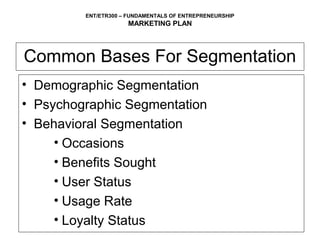
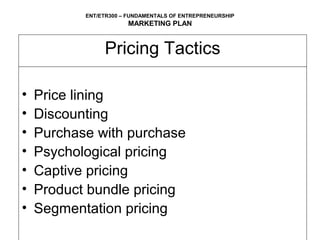
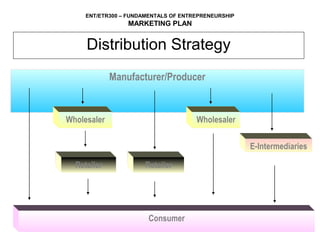
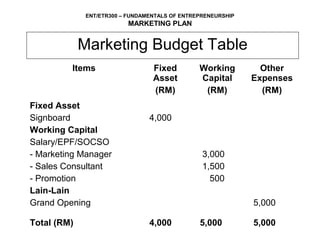
This document outlines the key components of a marketing plan, including setting objectives, analyzing the product/service, target market, competition, and developing strategies for pricing, placement, and promotion. It explains that a marketing plan helps entrepreneurs evaluate market acceptance, develop strategies, and identify required resources. The document provides guidance on how to prepare each section of a marketing plan and includes an example marketing budget table.