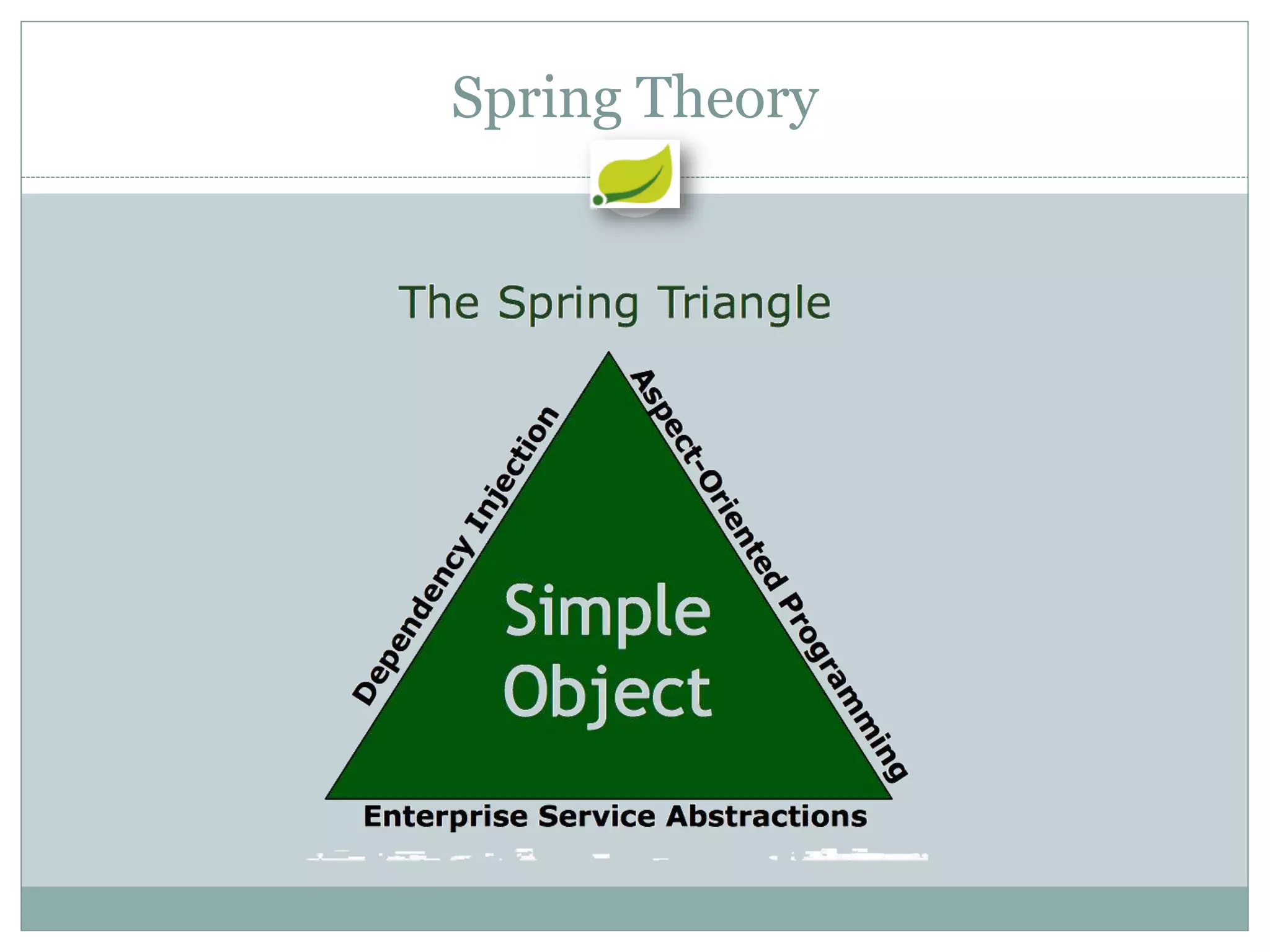
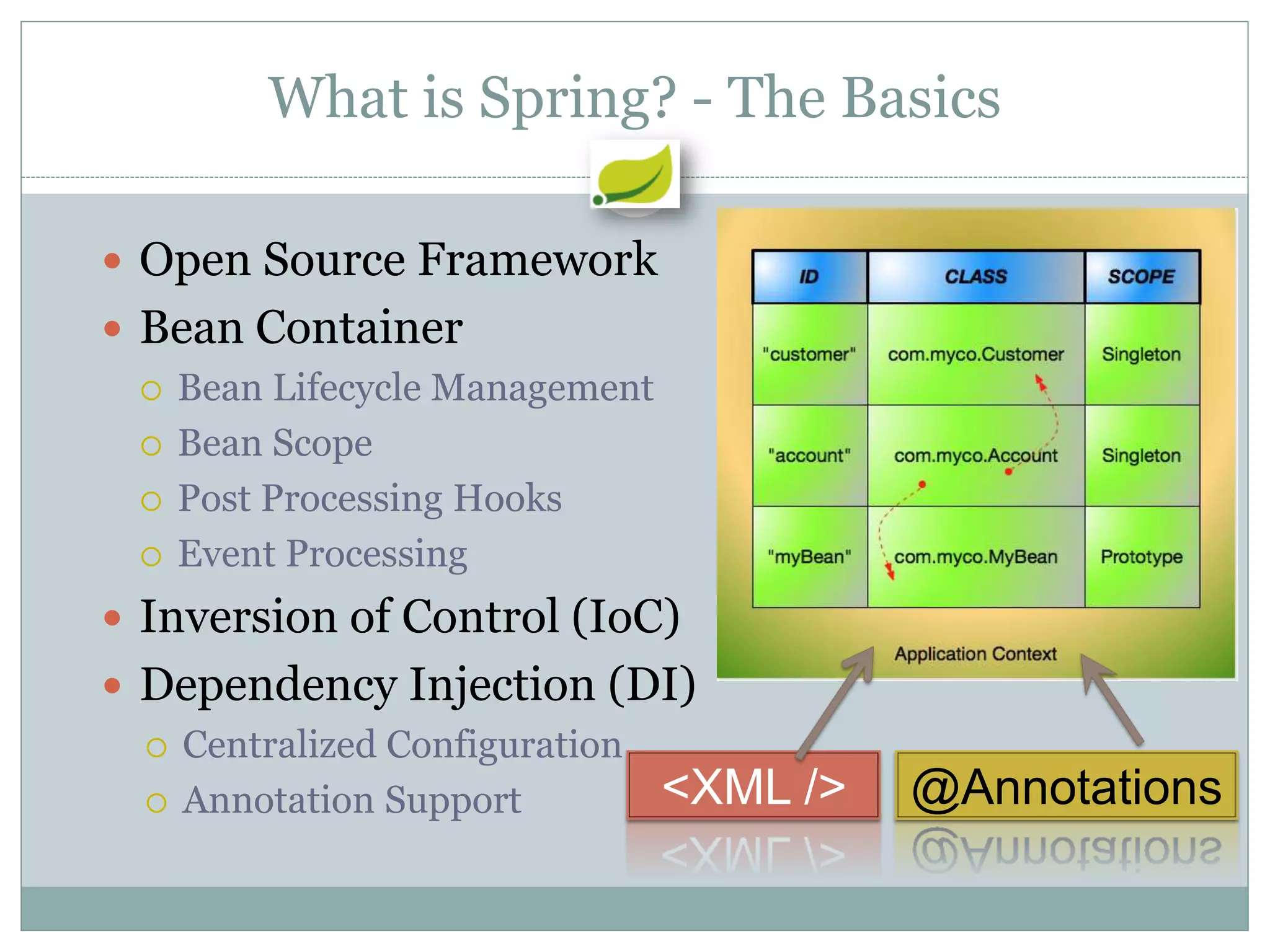
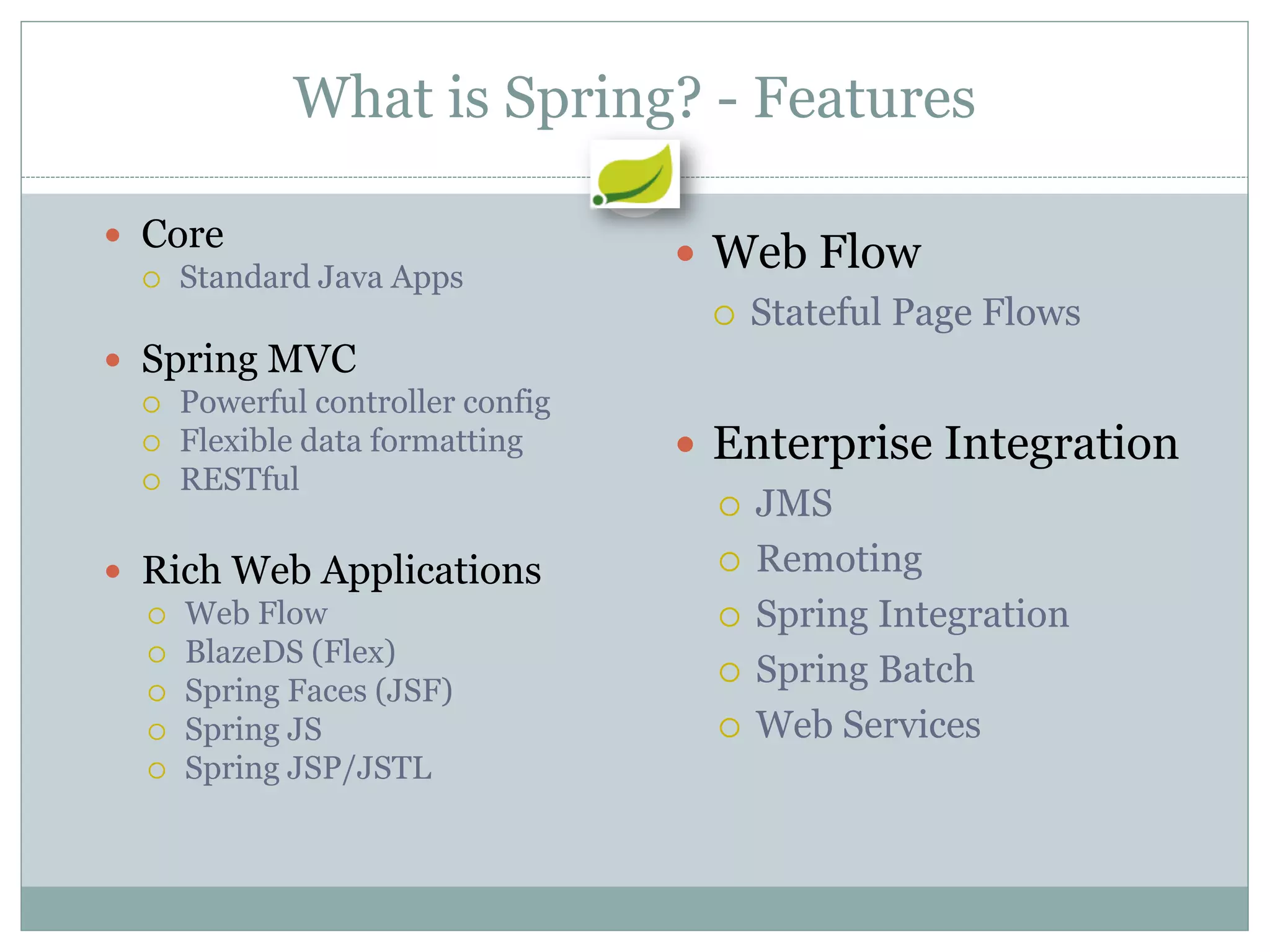
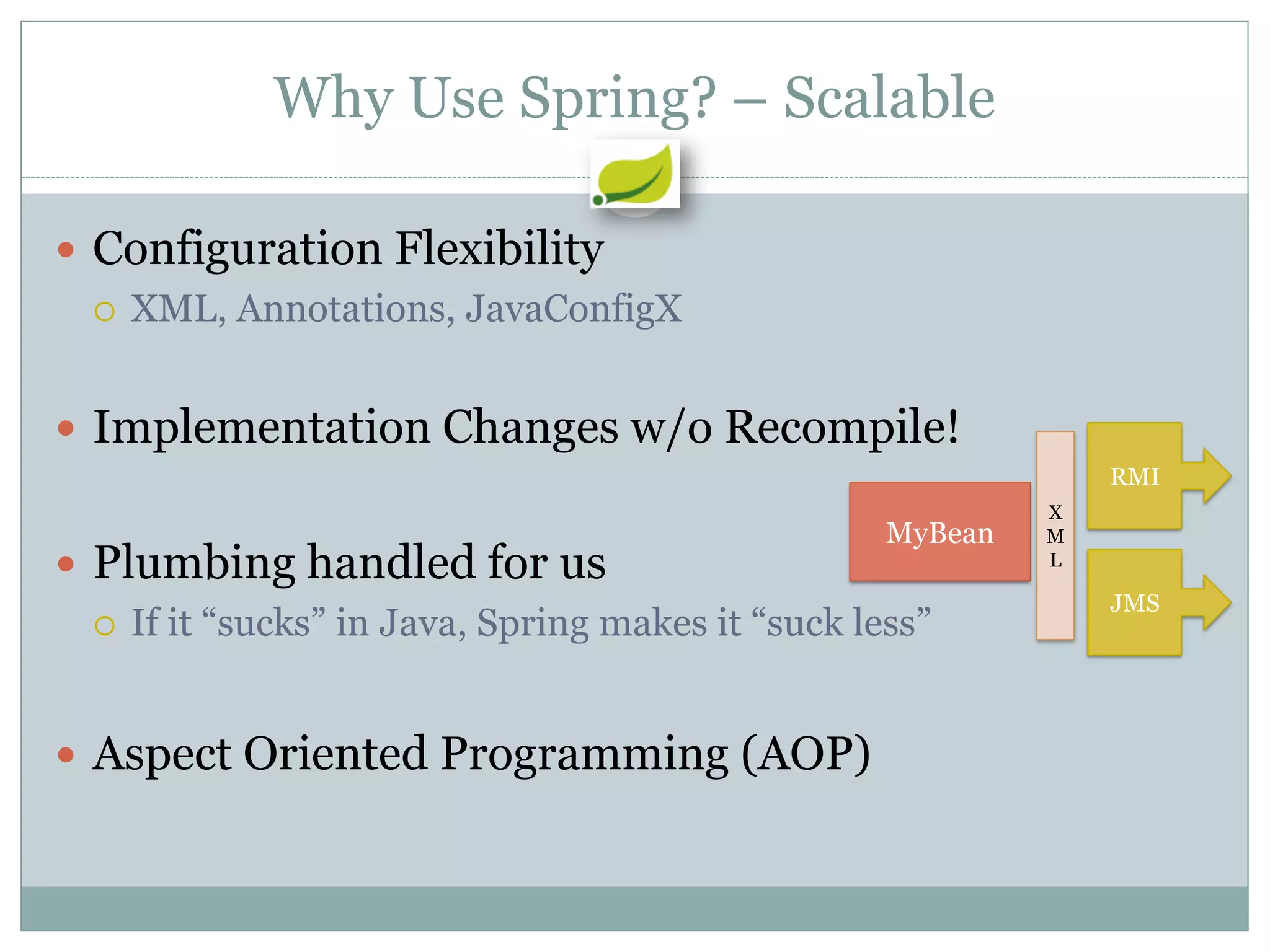
