Environment management concept
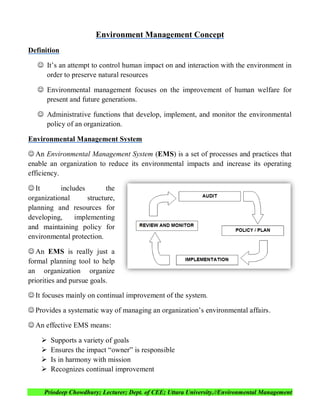
- 1. Priodeep Chowdhury; Lecturer; Dept. of CEE; Uttara University.//Environmental Management Environment Management Concept Definition It’s an attempt to control human impact on and interaction with the environment in order to preserve natural resources Environmental management focuses on the improvement of human welfare for present and future generations. Administrative functions that develop, implement, and monitor the environmental policy of an organization. Environmental Management System An Environmental Management System (EMS) is a set of processes and practices that enable an organization to reduce its environmental impacts and increase its operating efficiency. It includes the organizational structure, planning and resources for developing, implementing and maintaining policy for environmental protection. An EMS is really just a formal planning tool to help an organization organize priorities and pursue goals. It focuses mainly on continual improvement of the system. Provides a systematic way of managing an organization’s environmental affairs. An effective EMS means: Supports a variety of goals Ensures the impact “owner” is responsible Is in harmony with mission Recognizes continual improvement
- 2. Priodeep Chowdhury; Lecturer; Dept. of CEE; Uttara University.//Environmental Management The EMS Model Plan-Do-Check-Act Fig: EMS Model (Plan-Do-Check-Act Cycle) Policy An environmental policy defines our organization’s commitment to the environment through continual improvement in environmental performance. A strong, clear environmental policy can serve as a starting point for developing our EMS. The policy should be evaluated regularly and modified to reflect changing environmental priorities.
- 3. Priodeep Chowdhury; Lecturer; Dept. of CEE; Uttara University.//Environmental Management Planning In the planning phase of EMS, we will identify impacts the environment, and determine which of those impacts are significant, set objectives and targets to minimize environmental impacts and improve environmental performance, and establish action plans to meet the objectives and targets. EMS consists of: – Environmental Impacts and Aspects – Compliance – Objectives and Targets Environmental Impacts and Aspects According to ISO 14001 definitions: • An aspect is an element of an organization’s activities, products, or services that can interact with the environment. • An impact is any change to the environment…wholly or partially resulting from an organization’s activities, products, or services. Compliance • All EMSs must address compliance with applicable environmental regulations. • To comply with the laws and regulations we must know what the regulations are and implement procedures and install equipment to comply with those regulations. Objectives and Targets • An objective is a goal that is consistent with environmental policy, priority environmental aspects and impacts, and applicable environmental regulations. • A target is a more detailed performance goal related to and supporting a specific objective. • Specific targets must be met to achieve an objective of an EMS. • The objectives and targets will drive many other EMS elements, particularly measurement and monitoring activities. Implementation & Control The implementation phase of EMS involves systematically executing plans.
- 4. Priodeep Chowdhury; Lecturer; Dept. of CEE; Uttara University.//Environmental Management Review & Improvement Regular reviews are key to continual improvement and to ensuring that EMS will continue to meet needs over time. Trends in Environmental Management Impact Assessment and Planning (IAP) Assessing environmental and social impacts prior to setting up operations and obtaining environmental approval from the authorities is almost mandatory in most project categories. IAP may be required not only for newly constructed facilities, but also for new operations that will be housed in an existing building. Environmental Liability and Clean-up Foreign investment has resulted in heightened scrutiny of current and historic environmental liabilities associated with property transactions in Bangladesh. Sustainability and Regulatory Compliance The increasing desire of Bangladeshi companies to meet world class standards has caused established companies in India to take on sustainability initiatives as a means of improving their global brand and reputation. Climate Change While Bangladesh still lags the West in coming up with concrete regulations based on the development versus environment debate, there is an increasing awareness in Bangladesh that climate change is not about scoring points but about the existence of entire communities inside and outside of Bangladesh. Sustainable Development Is a pattern of resource use that aims to meet human needs while preserving the environment so that these needs can be met not only in the present, but also for generations to come. The development initiatives are to be initiated in such a way that the future generations can enjoy the benefits of Nature without any compromise. Using the resources to the extent to which it is sustained.
