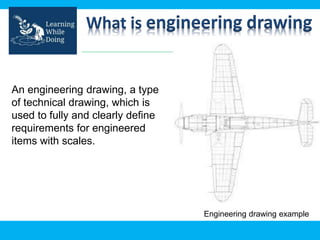
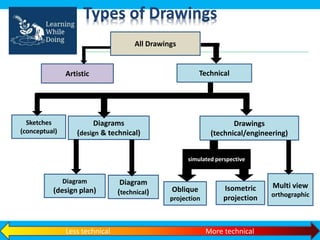
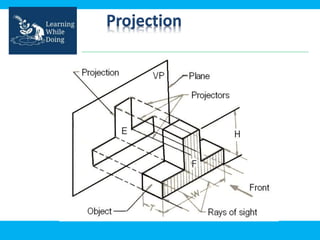
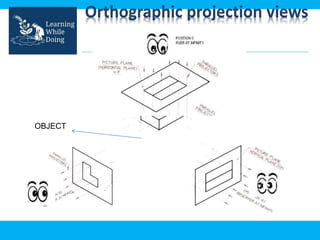
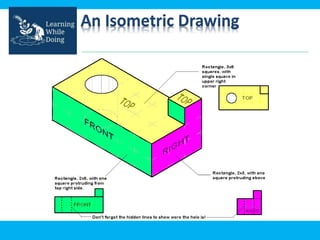
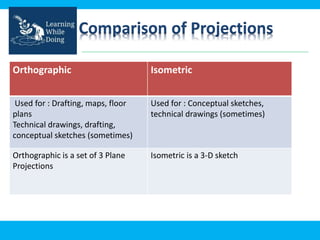
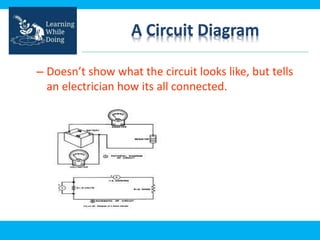
An engineering drawing is a type of technical drawing that is used to fully define engineered items using scales. There are different types of drawings for different purposes, from conceptual sketches to technical diagrams and drawings. Engineering drawings use techniques like multi-view orthographic projections and isometric projections to represent 3D objects in 2D views. They provide important technical information in a clear visual format and are used across various engineering fields.