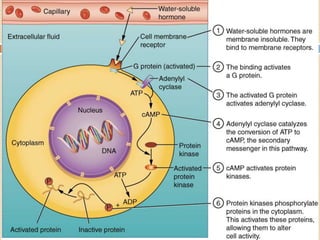
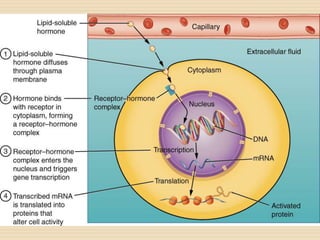
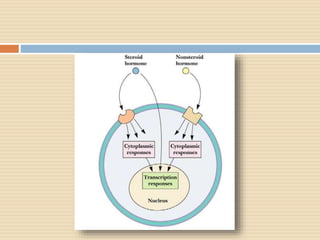
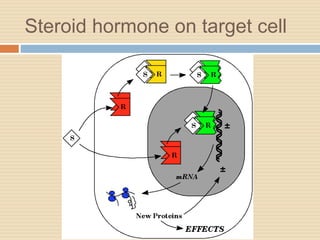
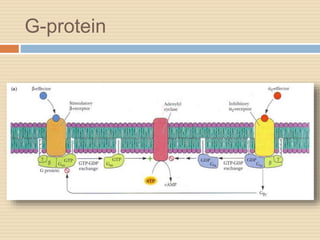
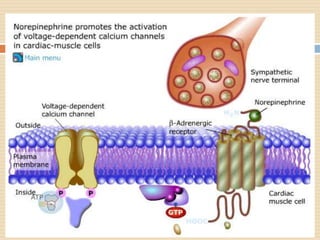
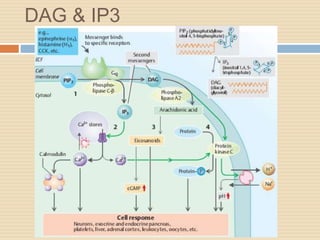
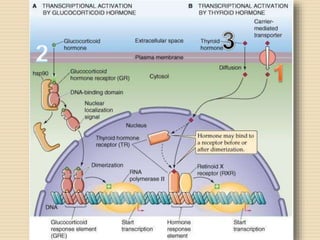
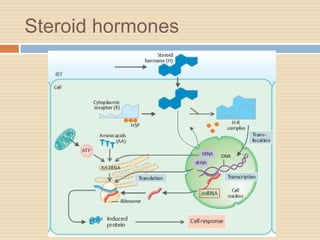
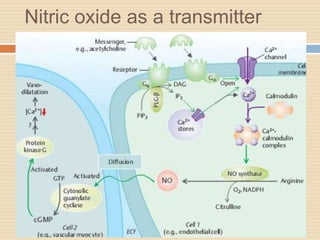
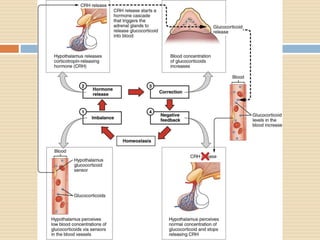
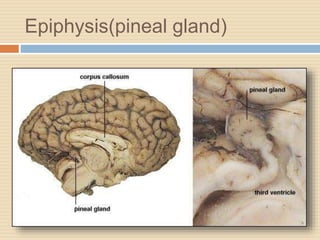
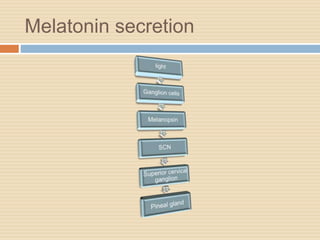
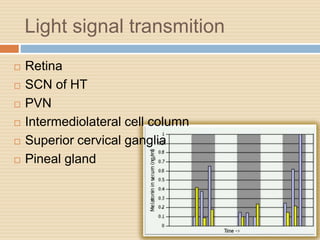
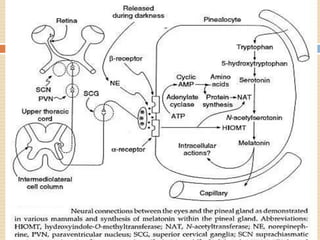
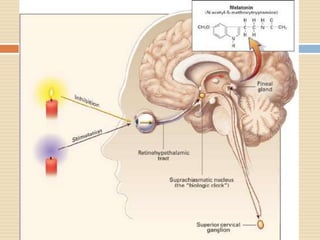
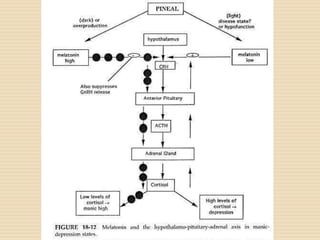
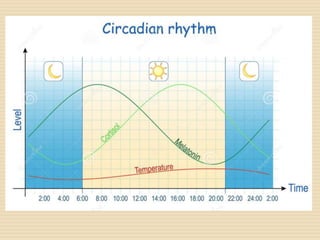
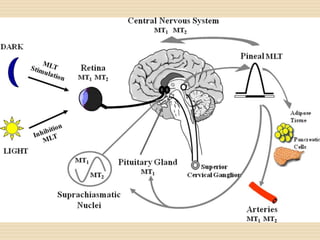
