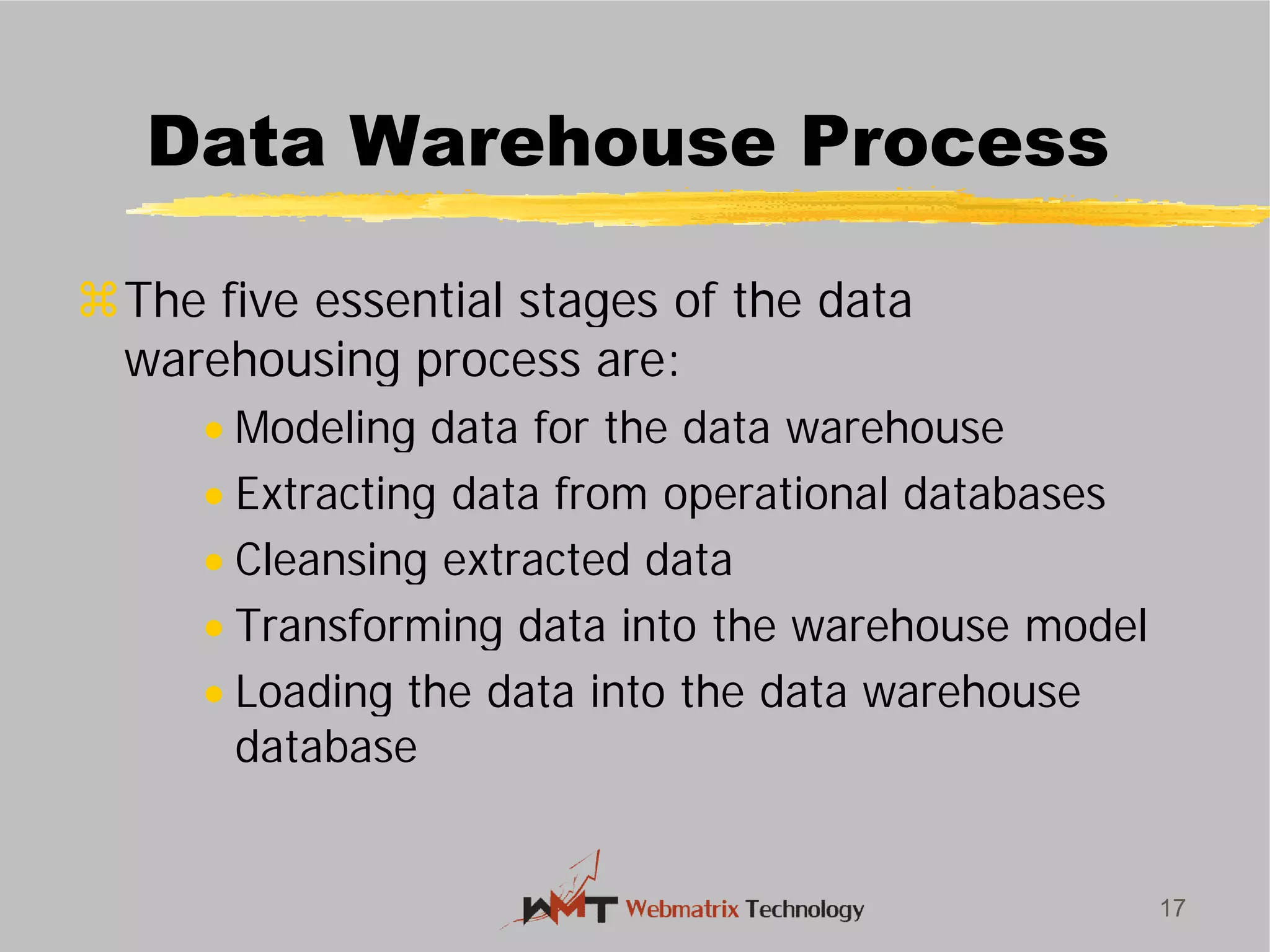
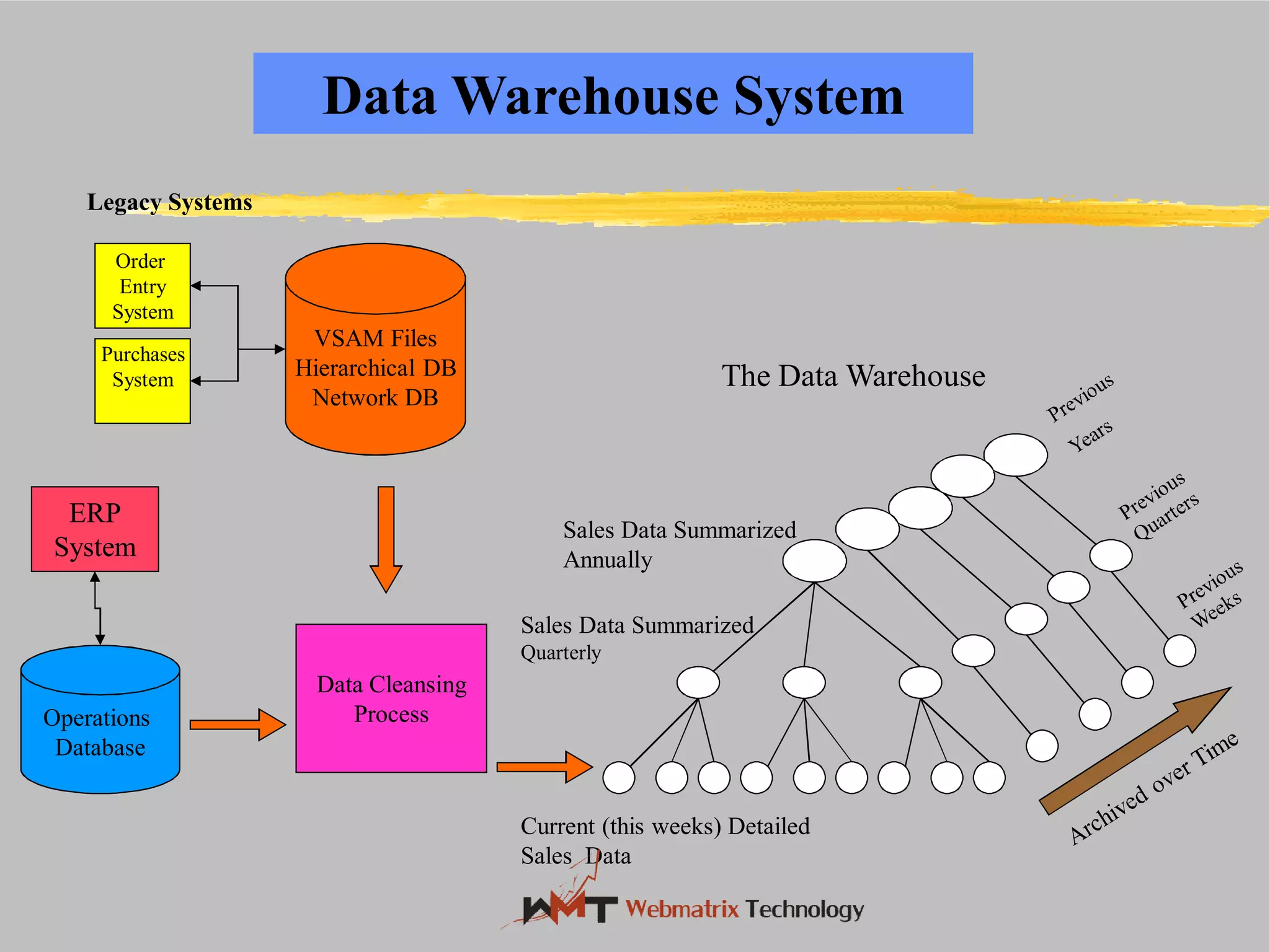
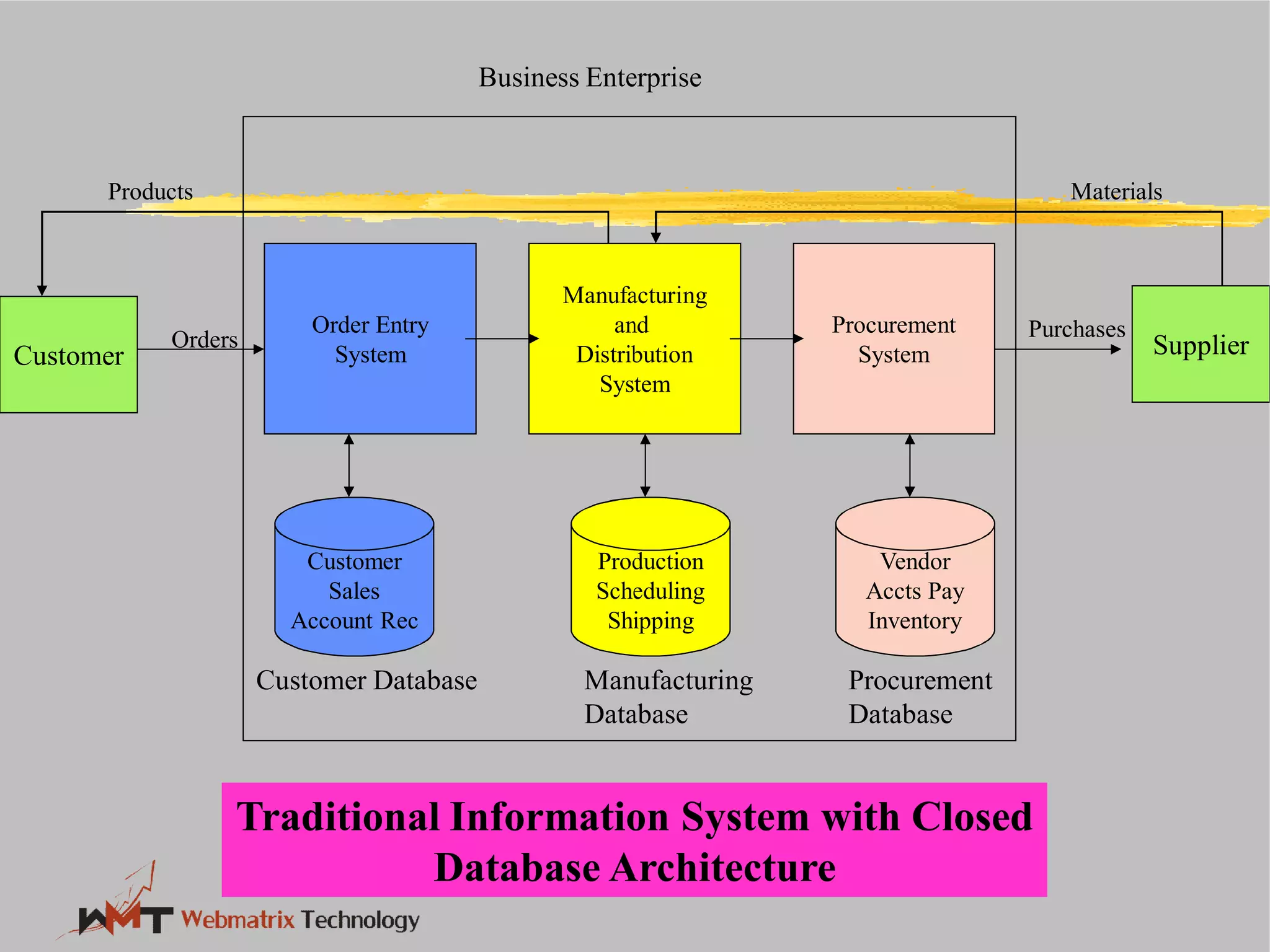
Non-ERP systems have several problems, including limited connectivity outside the company, separate information systems within the firm leading to lack of integration and communication issues, and high long-term maintenance costs. Traditional information systems use a closed database architecture with numerous distinct databases across different applications, leading to data redundancy, anomalies, and unknown data status. ERP systems address these issues through a standardized, integrated environment with a shared database and seamless information flow.