- 5. Priodeep Chowdhury; Lecturer; Dept. of CEE; Uttara University.//Environmental Management Sustainable development is development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) are a proposed set of targets relating to future international development. They are to replace the Millennium Development Goals once they expire at the end of 2015. The SDGs were first formally discussed at the United Nations Conference on Sustainable Development held in Rio de Janeiro in June 2012 (Rio+20). On 19 July 2014, the UN General Assembly's Open Working Group on Sustainable Development Goals (OWG) forwarded a proposal for the SDGs to the Assembly. The proposal contained 17 goals with 169 targets covering a broad range of sustainable development issues. These included ending poverty and hunger, improving health and education, making cities more sustainable, combating climate change, and protecting oceans and forests. On 4 December 2014, the UN General Assembly accepted the Secretary-General's Synthesis Report which stated that the agenda for the post-2015 SDG process would be based on the OWG proposals.
- 6. Priodeep Chowdhury; Lecturer; Dept. of CEE; Uttara University.//Environmental Management As of March 2015, there were 17 proposed goals: 1. End poverty in all its forms everywhere 2. End hunger, achieve food security and improved nutrition and promote sustainable agriculture 3. Ensure healthy lives and promote well-being for all at all ages 4. Ensure inclusive and equitable quality education and promote lifelong learning opportunities for all 5. Achieve gender equality and empower all women and girls 6. Ensure availability and sustainable management of water and sanitation for all 7. Ensure access to affordable, reliable, sustainable and modern energy for all 8. Promote sustained, inclusive and sustainable economic growth, full and productive employment and decent work for all 9. Build resilient infrastructure, promote inclusive and sustainable industrialization and foster innovation 10. Reduce inequality within and among countries 11. Make cities and human settlements inclusive, safe, resilient and sustainable 12. Ensure sustainable consumption and production patterns 13. Take urgent action to combat climate change and its impacts 14. Conserve and sustainably use the oceans, seas and marine resources for sustainable development 15. Protect, restore and promote sustainable use of terrestrial ecosystems, sustainably manage forests, combat desertification, and halt and reverse land degradation and halt biodiversity loss 16. Promote peaceful and inclusive societies for sustainable development, provide access to justice for all and build effective, accountable and inclusive institutions at all levels 17. Strengthen the means of implementation and revitalize the global partnership for sustainable development
- 7. Priodeep Chowdhury; Lecturer; Dept. of CEE; Uttara University.//Environmental Management Environmental Policy An environmental policy may be defined as the statement of intentions and principles, which provides a framework for action and for setting of environmental objectives and goals. Policies are broad-based, outlining key objectives and aspects of the overall environmental program. For implementation of policies, procedures, guidelines and regulations are formed. Most environmental policies are formulated based on some guiding principles such as those proposed by the two UN conferences: 1972 conference on the Human Environment in Stockholm 1992 ‘Earth Summit’ held in Rio De Janeiro Formulation of Environment The guiding principles primarily deal with the following issues: Protection of biosphere Sustainable use of natural resources Reduction and disposal of wastes Energy conservation Risk reduction Safe products and services Environmental restoration Informing the people Management commitment and Assessment Key elements of the Environment Policy are : Maintenance of the ecological balance and overall progress and development of the country through protection and improvement of the environment. Protection of the country against natural disasters. Identification and regulation of all types of activities which pollute and degrade the environment. Ensuring proper Environment Impact Assessment prior to undertaking of industrial and other development projects. Ensuring sustainable use of all natural resources.