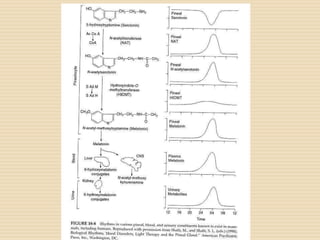
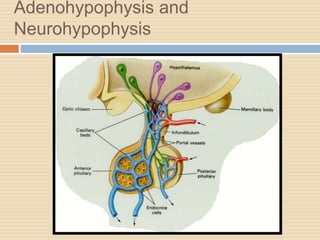
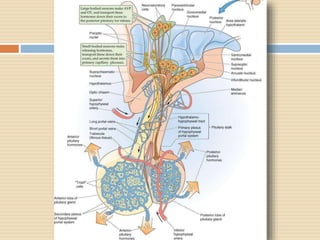
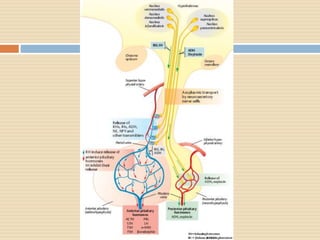
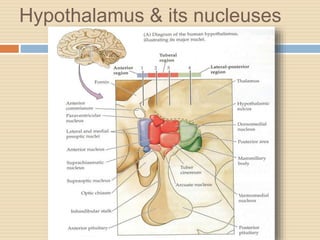
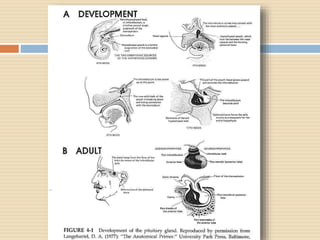
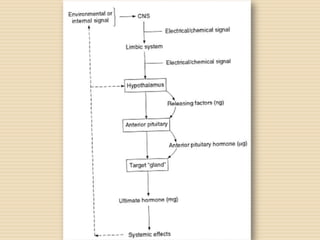
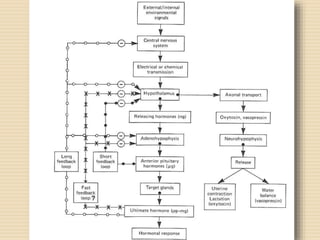
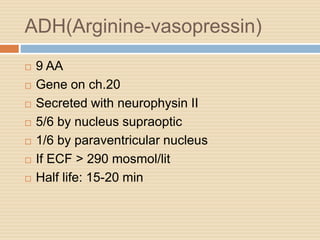
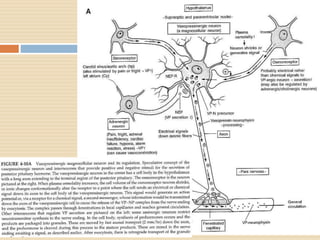
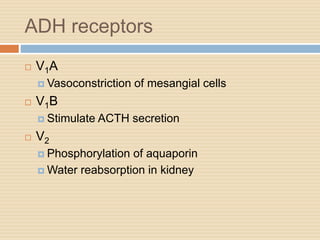
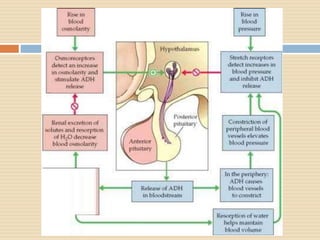
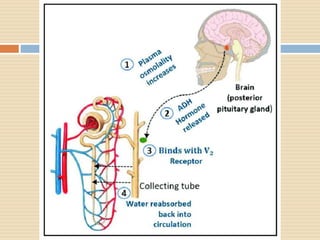
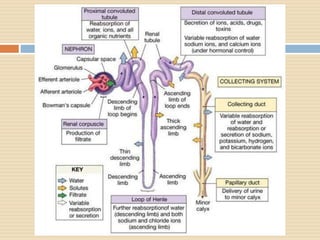
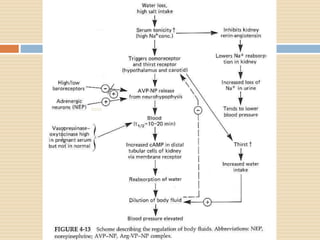
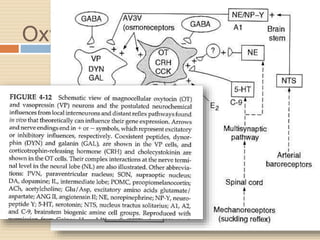
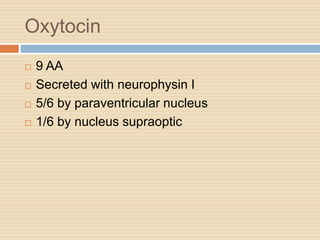
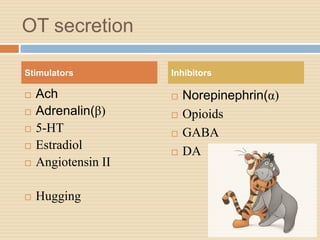
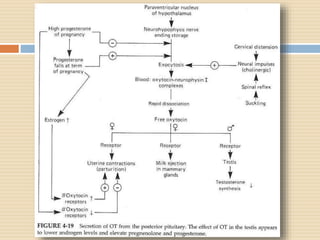
