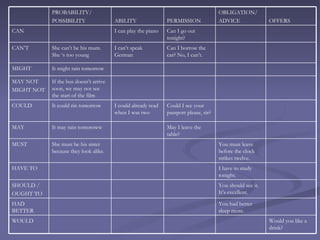
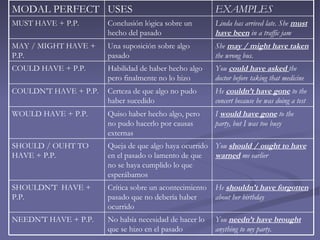
Modal verbs are incomplete verbs that do not have all tenses and are used with other verbs to complete their meaning. They are not conjugated for third person singular present tense and are followed by an infinitive without "to" in most cases. Modal verbs do not require an auxiliary verb in questions or negatives. There are different modal verbs that express ideas like ability, permission, obligation, advice, offers, and past possibilities or necessities. Modal perfect tenses are formed with a modal verb plus "have" and the past participle to refer to past actions, and are used to express conclusions, suppositions, abilities, criticisms and regrets about past events.