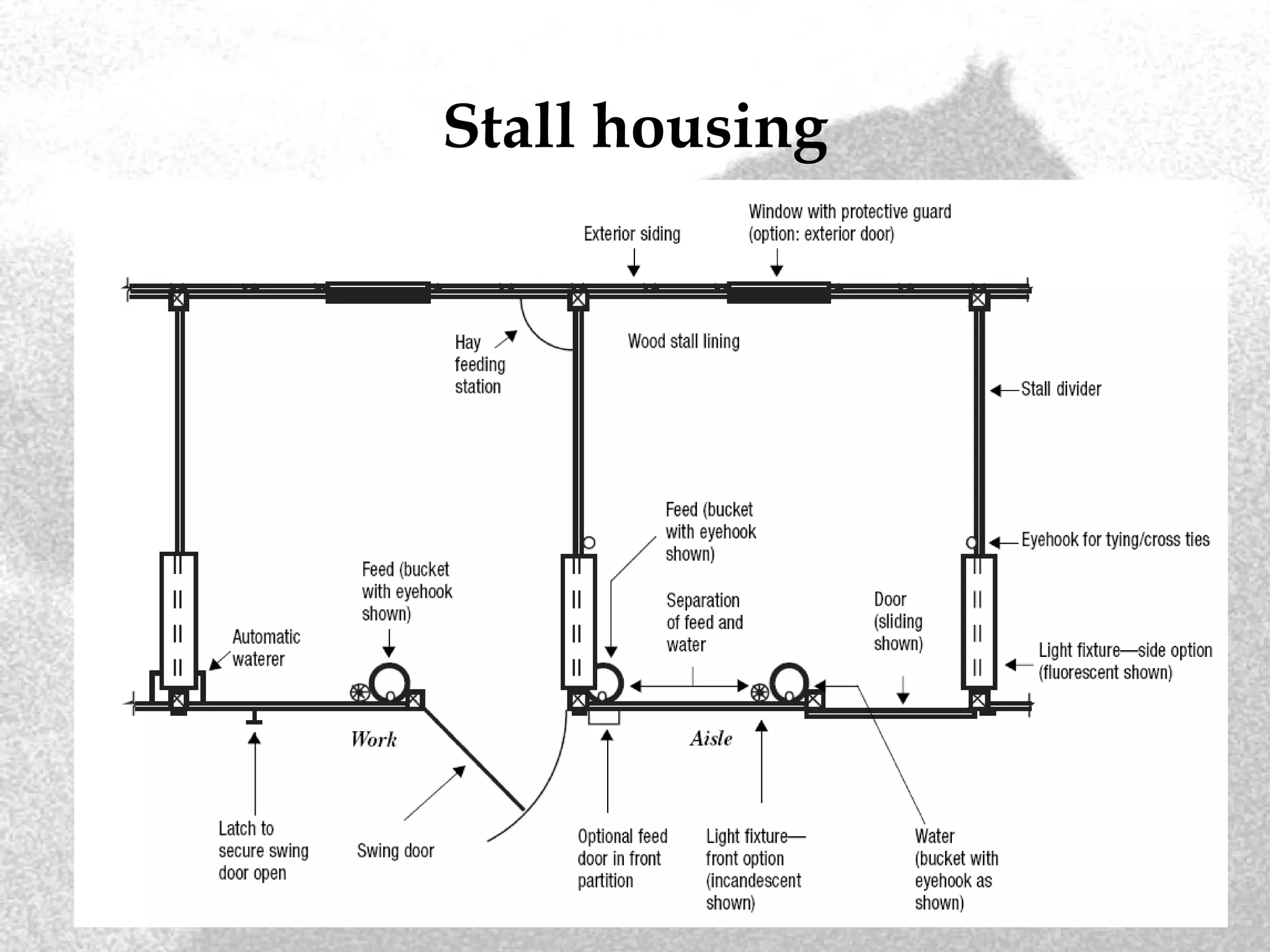
This document outlines the basic requirements and considerations for proper horse management, including nutrition, shelter, health care, hoof care, and exercise. It discusses feeding plans, water needs, housing options, fencing types, bedding materials, waste management, and health protocols. Key requirements are daily exercise, deworming every 6-8 weeks, annual dental exams, and basic costs of ownership averaging $2,458.50 per year. Proper care of horses involves addressing all of their physical, nutritional and environmental needs.