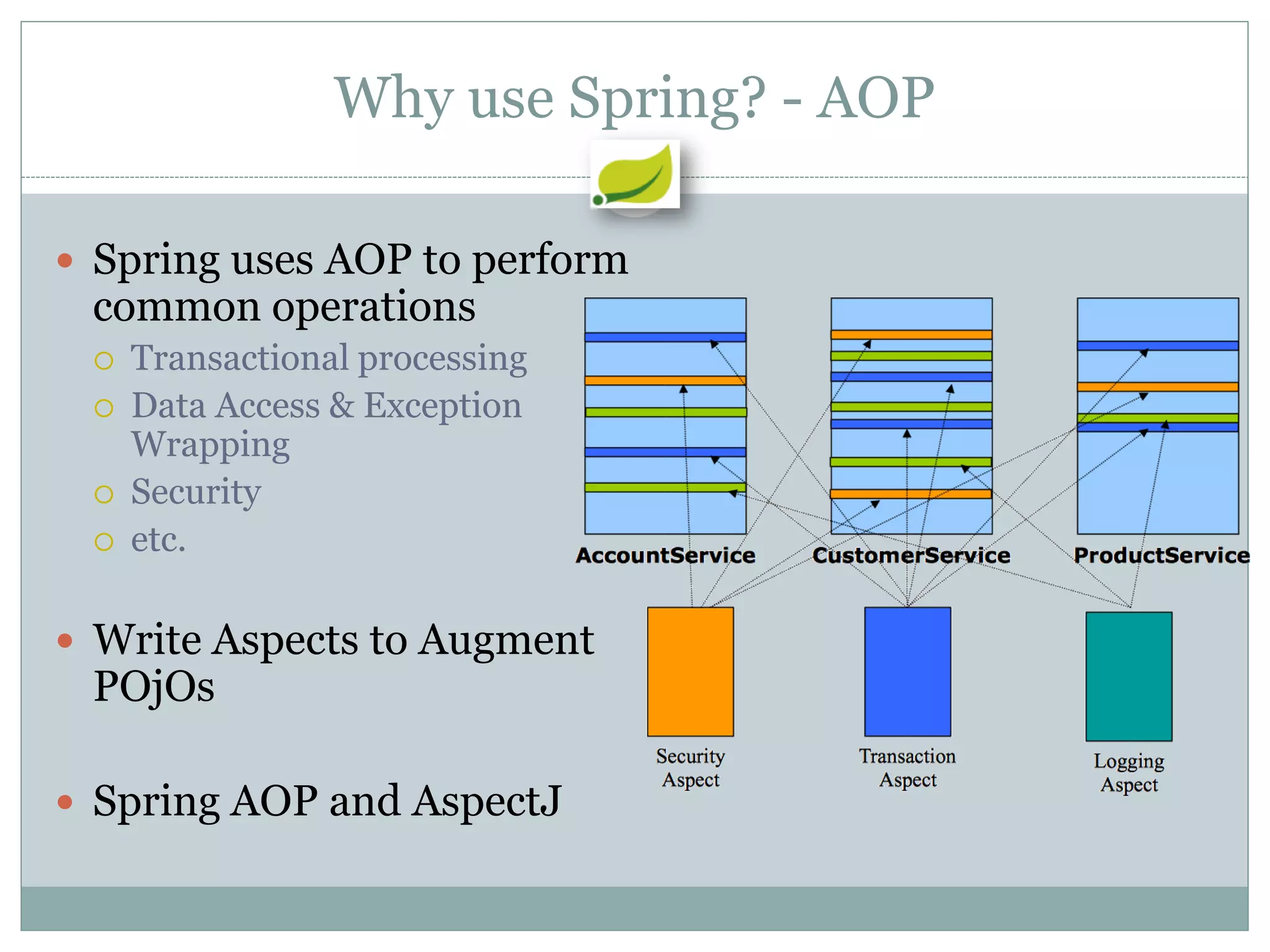
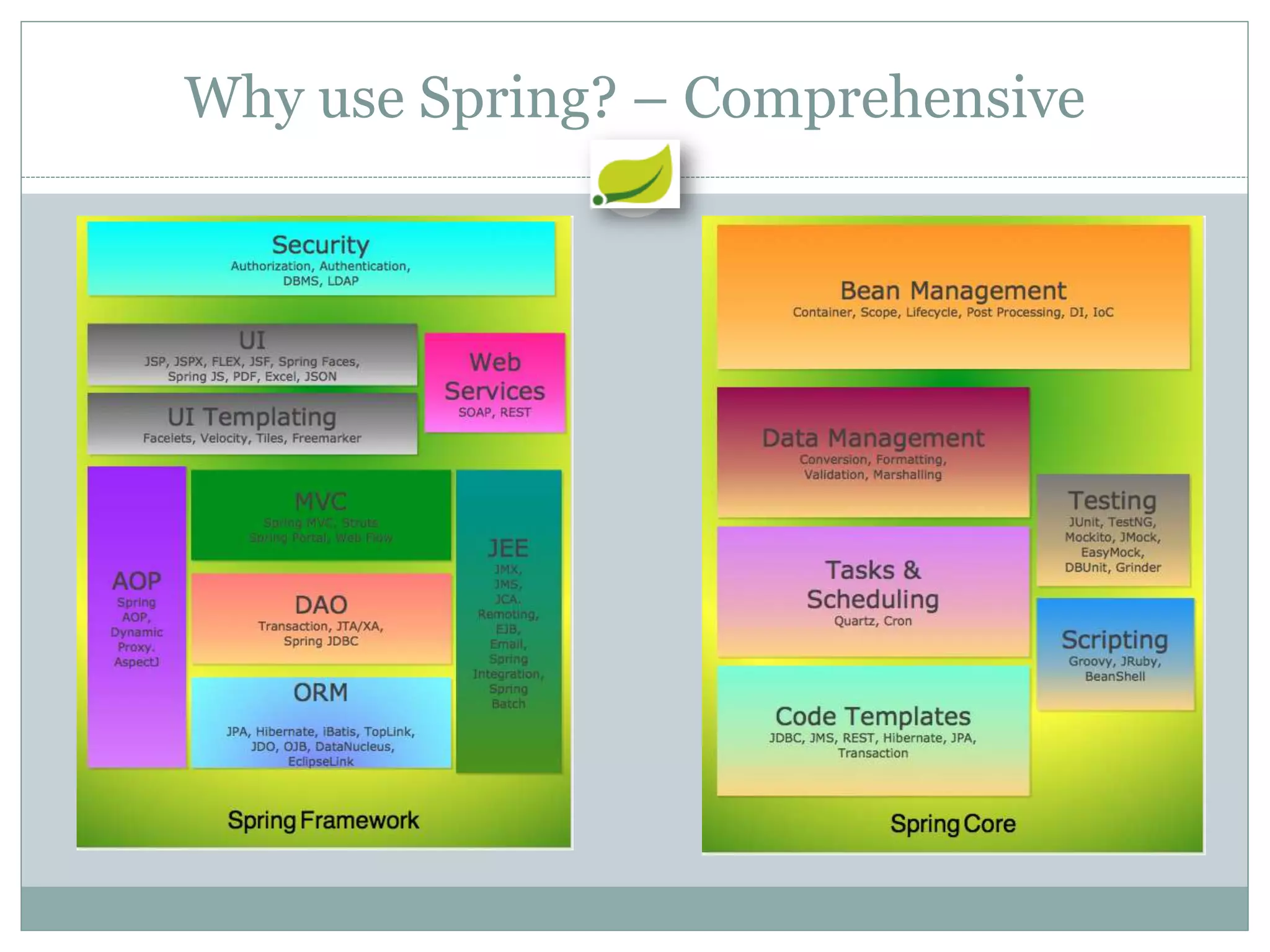
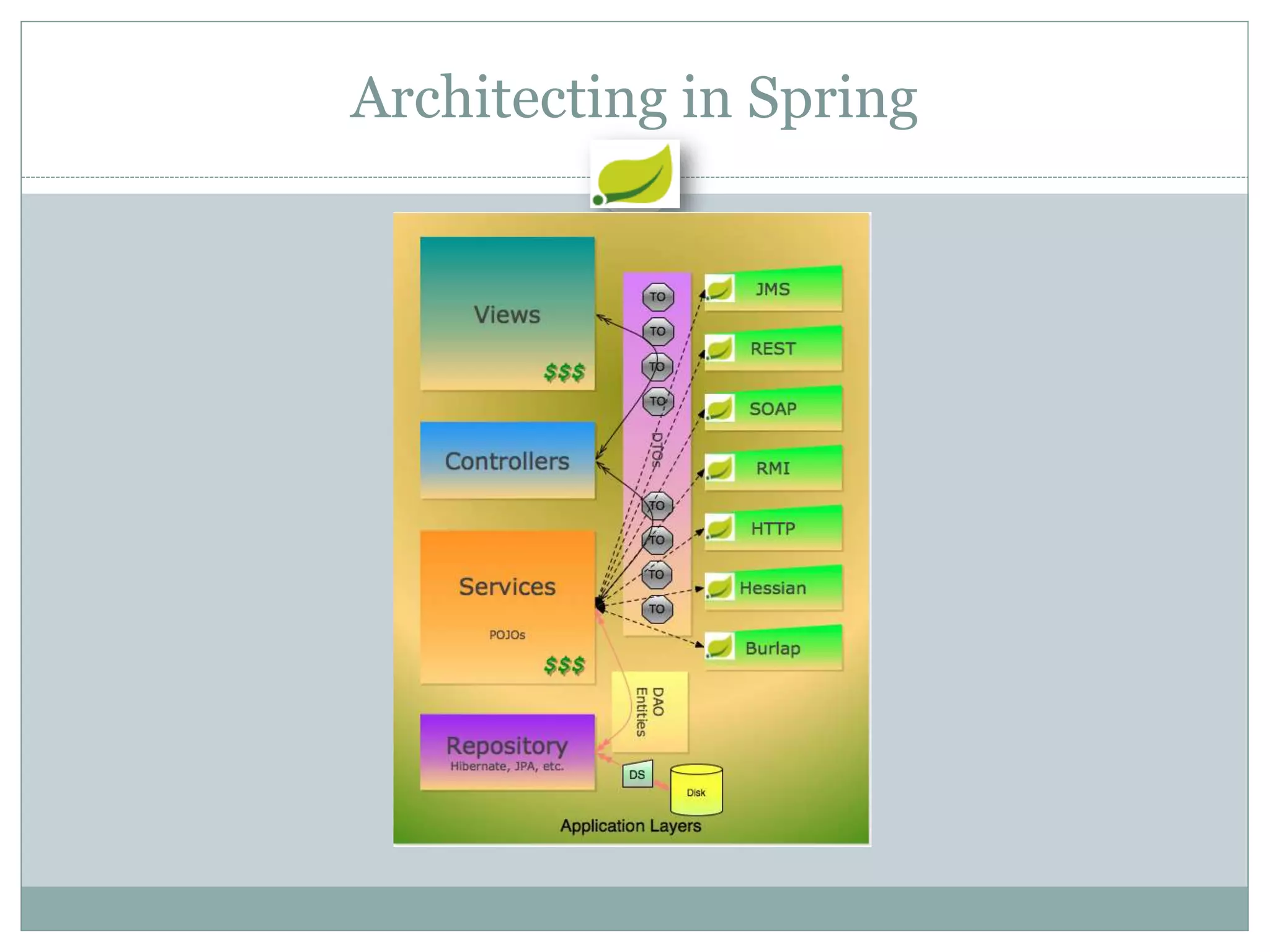