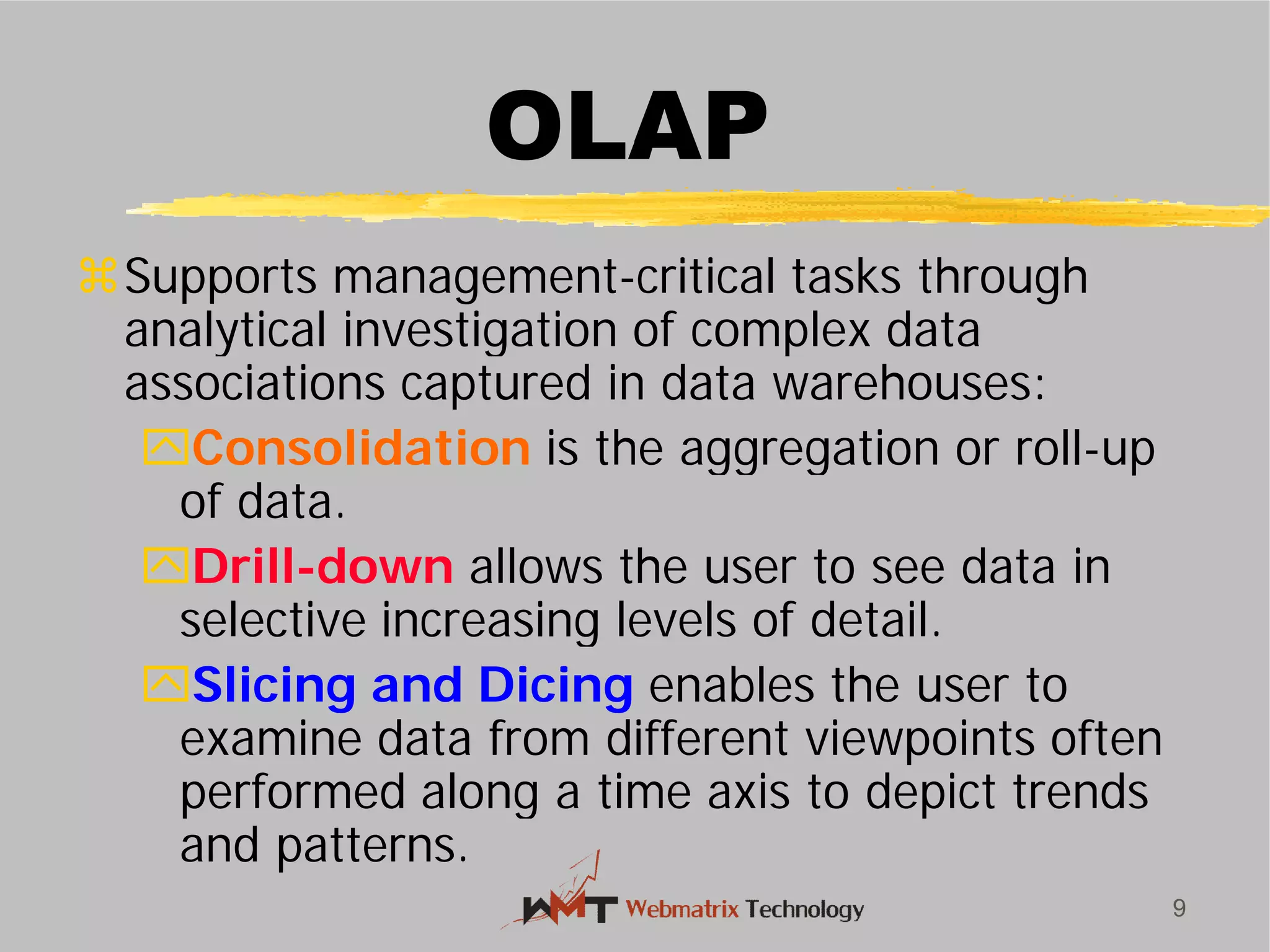
![Data Warehouse
On-Line Analytical Processing
(OLAP)
Sales
&
Distribution
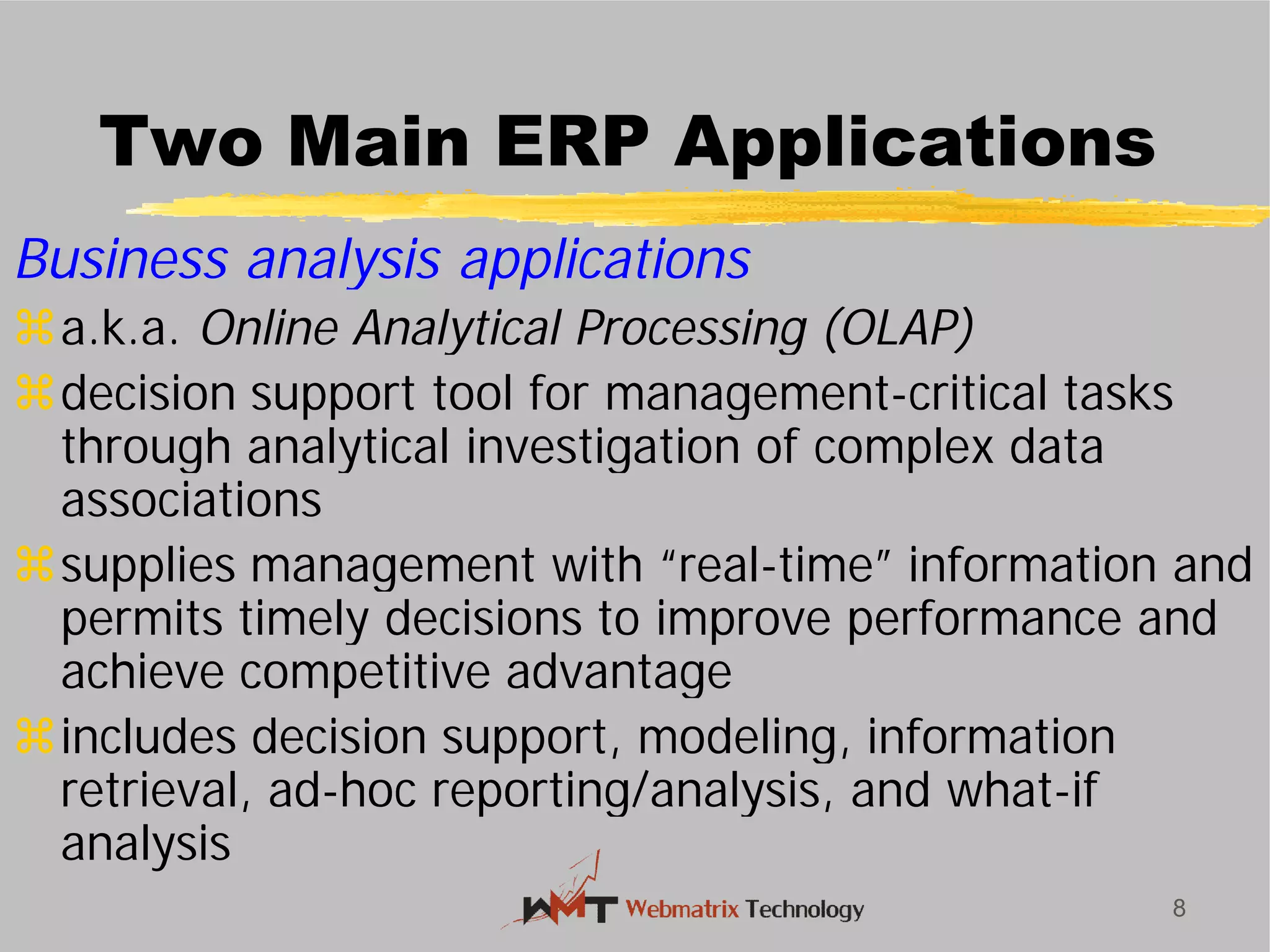
Business
Planning
Customers
Operational Database
Customers, Production,
Vendor, Inventory, etc.
Core Functions [On-Line Transaction Processing (OLTP)]
ERP System
Business EnterpriseERP System
Bolt-On Applications
(Industry Specific Functions)
Shop Floor
Control
Logistics
Suppliers
Operational Database
Customers, Production,
Vendor, Inventory, etc.
Legacy
Systems
Line Transaction Processing (OLTP)]
ERP System
Business Enterprise](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/9e609fac-18ef-4bef-8964-585346d38d70-141230014456-conversion-gate01/75/ERP-Compatibility-Mode-6-2048.jpg)