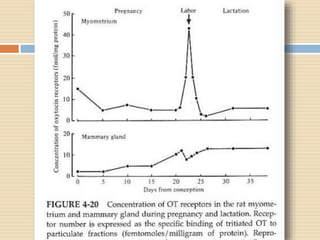
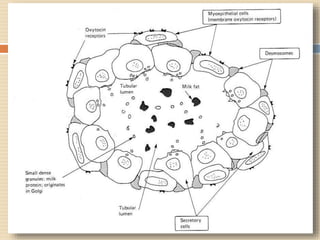
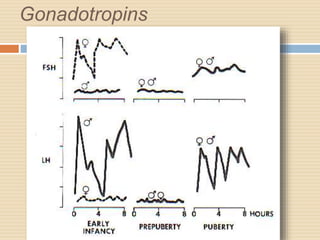
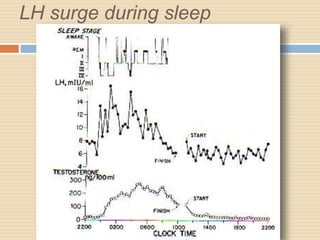
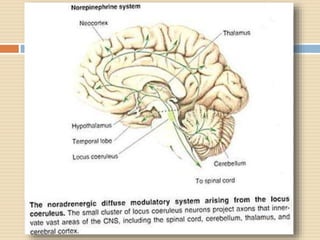
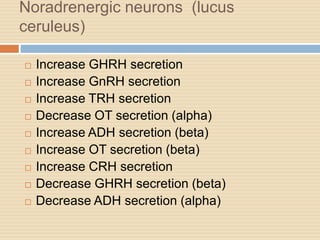
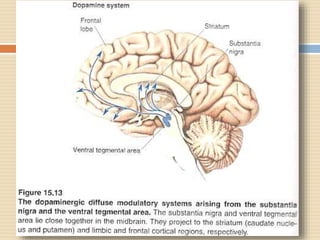
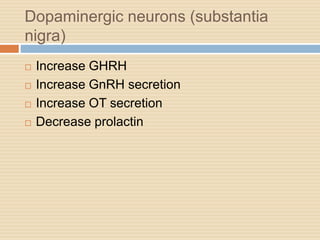
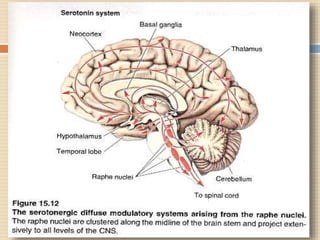
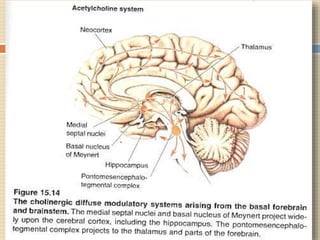
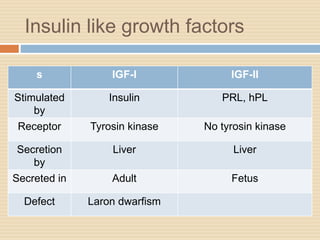
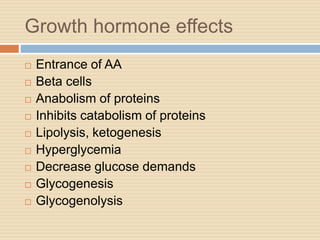
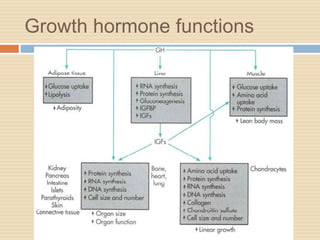
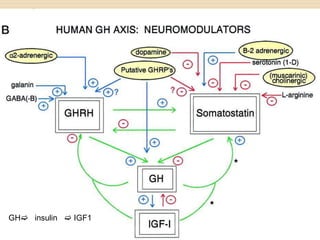
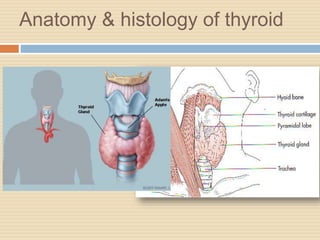
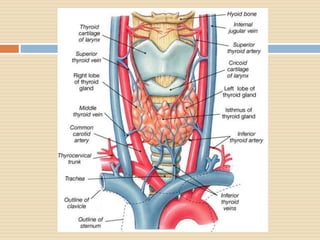
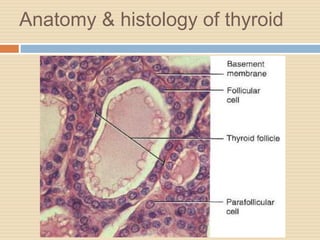
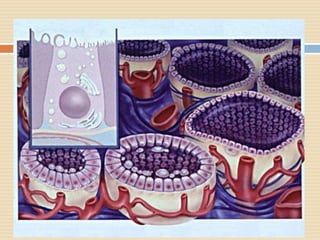
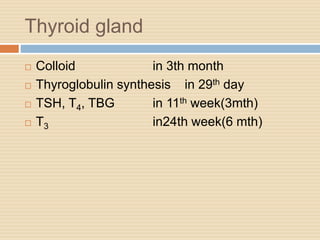
