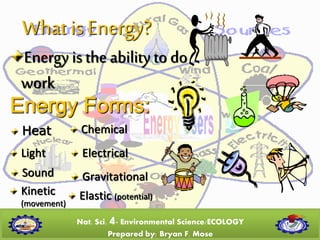
This document is a lecture on energy sources presented by Bryan F. Mose. It defines energy and lists different types of energy sources including renewable and non-renewable sources. Renewable energy sources can be replenished naturally, such as sunlight, wind, water, and biomass. Non-renewable sources such as fossil fuels are limited in supply. The document then discusses various non-renewable energy sources used in the Philippines like oil, natural gas, coal, and their impacts. Other domestic energy sources in the Philippines highlighted include geothermal, hydroelectric, solar and wind energy. Methods for conserving energy are also presented.