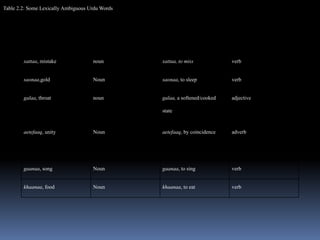
Urdu is the national language of Pakistan and is also spoken in India. While traditionally written right-to-left using its own script, some in Pakistan use the Roman alphabet instead. Key differences between English and Urdu include Urdu using a subject-object-verb structure and postpositions placed after nouns to indicate location, while English uses subject-verb-object order and prepositions before nouns. Urdu verbs have multiple forms to indicate aspects like causation, tense, and formality level.