- 8. Priodeep Chowdhury; Lecturer; Dept. of CEE; Uttara University.//Environmental Management The Bangladesh Environmental Policy, 1992 Objectives: To maintain ecological balance and overall development through protection and improvement of the environment To protect the country against natural disasters To identify and regulate activities which pollute and degrade the environment To ensure environmentally sound development in all sectors To ensure sustainable, long-term and environmentally sound use of national resources To actively remain associated with all the international environmental initiatives to the maximum possible extent Sectors Policies were formulated for 15 different sectors: 1. Agriculture 2. Industry 3. Health and sanitation 4. Energy and fuel 5. Water development, flood control and irrigation 6. Land 7. Forest, wildlife and biodiversity 8. Fisheries and livestock 9. Food 10. Coastal and marine environment 11. Transport and communication 12. Housing and urbanization 13. Population 14. Education and public awareness 15. Science, technology and research Legal framework proposed: Amend all laws to meet the present day needs Frame new laws in all sectors necessary to control pollution and degradation Ensure implementation of laws and create public awareness Ratify all concerned international laws/conventions/protocols and modify existing national laws in line with ratified international laws
- 9. Priodeep Chowdhury; Lecturer; Dept. of CEE; Uttara University.//Environmental Management Institutional Arrangements considered Ministry of Environment and Forest to coordinate the policy implementation A National Environment Committee chaired by head of govt. to give overall direction MoEF will perform timely amendments on the backdrop of changing state of environment and socio-economic another needs of the country Department of Environment will review/approve all EIAs Bangladesh Environment Conservation Act 1995 Introduced by the Govt. as the Environment Conservation Bill in the parliament in 1994 to prevent the escalation of pollution problems in the country and recognizing the importance of environmental protection and sound management practice for long-term sustainable development. Enacted by the parliament in 1995 as Environment Conservation Act through gazette notification repealing the earlier Environment Pollution Control Ordinance 1977. Basic features: First to address the environment in a comprehensive way Establishment of the Department of Environment (DoE) Environmental Clearance Certificate Power to make Rules Legal Action Good faith clause Providing substantive and procedural provisions Declaration of ecologically critical area Declaring an Ecologically Critical The following factors to be taken into consideration: Human habitat Ancient monument Archeological site Forest sanctuary National Park Game Reserve Wild animals habitat Wetland Mangrove
- 10. Priodeep Chowdhury; Lecturer; Dept. of CEE; Uttara University.//Environmental Management Forest area Biodiversity of the relevant area etc. Environmental Clearance Both new and existing projects/industries are given environmental clearance based on their respective classification: -Need to apply to the respective Divisional Administrator of the DoE in prescribed form with appropriate fees and necessary documents -May appeal, if rejected -Must renew the clearance certificate after a certain period (A) GREEN Category 1. Assembling and manufacturing of TV, Radio, etc. 2. Assembling and manufacturing of clocks and watches. 3. Assembling of telephones. 4. Assembling and manufacturing of toys (plastic made items excluded). 5. Book-binding. 6. Rope and mats (made of cotton, jute and artificial fibers). 7. Photography (movie and x-ray excluded). 8. Production of artificial leather goods. 9. Assembling of motorcycles, bicycles and toy cycles. 10. Assembling of scientific and mathematical instruments (excluding manufacturing). 11. Musical instruments. 12. Sports goods (excluding plastic made items). 13. Tea packaging (excluding processing). 14. Re-packing of milk powder (excluding production). 15. Bamboo and cane goods. 16. Artificial flower (excluding plastic made items). 17. Pen and ball-pen. 18. Gold ornaments (excluding production) (shops only). 19. Candle. 20. Medical and surgical instrument (excluding production). 21. Factory for production of cork items (excluding metalic items). 22. Laundry (excluding washing).
- 11. Priodeep Chowdhury; Lecturer; Dept. of CEE; Uttara University.//Environmental Management Foot Notes: (a) Units of all kinds of cottage industries other than those listed in this Schedule shall remain outside the purview of Environmental Clearance Certificate (Unit of cottage industry means all industrial units producing goods or services in which by full-time or part-time labor of family members are engaged and the capital investment of which does not exceed Taka 5 (five) hundred thousand). (b) No industrial unit listed in this Schedule shall be located in any residential area. (c) Industrial units shall preferably be located in areas declared as industrial zones or in areas where there is concentration of industries or in vacant areas. (d) Industrial units likely to produce sound, smoke, odor beyond permissible limit shall not be acceptable in commercial areas. (B) ORANGE-A Category 1. Dairy Farm, 10 (ten) cattle heads or below in urban areas and 25 cattle heads or below in rural areas. 2. Poultry (up to 250 in urban areas and up to 1000 in rural areas). 3. Grinding/husking of wheat, rice, turmeric, pepper, pulses (up to 20 Horse Power). 4. Weaving and handloom. 5. Production of shoes and leather goods (capital up to 5 hundred thousand Taka). 6. Saw mill/wood sawing. 7. Furniture of wood/iron, aluminum, etc.,(capital up to 5 hundred thousand Taka). 8. Printing Press. 9. Plastic & rubber goods (excluding PVC). 10. Restaurant. 11. Cartoon/box manufacturing/printing packaging. 12. Cinema Hall. 13. Dry-cleaning. 14. Production of artificial leather goods (capital up to 5 hundred thousand Taka). 15. Sports goods. 16. Production of salt (capital up to 10 hundred thousand Taka). 17. Agricultural machinery and equipment. 18. Industrial machinery and equipment. 19. Production of gold ornaments. 20. Pin, U Pin. 21. Frames of spectacles. 22. Comb. 23. Production of utensils and souvenirs of brass and bronze. 24. Factory for production of biscuit and bread (capital up to 5 hundred thousand Taka). 25. Factory for production of chocolate and lozenge. (Capital up to 5 hundred thousand Taka). 26. Manufacturing of wooden water vessels.
