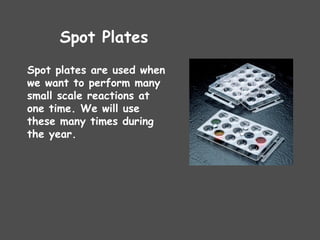
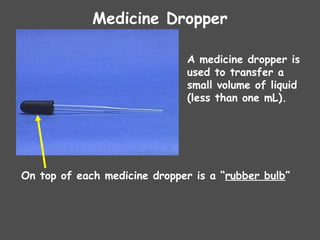
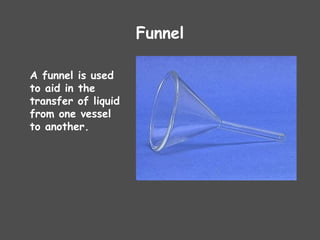
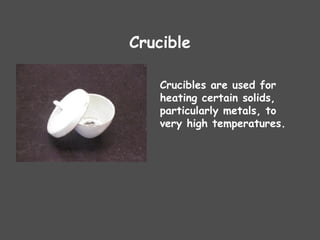
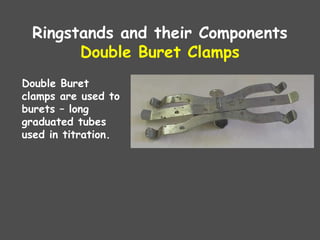
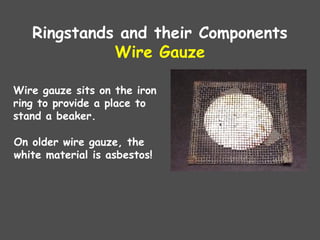
The document describes various laboratory equipment used in chemistry, including beakers, flasks, graduated cylinders, and more, highlighting their functions and usage. It also covers essential science process skills such as observing, inferring, measuring, and experimenting, alongside examples of each skill. Additionally, it emphasizes safety and proper techniques for handling chemicals and equipment in a laboratory setting.