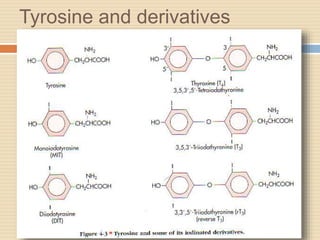
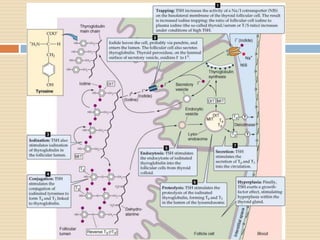
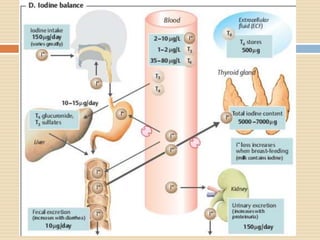
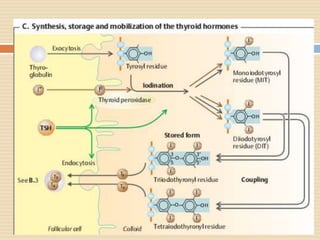
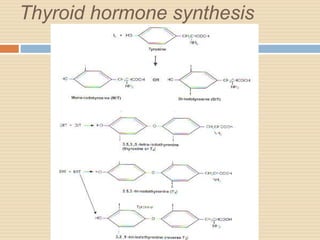
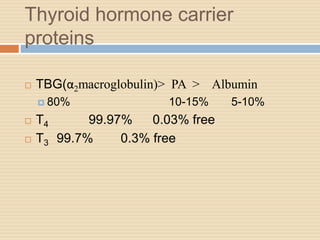
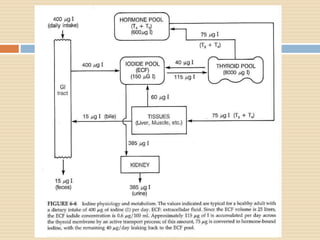
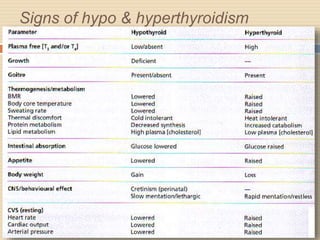
The document provides information about the endocrine system. It discusses hormones, their classifications, target cell responses, and hormone receptors. It also describes the pineal gland and its hormone melatonin. The hypothalamus and pituitary gland are examined, including the hormones they regulate such as ADH, oxytocin, gonadotropins, growth hormone, and thyroid stimulating hormone. The thyroid gland and thyroid hormones are also summarized.