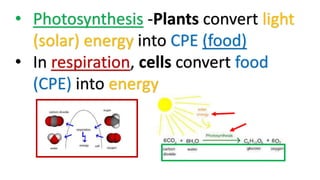
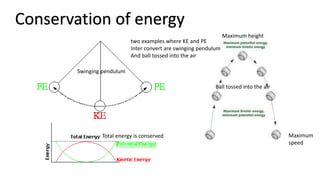
- Energy exists in various forms including electrical, heat, light, sound, chemical, and kinetic. Energy can be converted from one form to another but cannot be created or destroyed.
- Potential energy is stored energy and includes gravitational potential energy due to height, elastic potential energy from stretched objects, and chemical potential energy in fuels and food.
- The sun is the primary indirect energy source for Earth, providing light and heat energy that powers photosynthesis in plants and fuels most life on the planet. When the sun's energy is blocked, mass extinctions can occur.