- 12. Priodeep Chowdhury; Lecturer; Dept. of CEE; Uttara University.//Environmental Management (C) ORANGE-B Category 1. PVC items. 2. Artificial fiber (raw material). 3. Glass factory. 4. Life saving drug (applicable to formulation only). 5. Edible oil. 6. Tar. 7. Jute mill. 8. Hotel, multi-storied commercial & apartment building. 9. Casting. 10. Aluminum products. 11. Glue (excluding animal glue). 12. Bricks/tiles. 13. Lime. 14. Plastic products. 15. Processing and bottling of drinking water and carbonated drinks. 16. Galvanizing. 17. Perfumes, cosmetics. 18. Flour (large). 19. Carbon rod. 20. Stone grinding, cutting, and polishing. 21. Processing fish, meat, and food. 22. Printing and writing ink. 23. Animal feed. 24. Ice-cream. 25. Clinic and pathological lab. 26. Utensils made of clay and china clay/sanitary wares (ceramics). 27. Processing of prawns & shrimps. 28. Water purification plant. 29. Metal utensils/spoons etc. 30. Sodium silicate. 31. Matches. 32. Starch and glucose. 33. Animal feed. 34. Automatic rice mill. 35. Assembling of motor vehicles. 36. Manufacturing of wooden vessel. 37. Photography (activities related to production of films for movie and x-ray). 38. Tea processing. 39. Production of powder milk/condensed milk/dairy. 40. Re-rolling. 41. Wood treatment.
- 13. Priodeep Chowdhury; Lecturer; Dept. of CEE; Uttara University.//Environmental Management 42. Soap. 43. Repairing of refrigerators. 44. Repairing of metal vessel. 45. Engineering works (up to 10 hundred thousand Taka capital.) 46. Spinning mill. 47. Electric cable. 48. Cold storage. 49. Tire re-treading. 50. Motor vehicles repairing works (up to 10 hundred thousand Taka capital). 51. Cattle farm: above 10 (ten) numbers in urban area, and above 25 (twenty five) numbers in rural area. 52. Poultry: Number of birds above 250 (two hundred fifty) in urban area and above 1000 (one thousand) in rural area. 53. Grinding/husking wheat, rice, turmeric, chilly, pulses – machine above 20 Horse Power. 54. Production of shoes and leather goods, above 5(five) hundred thousand Taka capital. 55. Furniture of wood/iron, aluminum, etc., above 5(five) hundred thousand Taka capital. 56. Production of artificial leather goods, above 5(five) hundred thousand Taka capital. 57. Salt production, above 10(ten) hundred thousand Taka capital. 58. Biscuit and bread factory, above 5 (five) hundred thousand Taka capital. 59. Factory for production of chocolate and lozenge, above 5(five) hundred thousand Taka capital. 60. Garments and sweater production. 61. Fabric washing. 62. Power loom. 63. Construction, re-construction and extension of road (feeder road, local road). 64. Construction, re-construction and extension of bridge (length below 100 meters). 65. Public toilet. 66. Ship-breaking. 67. G.I. Wire. 68. Assembling batteries. 69. Dairy and food. Foot Notes: (a) No industrial unit included in this list shall be located in any residential area. (b) Industrial units shall preferably be located in areas declared as industrial zones or in areas where there is concentration of industries or in vacant areas. (c) Industrial units likely to produce sound, smoke, odor beyond permissible limit shall not be acceptable in commercial areas.