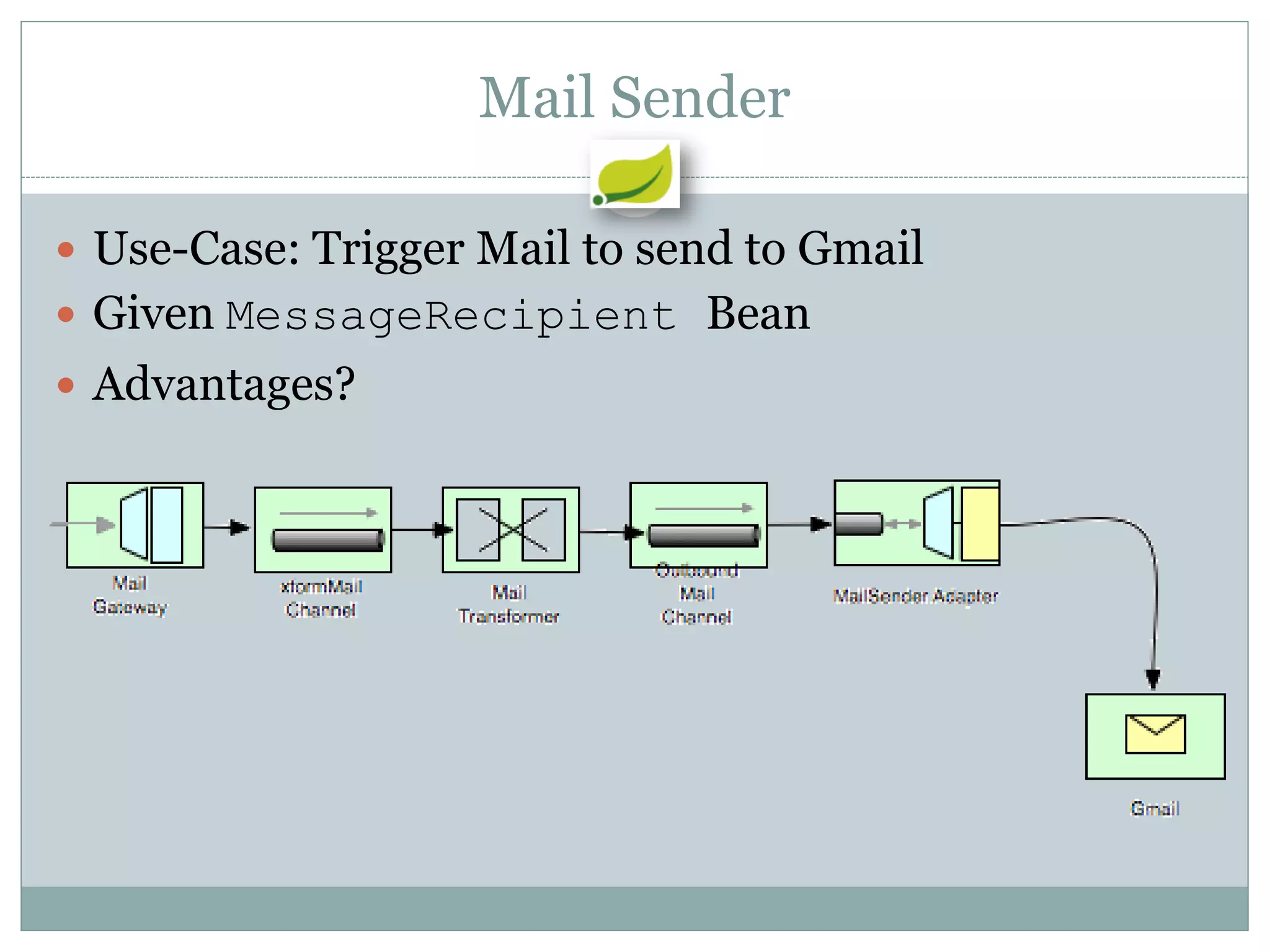
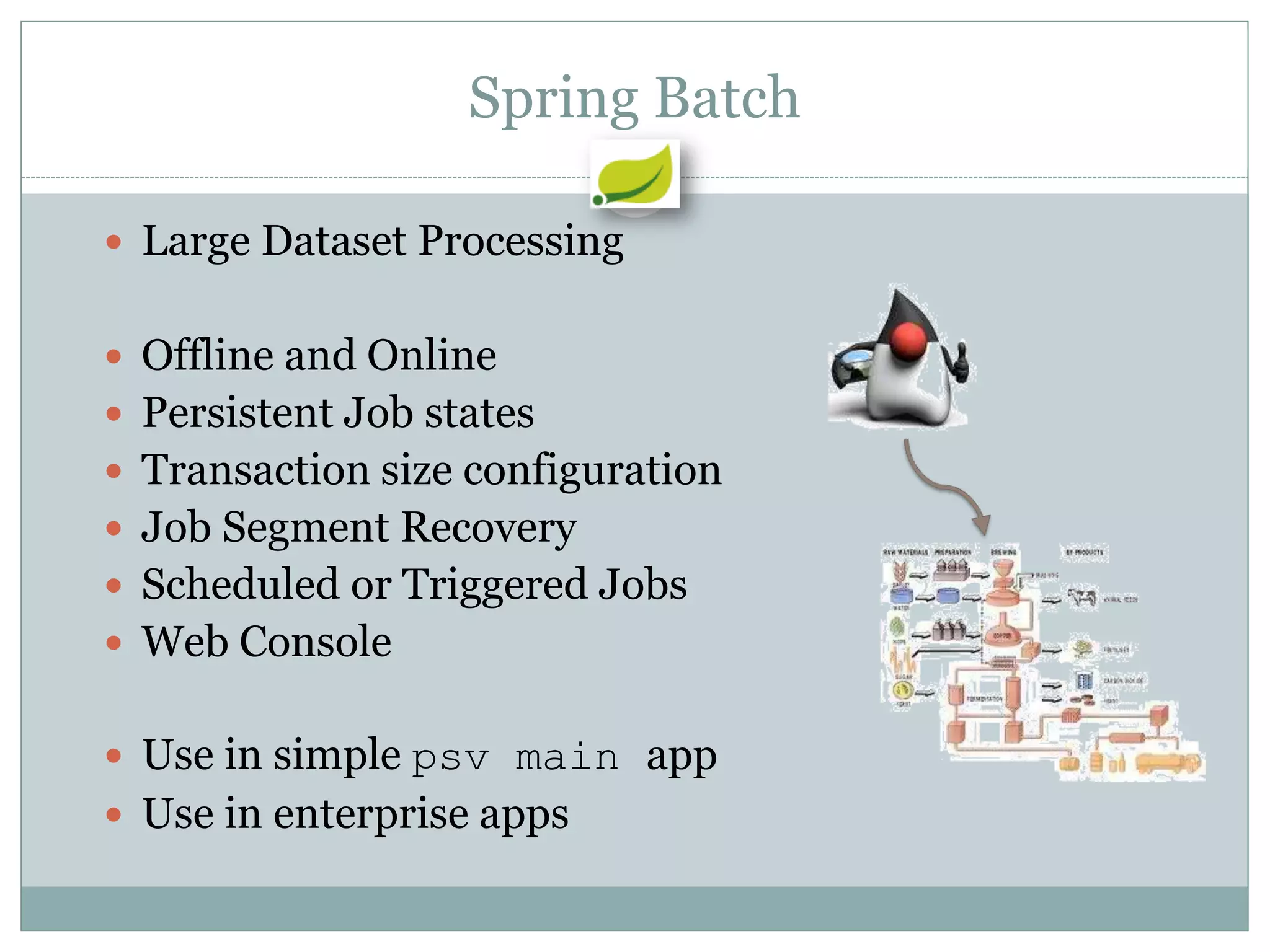
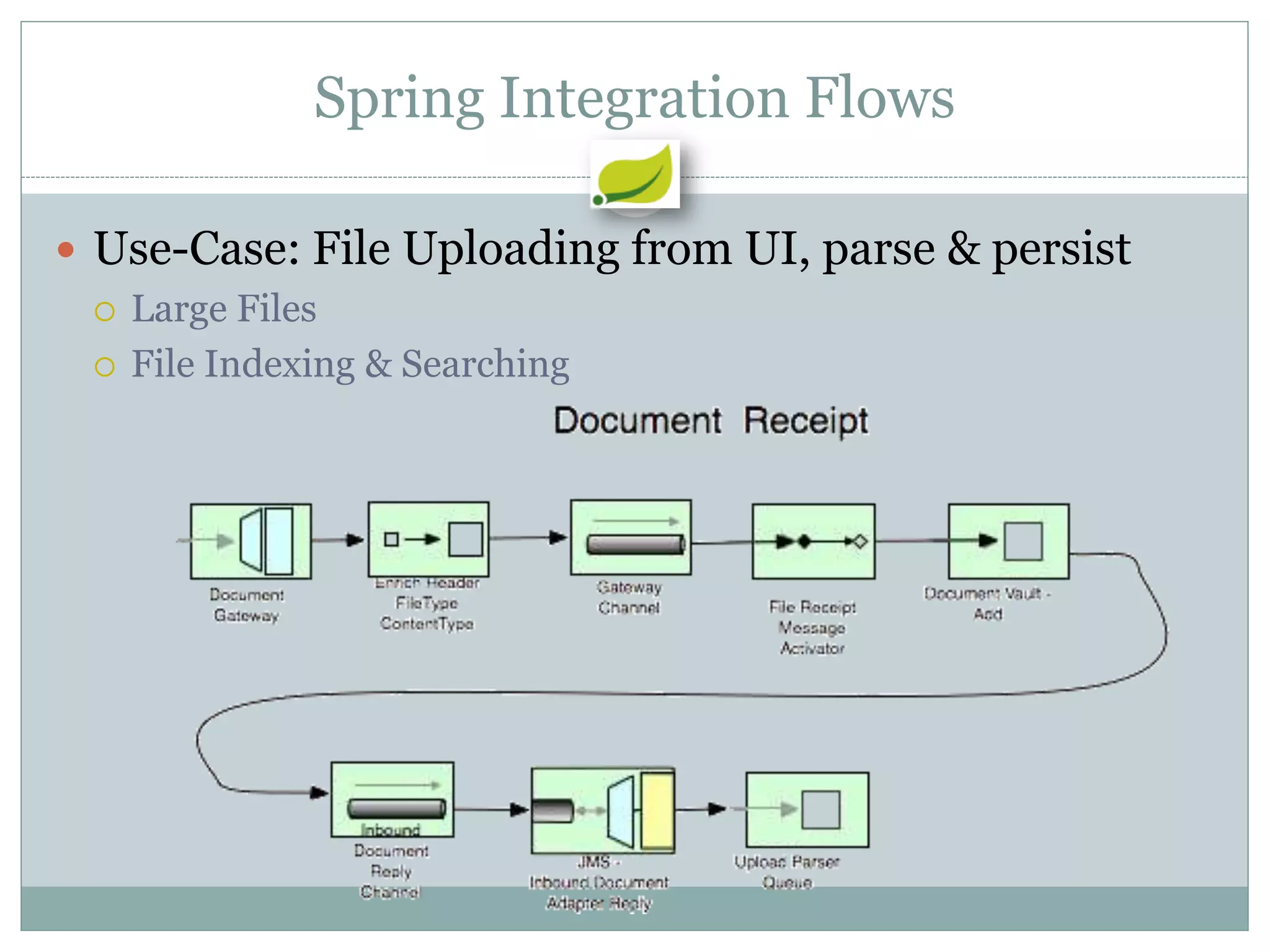
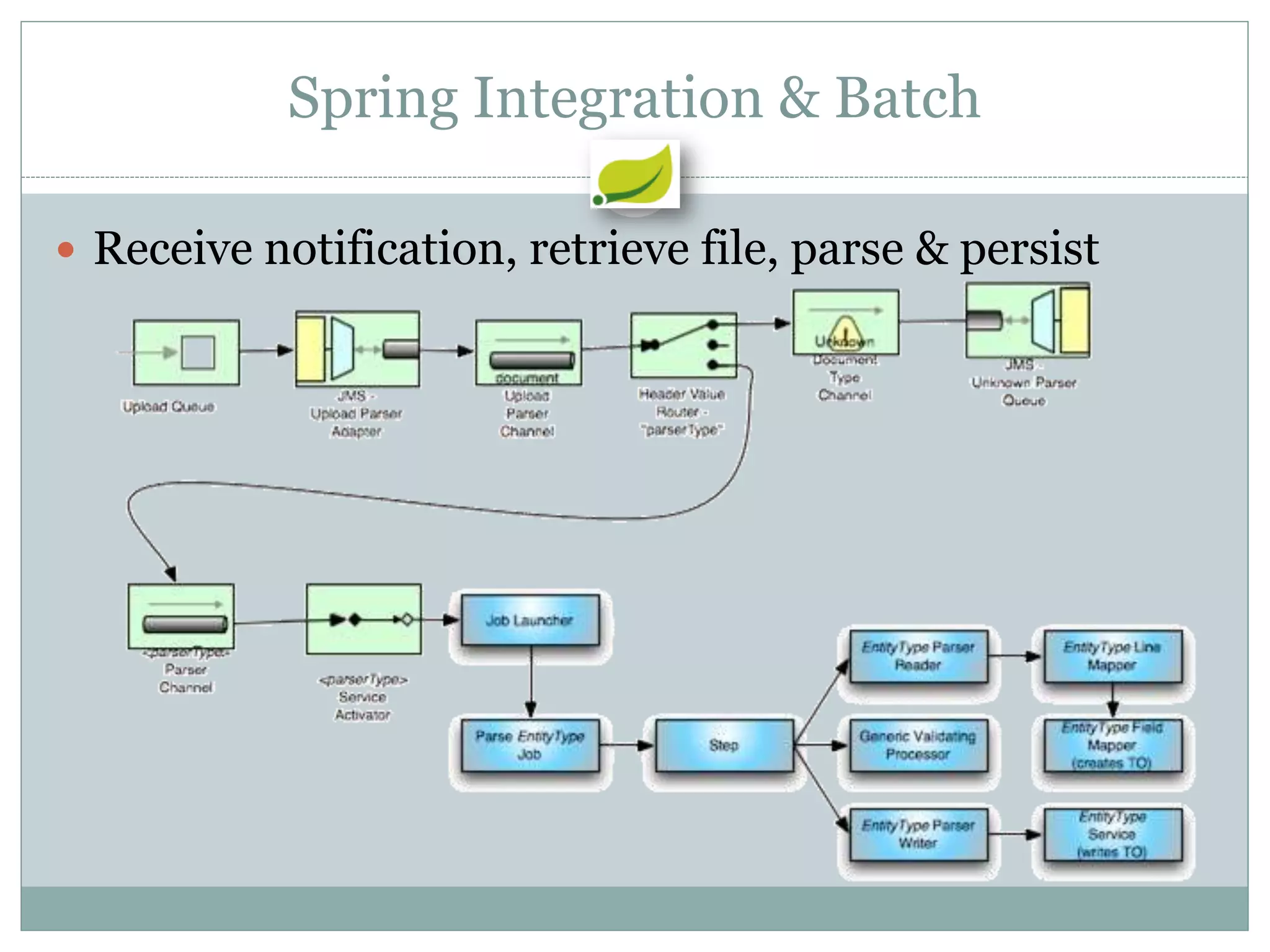
