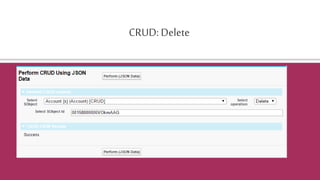
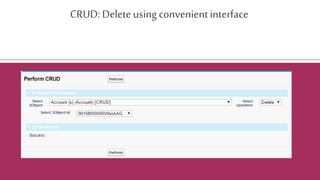
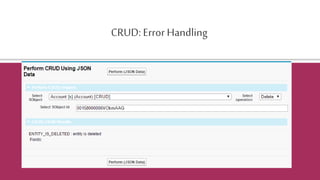
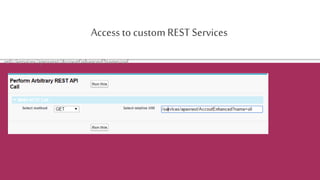
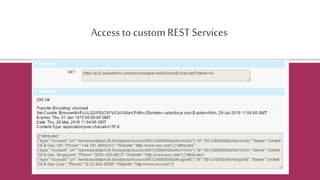
The document provides an overview of the Salesforce REST API, explaining its architecture, principles, and functionalities, including how to interact with Salesforce resources through HTTP methods. It details the REST architectural style, emphasizing the importance of statelessness, caching, uniform interfaces, and the use of friendly URLs to optimize API calls. Additionally, it discusses the differences between REST, SOAP, and Bulk APIs, and outlines how to access available API versions and perform CRUD operations.
















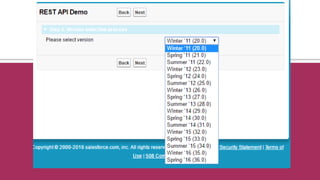



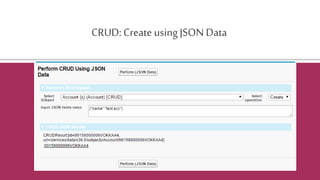
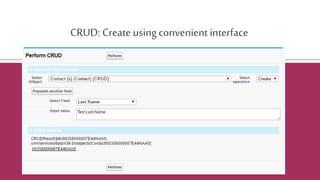
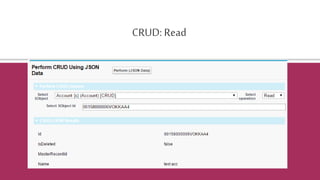
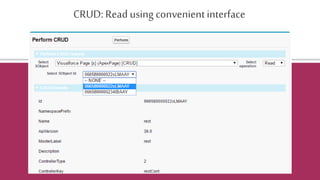
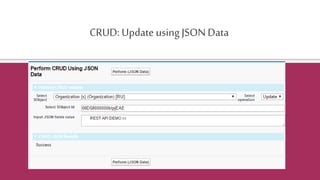
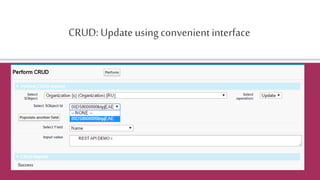
![Certainobjectsdo not allow DML in Apex
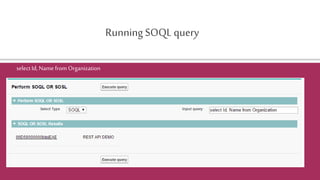
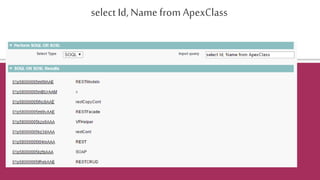
Organizationo=[selectId,NamefromOrganization];
o.Name+='x';
updateo;
yields: Line:3,Column:1DMLnotallowedonOrganization
However,someofthemallowRESTAPIUpdateoperations](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pluralsightauditionrestapi-160528131954/85/SFDC-REST-API-33-320.jpg)