- 14. Priodeep Chowdhury; Lecturer; Dept. of CEE; Uttara University.//Environmental Management (D) RED Category 1. Tannery. 2. Formaldehyde. 3. Urea fertilizer. 4. T.S.P. Fertilizer. 5. Chemical dyes, polish, varnish, enamel. 6. Power plant. 7. All mining projects (coal, limestone, hard rock, natural gas, mineral oil, etc.) 8. Cement. 9. Fuel oil refinery. 10. Artificial rubber. 11. Paper and pulp. 12. Sugar. 13. Distillery. 14. Fabric dying and chemical processing. 15. Caustic soda, potash. 16. Other alkalis. 17. Production of iron and steel. 18. Raw materials of medicines and basic drugs. 19. Electroplating. 20. Photo films, photo papers and photo chemicals. 21. Various products made from petroleum and coal. 22. Explosives. 23. Acids and their salts (organic or inorganic). 24. Nitrogen compounds (Cyanide, Cyanamid etc.). 25. Production of plastic raw materials (PVC, PP/Iron, Polyesterin etc.) 26. Asbestos. 27. Fiberglass. 28. Pesticides, fungicides and herbicides. 29. Phosphorus and its compounds/derivatives. 30. Chlorine, fluorine, bromine, iodine and their compounds/derivatives. 31. Industry (excluding nitrogen, oxygen and carbon dioxide). 32. Waste incinerator. 33. Other chemicals. 34. Ordnance. 35. Nuclear power. 36. Wine. 37. Non-metallic chemicals not listed elsewhere. 38. Non-metals not listed elsewhere. 39. Industrial estate. 40. Basic industrial chemicals. 41. Non-iron basic metals.
- 15. Priodeep Chowdhury; Lecturer; Dept. of CEE; Uttara University.//Environmental Management 42. Detergent. 43. Land-filling by industrial, household and commercial wastes. 44. Sewage treatment plant. 45. Life saving drugs. 46. Animal glue. 47. Rodenticide. 48. Refractories. 49. Industrial gas (Oxygen, Nitrogen & Carbon-dioxide). 50. Battery. 51. Hospital. 52. Ship manufacturing. 53. Tobacco (processing/cigarette/Biri-making). 54. Metallic boat manufacturing. 55. Wooden boat manufacturing. 56. Refrigerator/air-conditioner/air-cooler manufacturing. 57. Tyre and tube. 58. Board mills. 59. Carpets. 60. Engineering works: capital above 10 (ten) hundred thousand Taka. 61. Repairing of motor vehicles: capital above 10 (ten) hundred thousand Taka. 62. Water treatment plant. 63. Sewerage pipe line laying/relaying/extension. 64. Water, power and gas distribution line laying/relaying/extension. 65. Exploration/extraction/distribution of mineral resources. 66. Construction/reconstruction/expansion of flood control embankment, polder, dike, etc. 67. Construction/reconstruction/expansion of road (regional, national & international). 68. Construction/reconstruction/expansion of bridge (length 100 meter and above). 69. Murate of Potash (manufacturing). Foot Notes: (a) No industrial unit included in this list shall be allowed to be located in any residential area. (b) Industrial units shall preferably be located in areas declared as industrial zones or in areas where there is concentration of industries or in vacant areas. (c) Industrial units likely to produce sound, smoke, odor beyond permissible limit shall not be acceptable in commercial areas. (d) After obtaining location clearance on the basis of Initial Environment Examination (IEE) Report, the Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) Report in accordance with the approved terms of reference along with design of ETP and its time schedule shall be submitted within approved time limit.
- 16. Priodeep Chowdhury; Lecturer; Dept. of CEE; Uttara University.//Environmental Management Procedure for Environmental Clearance Certificate “Green” Category “Orange A” Category “Orange B” Category
- 17. Priodeep Chowdhury; Lecturer; Dept. of CEE; Uttara University.//Environmental Management “Red” Category Environmental laws: Reasons for Non-enforcement Lack of knowledge of law at the operational level Uncertainties and ambiguities in the provisions in expressing powers, functions, authorities and jurisdiction Lack of by-laws Institutional weakness and lack of policy orientations Conflict with traditional rights and practices Uncertainties over the legal status of resources Conflict between public and private tenure
- 18. Priodeep Chowdhury; Lecturer; Dept. of CEE; Uttara University.//Environmental Management Problems with resources survey, settlement and record or rights Lack of adequate monitoring and environmental quality measurement capabilities Establishment of evidence
