The document discusses key concepts in entity-relationship modeling including:
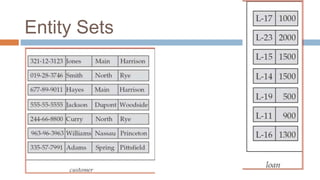
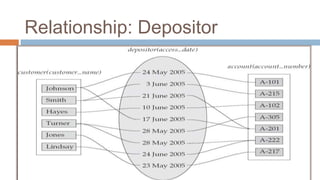
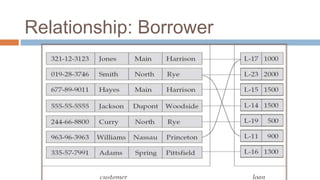
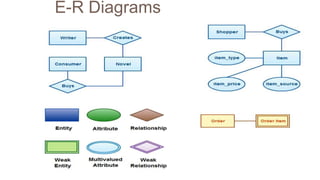
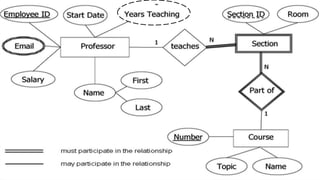
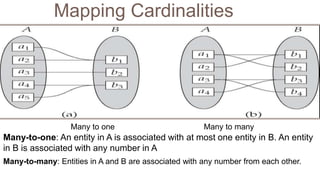
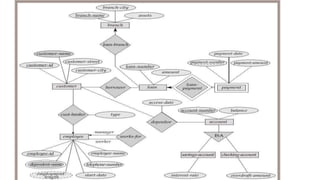
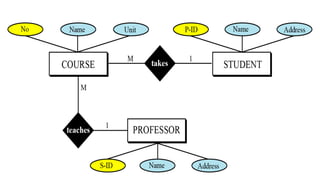
- Entity sets represent collections of similar real-world objects or entities with common attributes. Relationship sets define associations between two or more entities.
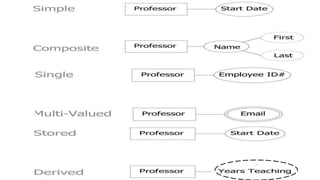
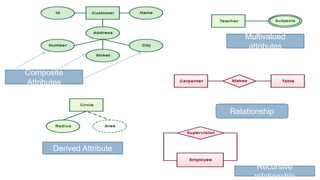
- Attributes describe entities and can be simple, composite, single-valued, multivalued, or derived.
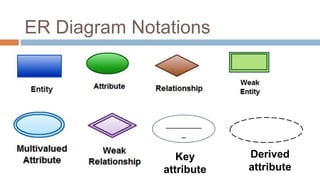
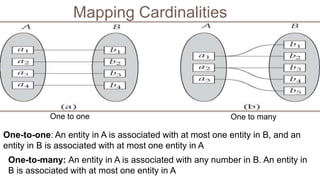
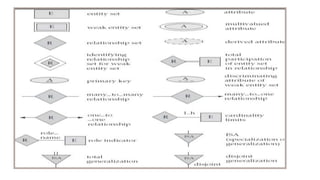
- ER diagrams use standard notations to represent these concepts including entities as rectangles, relationships as diamonds, and different lines and crow's feet to denote attribute types and cardinalities in relationships.