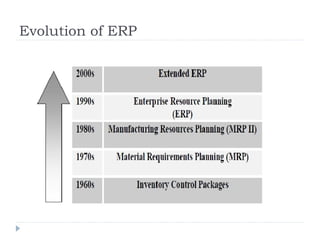
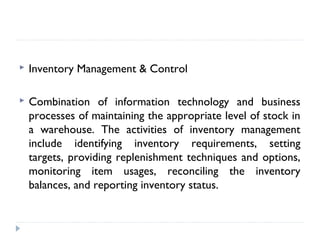
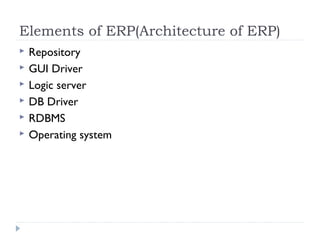
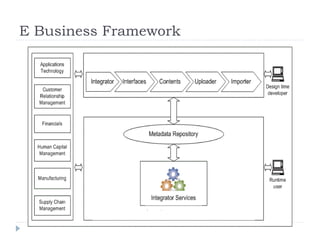
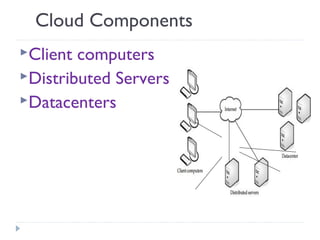
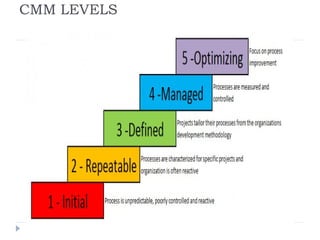
An ERP system attempts to integrate all functions of a company into a single computer system. ERP provides integrated databases and customized reports. It aims to standardize operations and processes. Major benefits include integration of data, increased productivity and reduced costs. Challenges include implementation costs, changes to business processes and organizational structure, and resistance to change.