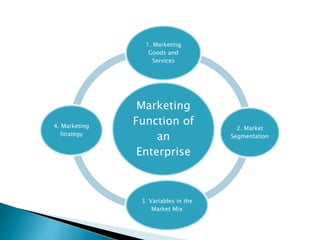
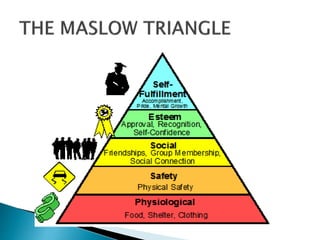
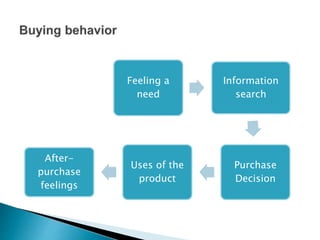
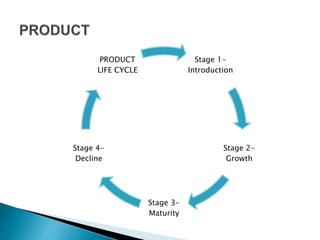
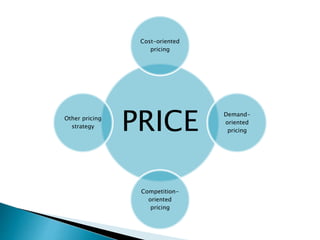
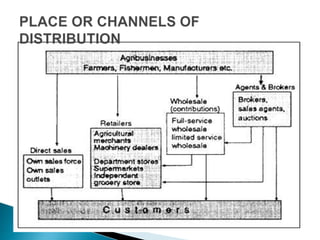
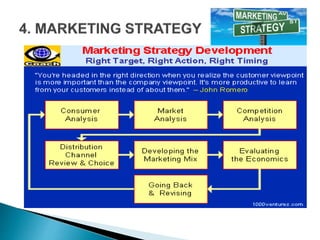
This document outlines the objectives and content of two lessons on marketing. The general objectives are to discuss the marketing function, explain the components of a marketing plan, and have students write a marketing plan. Lesson 1 will cover the marketing function of an enterprise, including goods, services, markets, and the marketing mix. Lesson 2 will provide a guide and example for developing a marketing plan, including describing the product, competitors, target market, demand, pricing, promotion, and marketing strategy. The specific objectives are to explain key marketing concepts and the responsibilities of marketing managers.