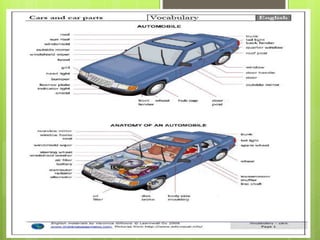
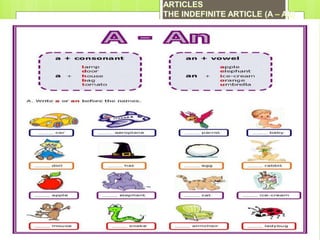
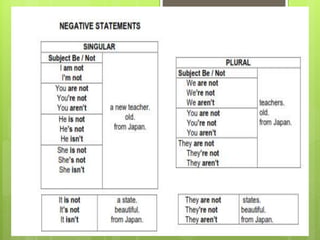
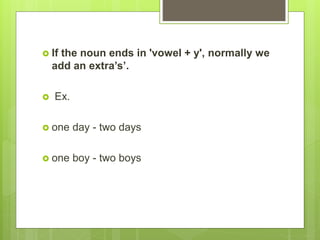This document provides an introduction to Spanish vocabulary and grammar concepts related to introducing oneself, telling time and dates, and describing people. It includes sample dialogues, exercises, and explanations of key terms like nouns, articles, adjectives, numbers and prepositions. The goal is to teach basic communication skills around greetings, schedules, and physical characteristics in order to introduce ideas and feelings in oral and written Spanish.