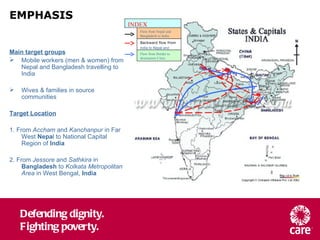
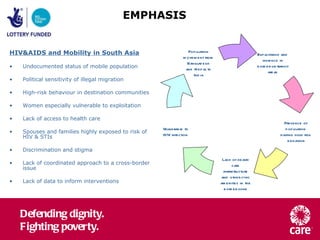
The document provides an overview of the EMPHASIS project which aims to address HIV vulnerability among mobile populations in South Asia. The project will work along mobility routes from Nepal and Bangladesh to India, setting up service networks to increase access to HIV prevention, treatment, and care. In the first year, the project will focus on building knowledge about the target populations to inform the design and delivery of effective HIV services tailored to their needs and experiences of mobility.