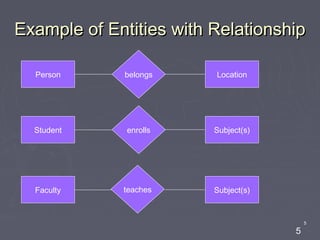
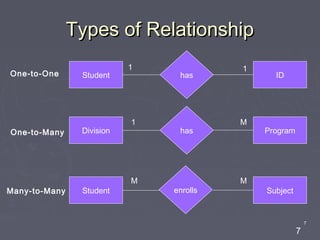
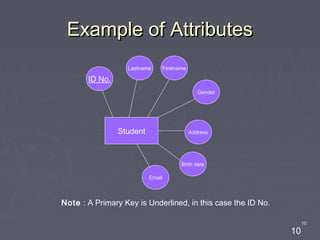
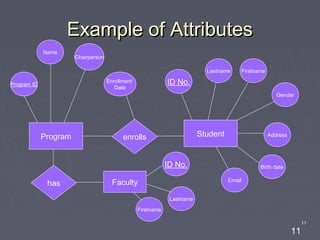
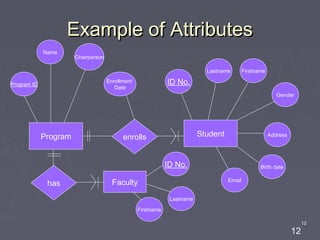
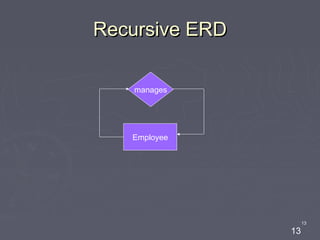
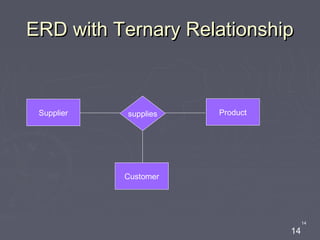
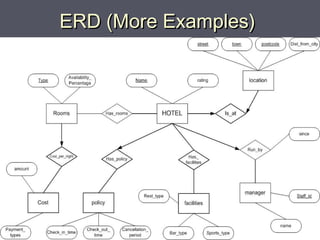
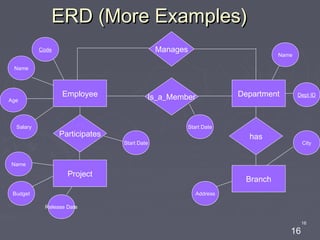
The document discusses entity relationship diagrams (ERDs), which are modeling tools used to graphically depict a database design before implementation. An ERD has three basic components: entities, relationships, and attributes. Entities represent real-world objects like people, places, or concepts. Relationships show how entities relate to each other and are depicted as verbs or nouns connecting entities. Attributes provide additional information about entities and relationships, such as names, IDs, and dates. The document provides examples of entities, relationships, and attributes in ERDs.