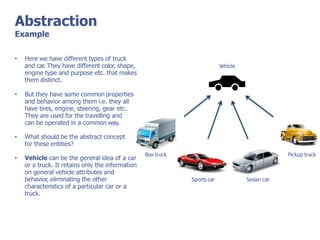
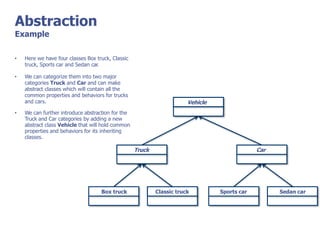
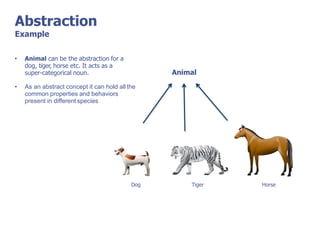
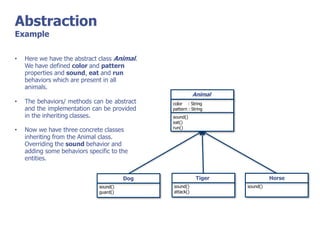
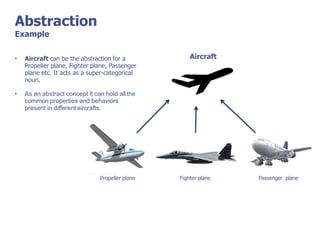
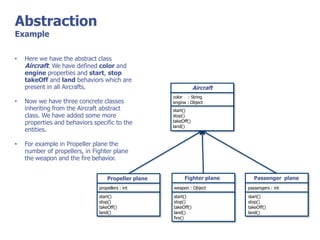
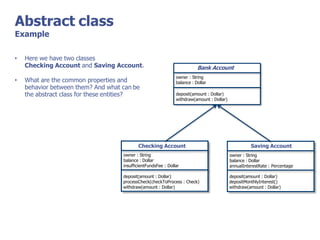
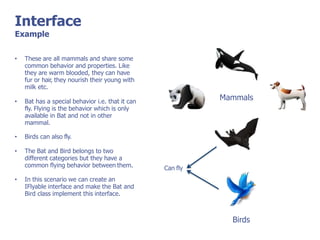
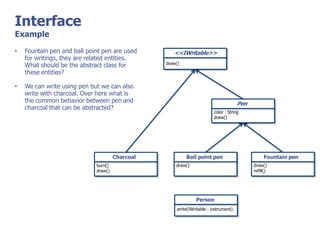
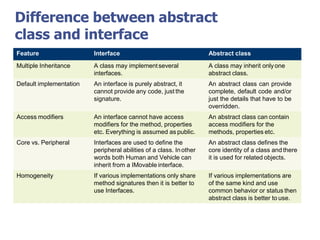
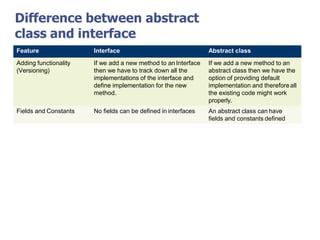
The document discusses abstract classes and interfaces in object-oriented programming. It provides formal definitions and examples of abstract classes and interfaces, and explains when each should be used. The key differences between abstract classes and interfaces are that abstract classes can provide default implementations, interfaces cannot, and a class can only inherit from one abstract class but can implement multiple interfaces.