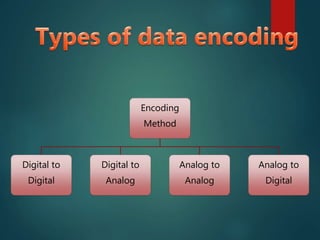
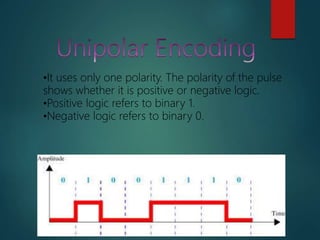
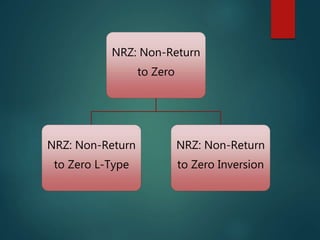
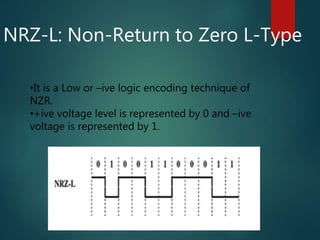
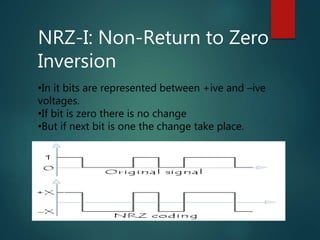
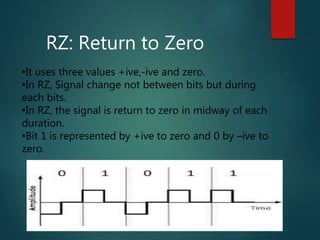
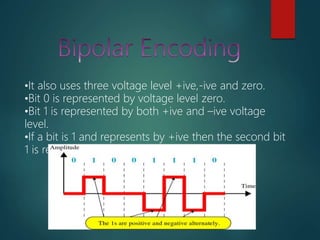
This document discusses various methods of data encoding for transmission. It explains that data must be converted to a signal form before transmission. The main encoding methods covered are digital to digital, digital to analog, analog to analog, and analog to digital. Specific digital encoding techniques described include NRZ (non-return to zero), NRZ-L (NRZ low-type), and NRZ-I (NRZ inversion). The document also covers RZ (return to zero) encoding and differences between NRZ-L and NRZ-I signals. Analog modulation techniques like amplitude, frequency and phase modulation are also briefly mentioned.