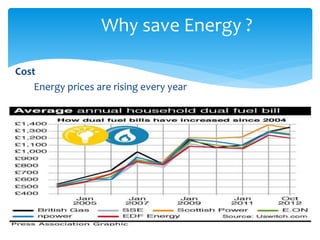
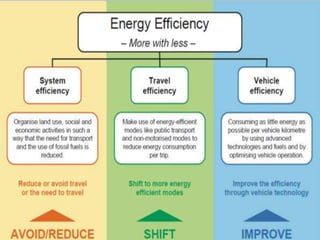
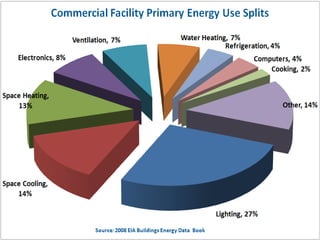
The document discusses energy conservation and climate change. It defines energy conservation as any behavior that results in less energy usage, such as turning off lights. It states that climate change poses a serious threat and that global temperatures are rising at an unprecedented rate due to human activity like carbon dioxide emissions. The document advocates for addressing this issue through improving energy efficiency in technology and changing energy-consuming behaviors to use less energy and reduce waste.