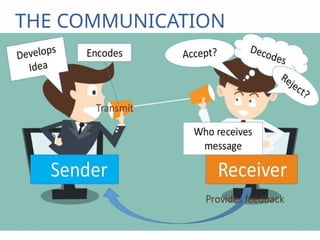
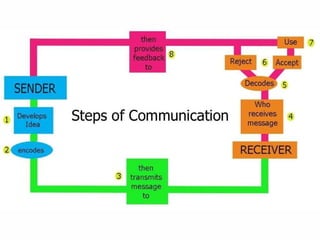
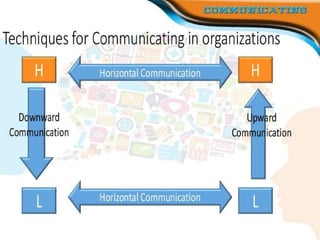
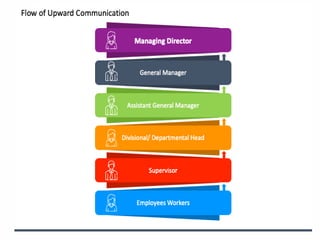
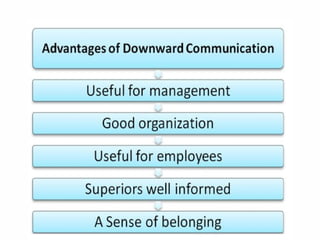
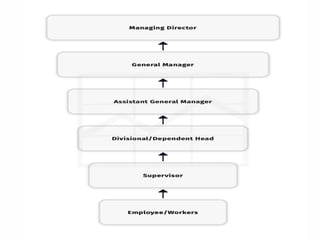
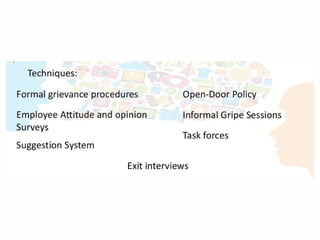
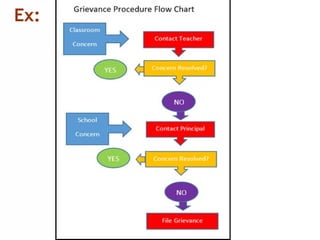
The document outlines the essential functions and processes of communication within an organization, emphasizing its importance for effective management. It describes the steps of the communication process, various forms of communication, and barriers that can hinder effective communication. Additionally, it mentions the significance of management information systems and provides examples of communication activities.