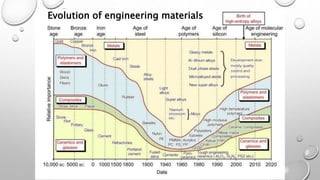
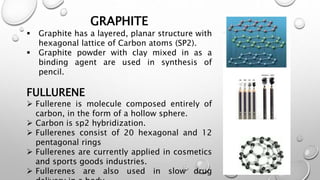
This document provides an introduction to engineering materials. It discusses the importance of studying engineering materials and outlines the course outcomes. The key classes of materials covered include ionic crystals, covalent materials, metals and alloys, semiconductors, superconductors, polymers, composite materials, and ceramics. Examples are provided for each class and their properties and applications are summarized. Catalysts are also introduced. The document concludes by outlining some of the mechanical, thermal, electrical, magnetic, optical and chemical properties of engineering materials.