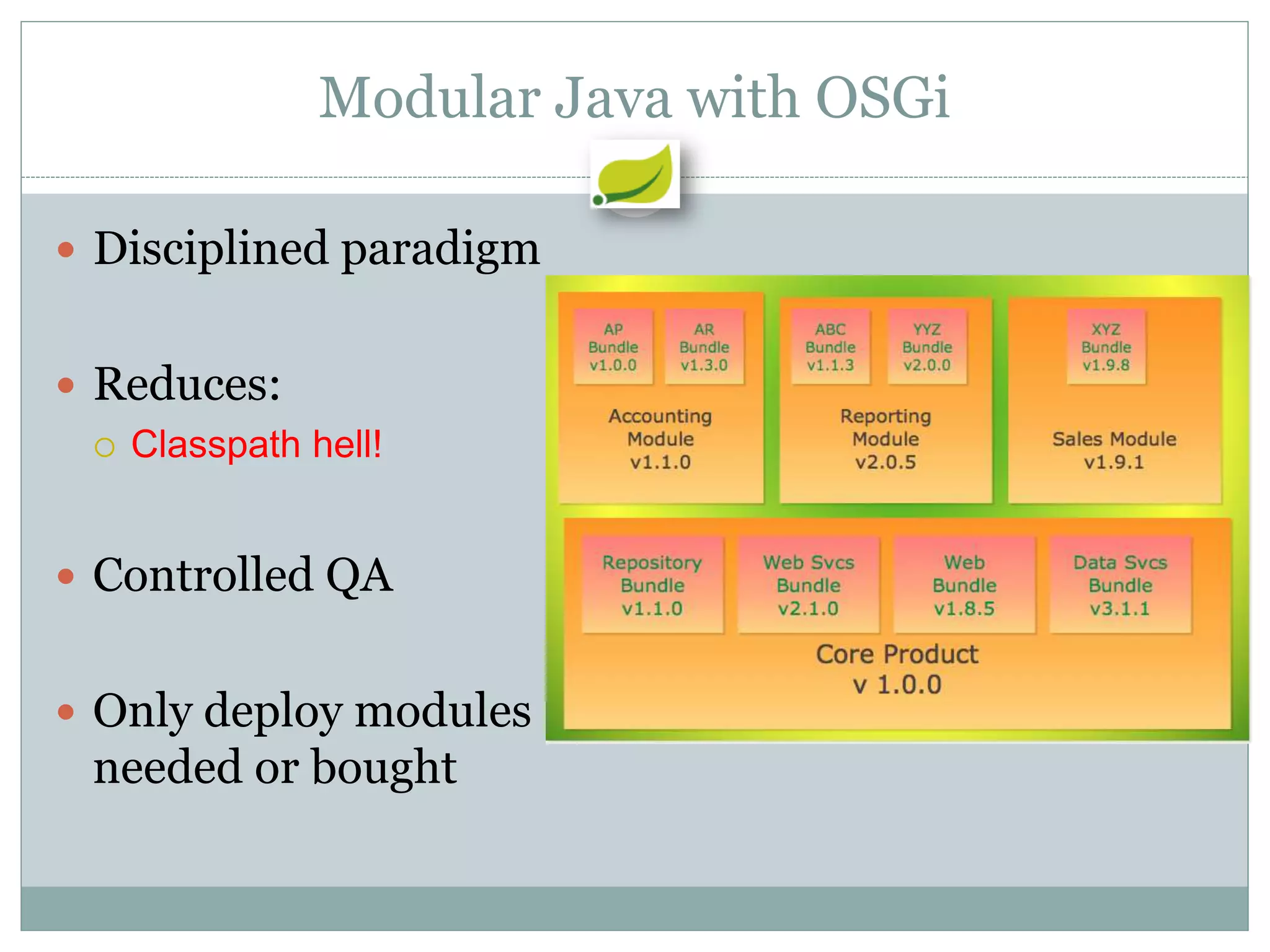
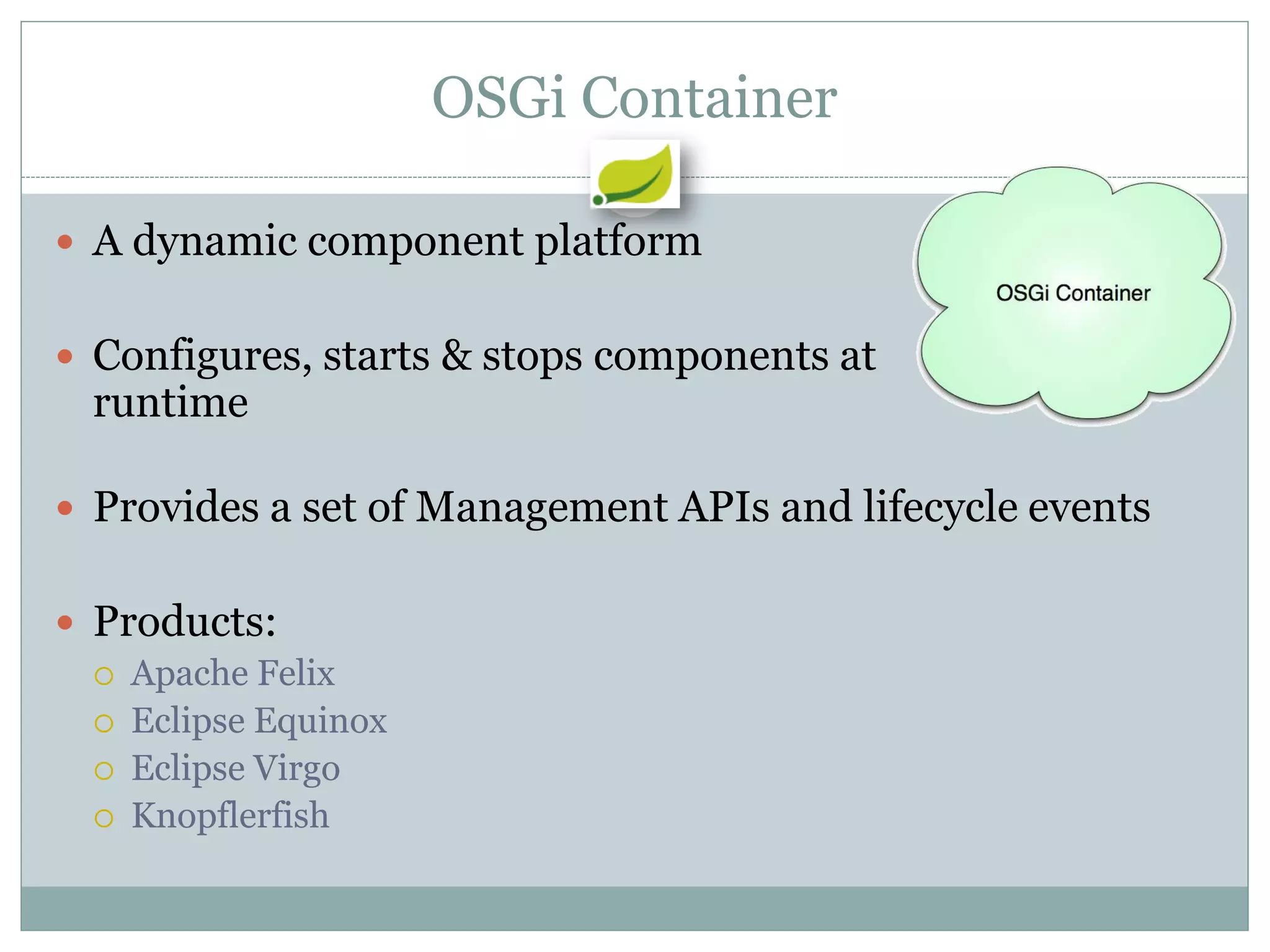
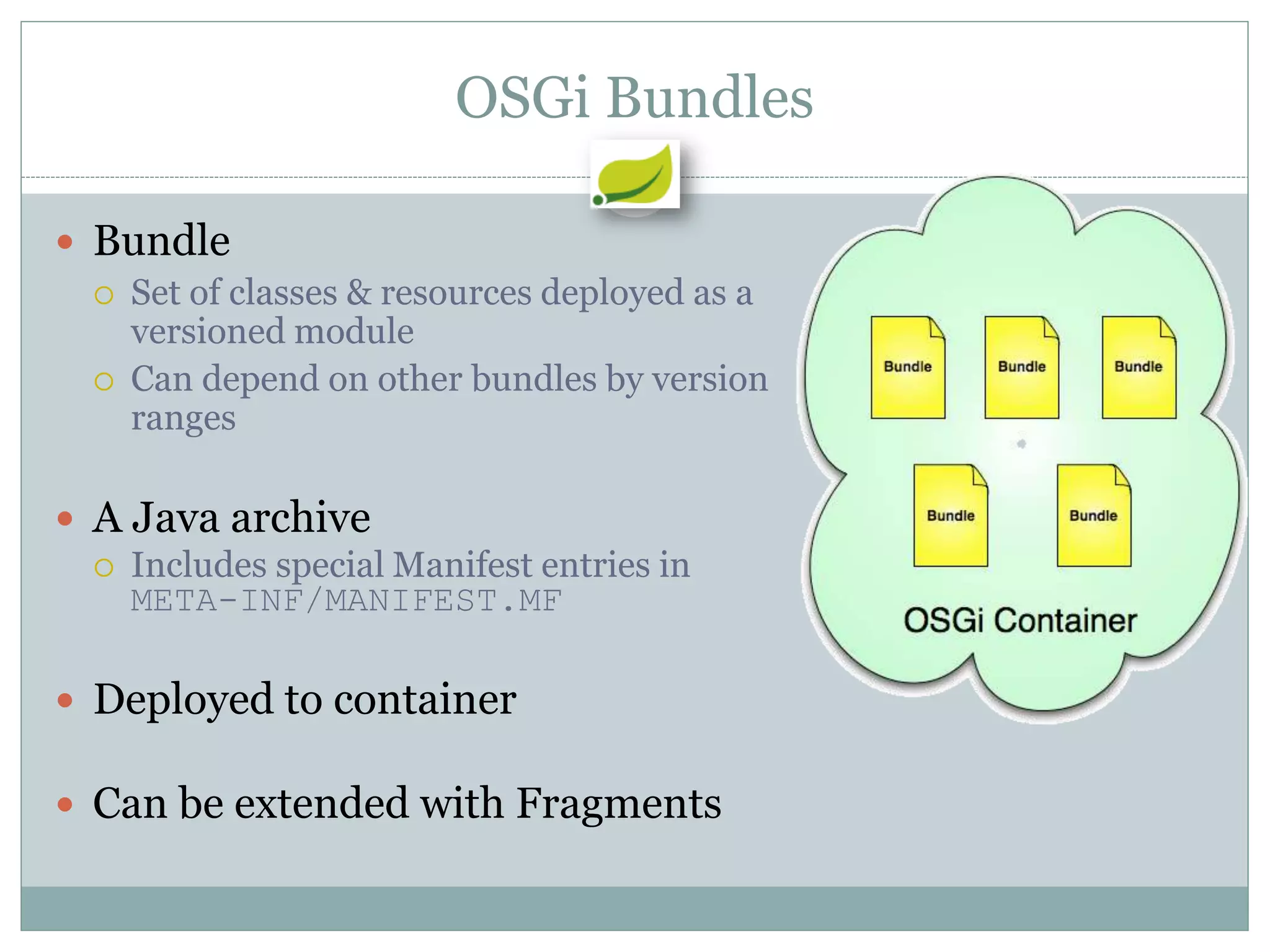
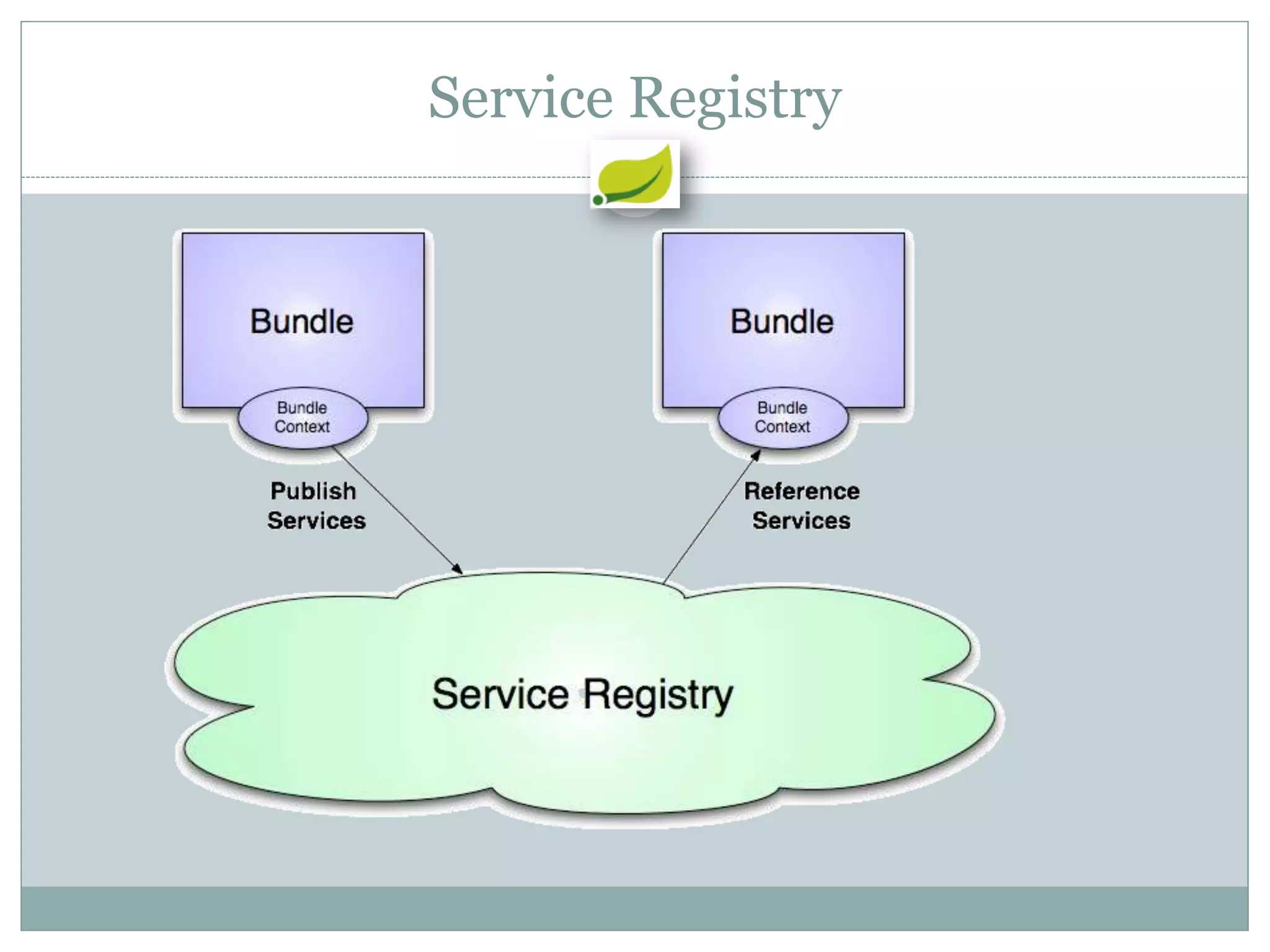
