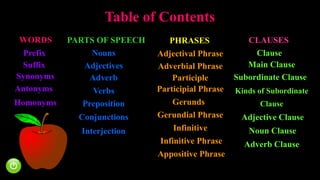
This document provides definitions and examples of English grammar terms including parts of speech, phrases, and clauses. It defines terms like prefix, suffix, synonym, antonym, and homonym. It also defines and categorizes nouns, adjectives, verbs, adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions, and interjections. Additionally, it explains phrases like adjectival phrases, adverbial phrases, participial phrases, gerund phrases, infinitive phrases, and appositive phrases. Finally, it defines clauses like main clauses, subordinate clauses, adjective clauses, noun clauses, and adverb clauses.