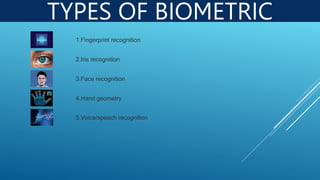
Biometrics is a technology that identifies individuals based on their unique physical and behavioral characteristics, such as fingerprints, iris patterns, and voice. The process involves enrollment, verification, and authorization to ensure secure access to systems and data. Various methods of biometric recognition, including fingerprint, iris, facial, hand geometry, and voice recognition, enhance security and convenience in various fields, including banking and healthcare.