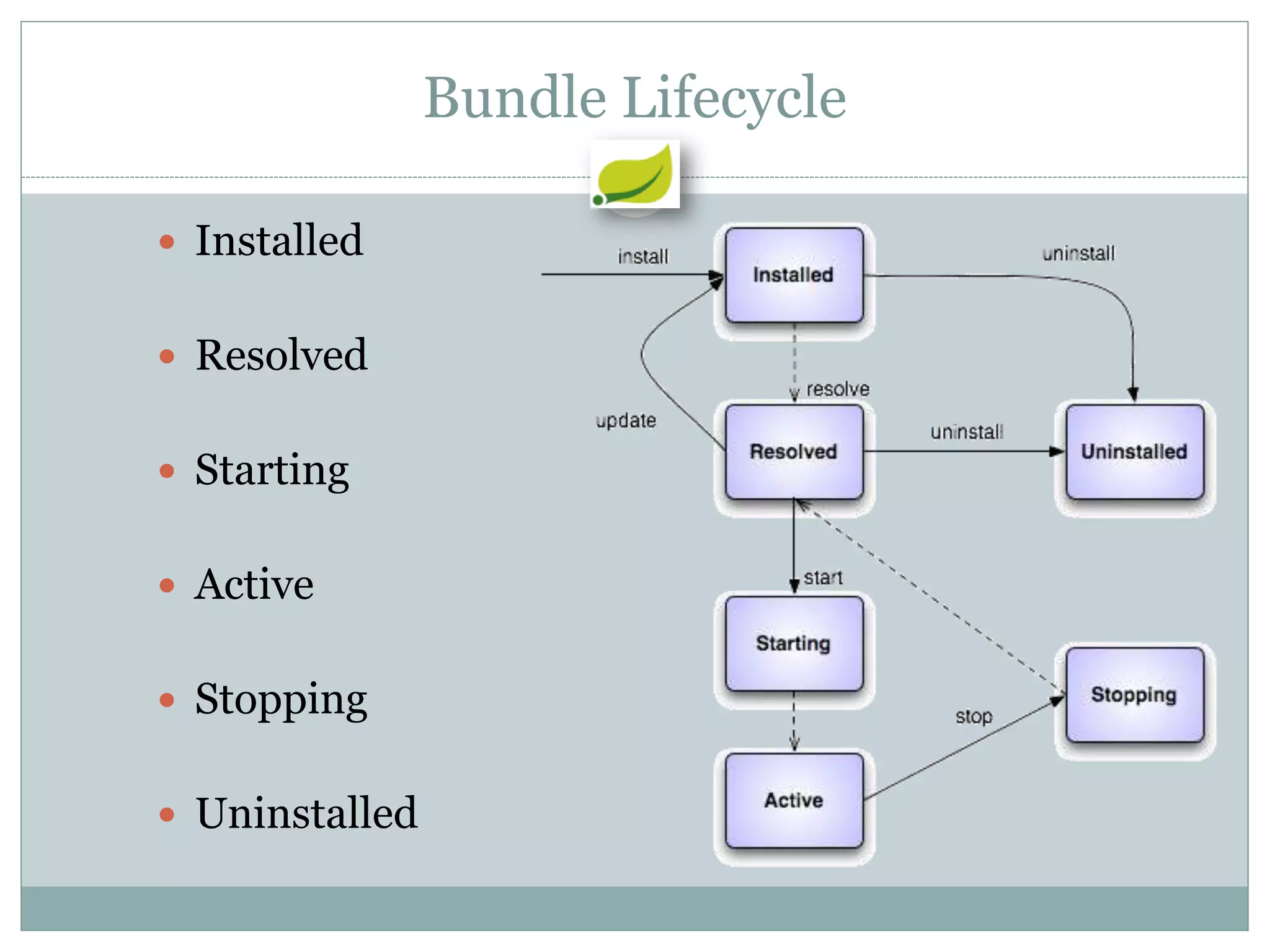
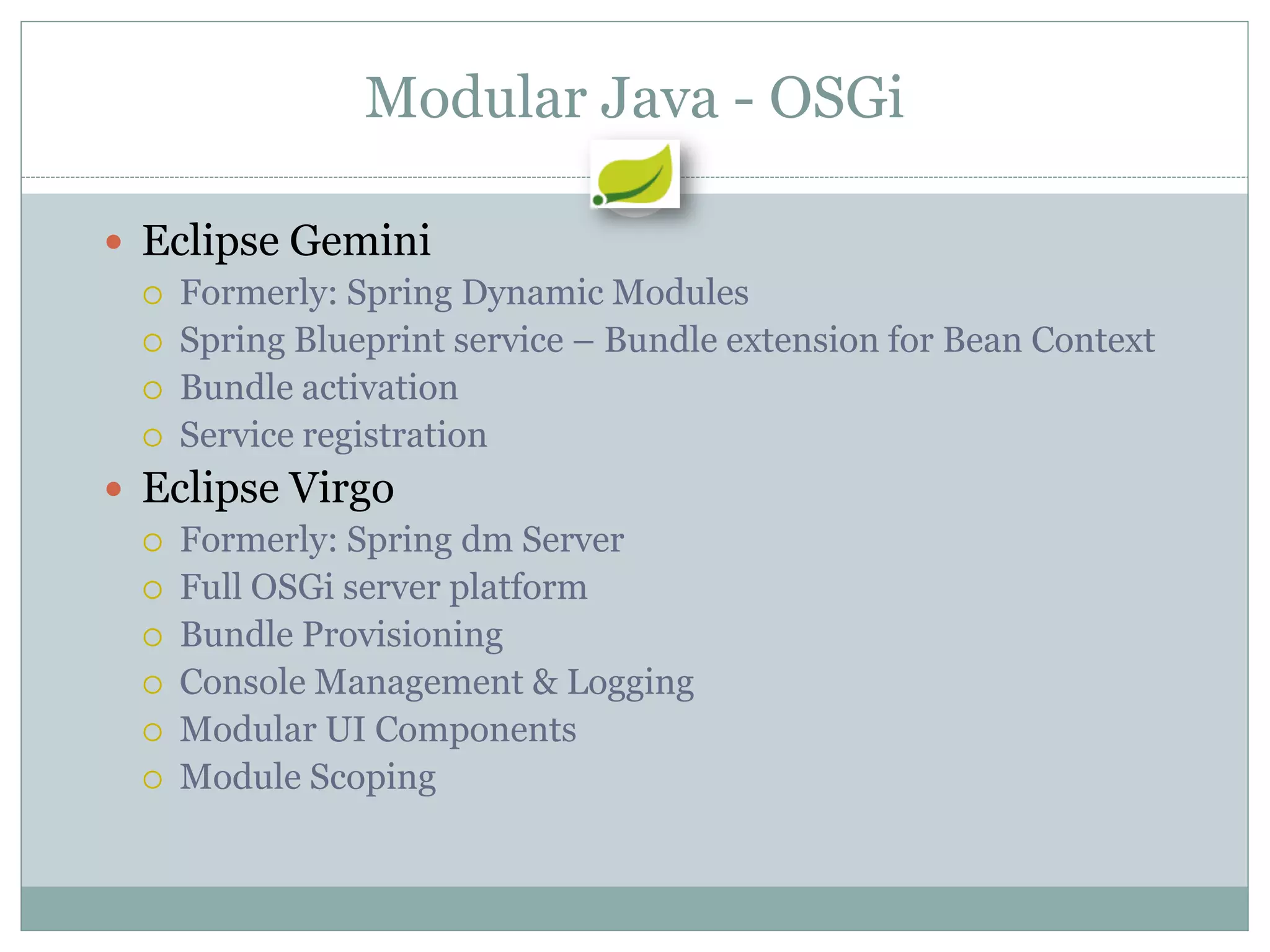
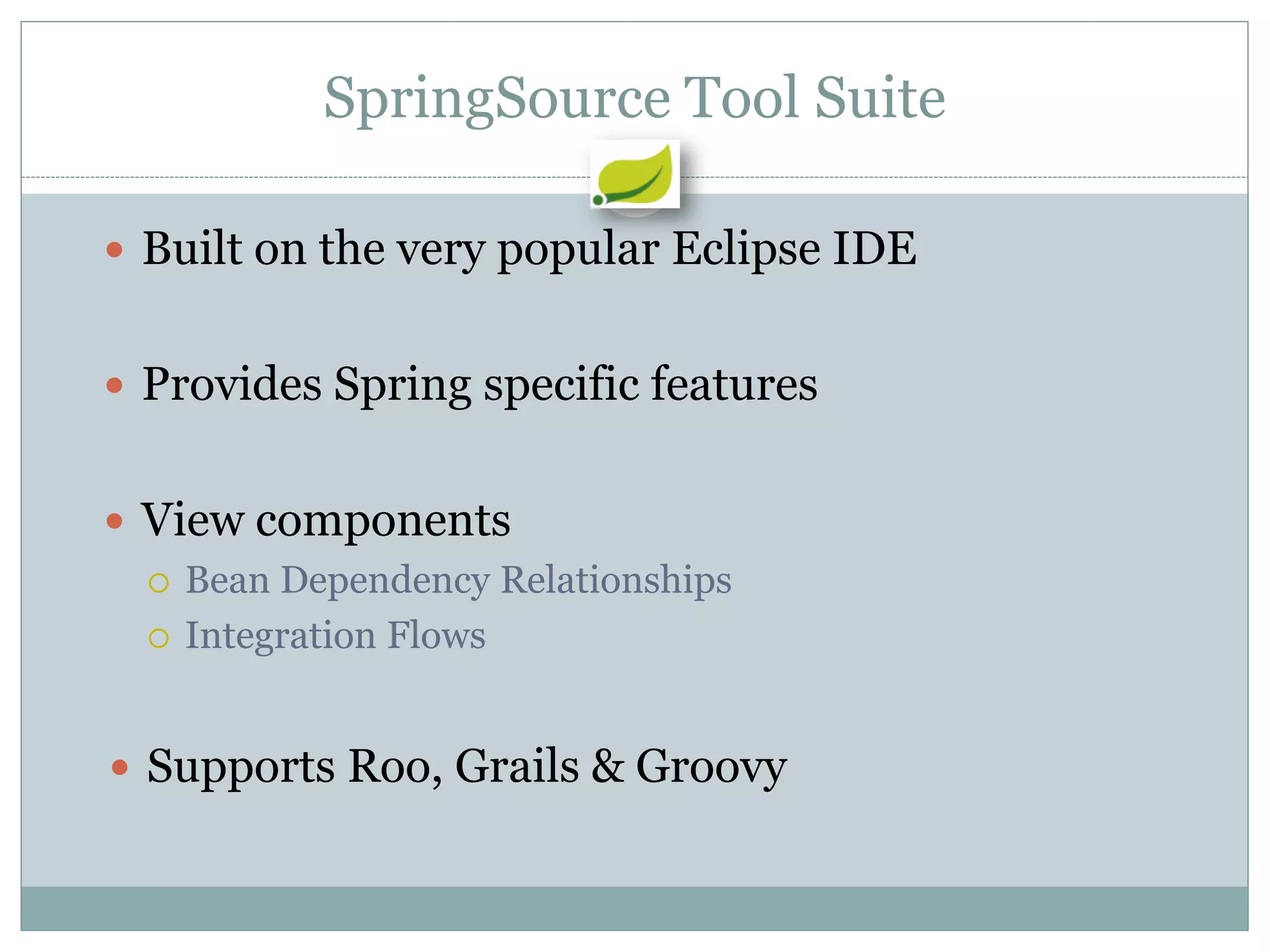
Spring is an open source framework for enterprise Java applications. It provides features like inversion of control, dependency injection, and aspect-oriented programming. Spring supports developing modular applications using OSGi and includes additional modules for web applications, integration, security, and batch processing. It aims to make enterprise Java development easier by reducing boilerplate code and providing a lightweight container for managing beans.