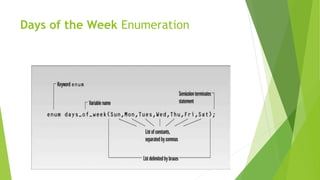
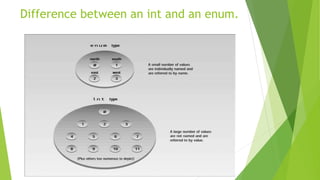
The document discusses C++ enumerations which allow the definition of custom data types with a fixed set of constants. An enumeration defines a list of named constants that can be used instead of regular integer values for improved type safety and clarity in code. Some key points covered include that enumerations are less crucial than structures but can simplify programming, enums can be used for things like days of the week or directions, and enums can have fields, constructors, methods but cannot extend classes. An example shows defining an enum for days of the week and using it in code.